Posts Tagged #behind the scenes @ the henry ford
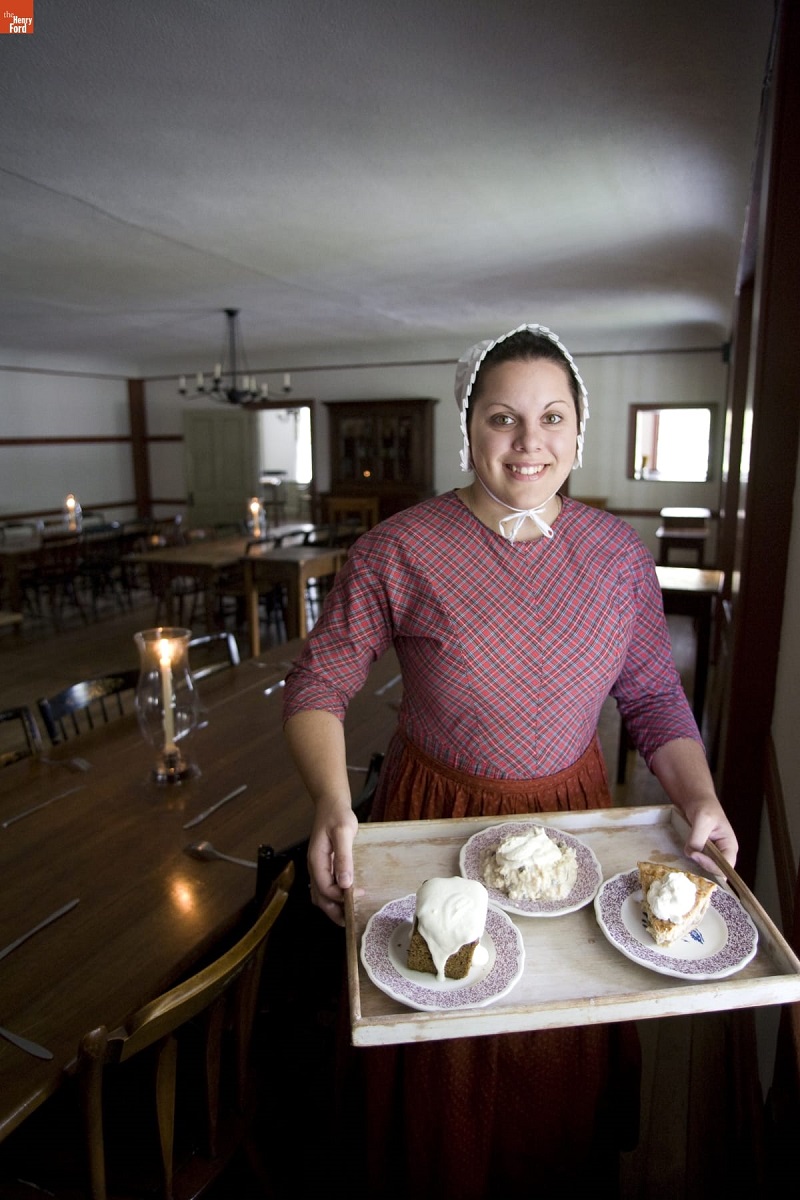 Server shows off an array of pastries at Eagle Tavern, 2007. Photograph by Michelle Andonian. / THF54295
Server shows off an array of pastries at Eagle Tavern, 2007. Photograph by Michelle Andonian. / THF54295
April 1, 1982, was a momentous day in Greenfield Village! That was the day that Eagle Tavern opened to the public. It was our first historic dining experience—the result of months of research, recipe selection and testing, and interpretive planning. How did all this come about?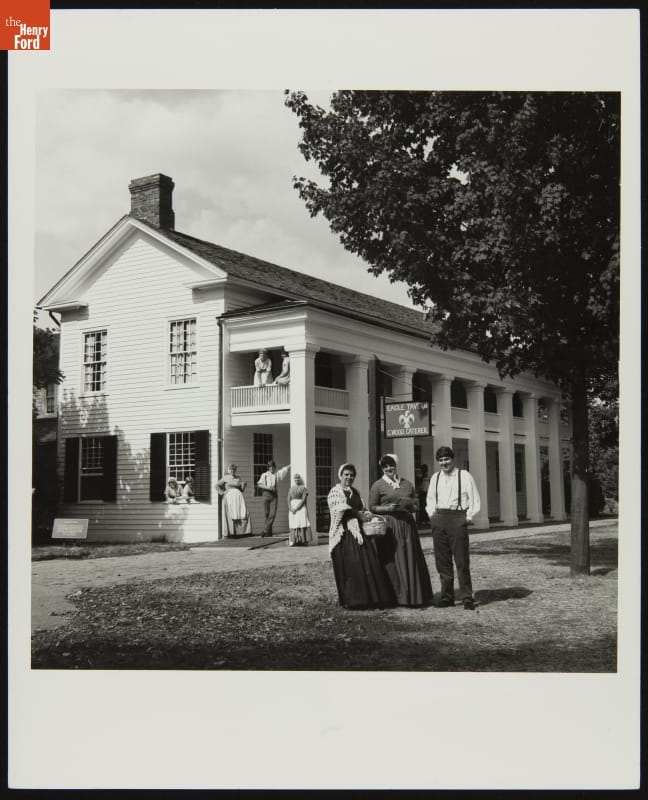
Historical presenters and food service staff pose in front of Eagle Tavern to celebrate the new dining experience, 1982. / THF237355
The Food Committee
It started when we took a chance on a young museum leader named Harold Skramstad, who became our president in 1981. Faced with a severe financial crisis at the time, Skramstad built a case around our “world-class” status and “unique historical resources.” This led to the creation of our first mission statement, which focused upon the process of change in America from a rural agricultural society to an urban industrial nation. Following that, Skramstad created several task forces and committees, each charged with developing plans to carry out our mission through a variety of public programs. This included the mysteriously named Food Committee. It turned out that this committee—comprised of curators, food service staff, and interpretation specialists—was charged with exploring ways to bring our food offerings in line with our overall interpretive framework.
Food vendor in Greenfield Village. / THF133689
Soon, new food experiences began to appear. Through the Food Committee’s collaborative efforts, vendors hawked fruit and penny candy from rolling carts like those that had been seen on urban street corners a century ago. At the Covered Bridge Lunch Stand (now Mrs. Fisher’s), visitors could partake of turn-of-the-century picnic lunches. With the help of diner expert Richard Gutman—who informed us that we possessed the last remaining lunch wagon in existence—the Owl Night Lunch Wagon was overhauled to look more like a late-19th-century lunch wagon, featuring a more historic menu. But Eagle Tavern became our “crown jewel,” as we proposed turning this historic inn into a sit-down full-service restaurant with period food and drink.
What had the building been like before this?
Clinton Inn
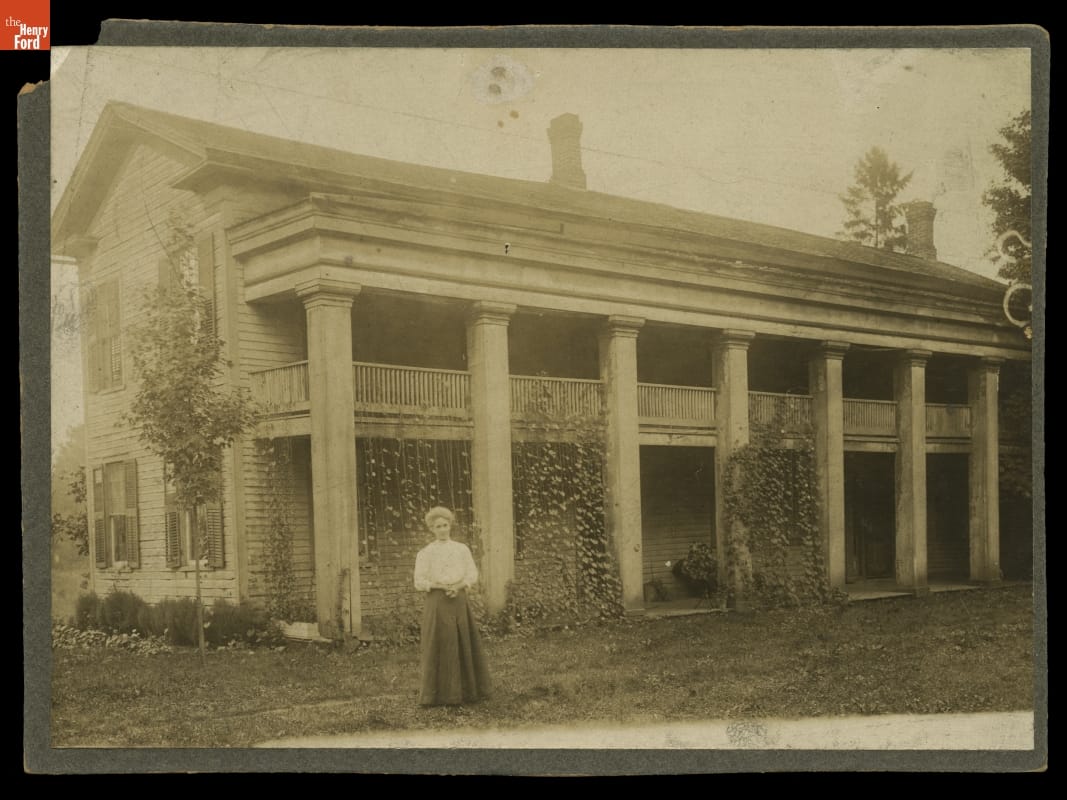

Ella Smith, the final owner, in front of the inn on its original site in Clinton, Michigan, circa 1905. / THF110475
In 1927—searching for a stagecoach tavern for his Village Green—Henry Ford found and purchased this imposing 1830s-era inn. From Clinton, Michigan, it was situated along what once had been the main stagecoach road between Detroit and Chicago. Over the years, the inn had gone through several proprietors and name changes, from Parks Tavern to Eagle Tavern to the Union Hotel to Smith’s Hotel. When Henry Ford had the building reconstructed in Greenfield Village, he gave it the generic name Clinton Inn.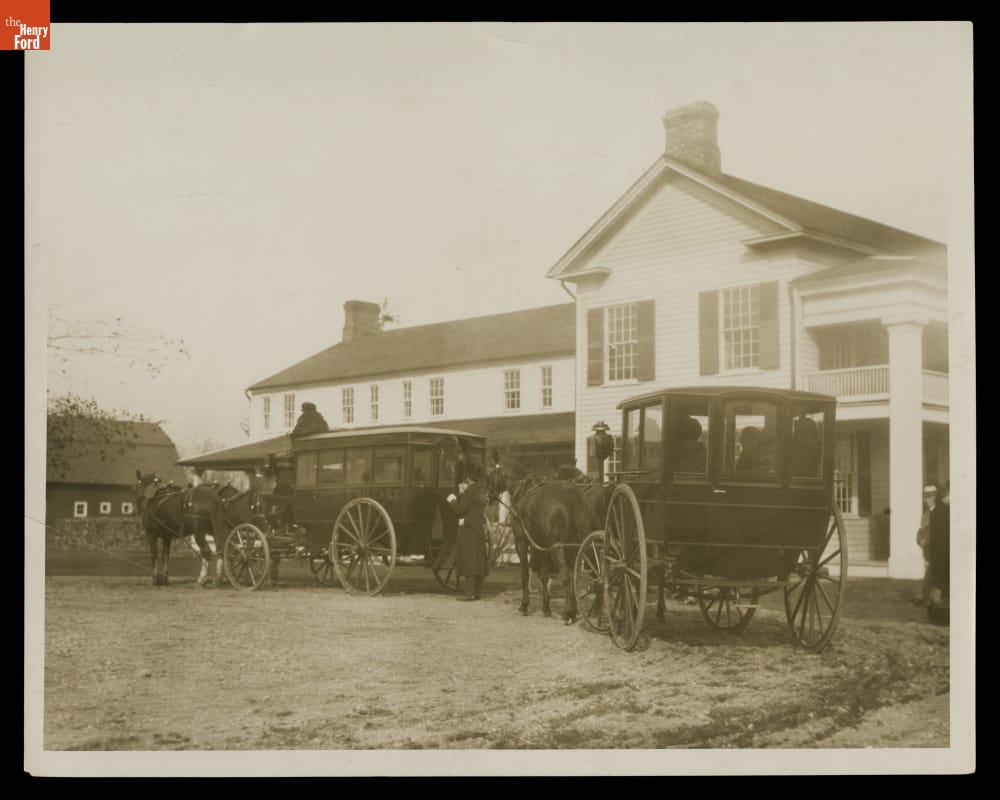
Carriages waiting for passengers at Clinton Inn. / THF120768
From 1929 into the 1950s, the building served as a cafeteria for students attending the Edison Institute schools. Ford enlarged the back of the structure for that purpose. When Greenfield Village officially opened to the public in 1933, Clinton Inn became the starting point for public carriage tours.
1950 calendar for Greenfield Village, featuring Clinton Inn. / THF8882
In the 1950s, the building transitioned from a student lunchroom to a public cafeteria. That was still its use when I first started working at The Henry Ford (then called Henry Ford Museum & Greenfield Village) in 1977. Also when I started, Clinton Inn’s so-called “colonial kitchen” was used for fireplace cooking classes as part of the institution’s Adult Education Program.
Why Eagle Tavern?
Why did we choose the Eagle Tavern era to interpret? To establish a date for the historic dining experience, we looked to primary sources, as we do when we research all of our historic structures. These sources, which help us uncover the esoteric details of the past, included probate records, property deeds, tax and census records, and local newspapers. Through this research, we found that a farmer named Calvin Wood ran this tavern from 1849 to 1854, with his wife Harriet, Harriet’s daughter Irene, and additional hired help from town or the neighboring countryside. In keeping with the patriotic spirit of the time, Wood named the place Eagle Tavern.
We decided that we liked this early 1850s date. Not only did we have decent documentation on Calvin Wood, but it was also an interesting era for changes in cooking ingredients and cookbooks (both more available than before) as well as public dining practices and customs (toward more choices for individual diners, better table etiquette, more formalized meals and menus, and more specialized table settings).
The 1850s date also dovetailed with our new mission statement—about change over time—in larger ways that were transforming the entire nation at the time. These included social movements like temperance, abolition, and women’s rights; advancements in transportation, from horse-drawn vehicles to speedy railroads; and improved communication networks, as the telegraph swiftly brought the latest news to the public. Significant national events like the California Gold Rush and the Mexican War were also impacting many people’s lives.
A variety of horse-drawn vehicles passing in front of a Middletown, Connecticut, tavern, 1842–47. / THF204148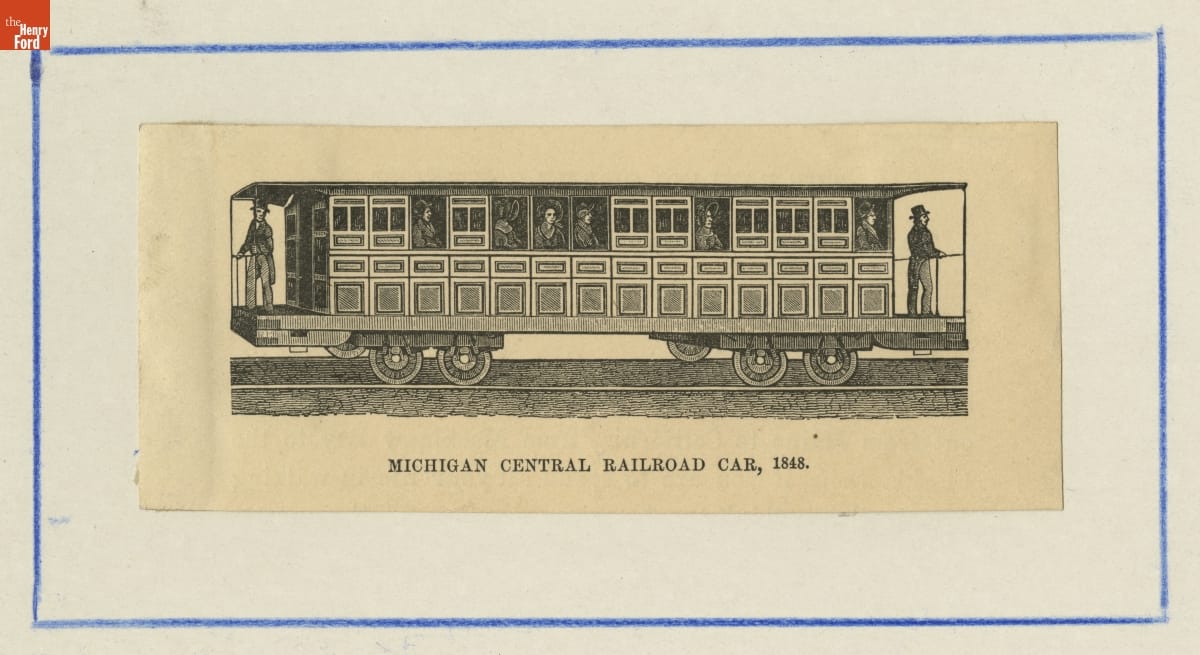
Michigan Central Railroad car, 1848. / THF147798
Researching the Food
My primary task in creating the Eagle Tavern dining experience was to find out what and how people ate during this era. I delved deeply into period sources looking for clues to these questions, including travelers’ accounts, etiquette books, merchants’ account books, newspaper ads, and historical reminiscences.
Within these sources, I found several quite eye-opening entries, like that of Isabella Bird, a British traveler who described this meal placed in front of her at a Chicago hotel in 1856: “…eight boiled legs of mutton, nearly raw; six antiquated fowls, whose legs were of the consistency of guitar-strings; baked pork with “onion fixings,” the meat swimming in grease; and for vegetables, yams, corn-cobs, and squash. A cup of stewed tea, sweetened by molasses, was at each plate…The second course consisted exclusively of pumpkin-pies.”
It’s probably good that we didn’t take these accounts completely literally when we developed the Eagle Tavern dining experience!
From these research sources, I learned that tavern fare would have come from a combination of local farms (especially, in this case, Calvin Wood’s own farm), from the fields and woods of the surrounding area, and using ingredients that would have been purchased from local merchants.
A cold plate featuring chicken salad, pictured in the 1988 Eagle Tavern Cookbook. / THF121002
The primary components of a tavern meal would have consisted of meat, vegetables and fruits (in various forms), and breadstuffs. Meat was the predominant component of the tavern meal, served in much greater quantity than today. Often, two or more meats were served at one meal. Pork, the staple food of many midwestern settlers, was the most popular meat, served in a variety of forms—including roasted, salted, baked, and as bacon, smoked ham, sausage, or spareribs. Chickens, easy to raise on farms, lent themselves to many dishes. They also could supply eggs. In fact, Lansing Swan, traveling through Sturgis, Michigan, in 1841, wrote: “We had an excellent dinner, warm cakes, tea, etc. bacon and eggs. I have eaten them until I am ashamed to see a hen and can hardly look a respectable porker in the face.”
Beef contributed to a portion of the tavern meals, as did wild game and fish from local lakes and rivers. Oysters were also popular at the time, packed on ice and transported in barrels from the East coast.
An array of vegetables for Eagle Tavern dishes, pictured in the 1988 Eagle Tavern Cookbook. / THF121001
As for vegetables, root crops lasted throughout the year and they stored easily. Potatoes were especially popular, as described in this southern Michigan meal by Charles Hoffman in 1833: “…hot rolls, tea, large pieces of pork swimming in its gravy, and a plate of potatoes that pulverized when you touched them.” Cabbage, onions, turnips, and carrots were other root crops frequently found in the research. Less hardy vegetables, like tomatoes and cucumbers, were served in season or preserved as catsups, sauces, or pickles. Pumpkins, squash, and corn were usually served in season or preserved for later use.
Fruits were served fresh in season, dried, or made into preserves, sauces, or pickles. Of these, apples were most frequently used as they were incredibly versatile—preserved, cooked, or baked into numerous dishes. Peaches, pears, apricots, grapes, and berries of all sorts were also found in the accounts. Wild strawberries were specifically called out several times by traveler Lansing Swan, in 1841. In Ypsilanti, Swan “got an excellent supper for 25 cents and many large delicious strawberries with rich cream.” Farther west, in Jackson, he happily remarked that he was, “Just in time for tea with strawberries and cream.” In Niles, he and his companion “came in time for another strawberry repast and a rich one it was. We had a new dish, ‘Strawberry Short Cake,’ very fine indeed.” And before leaving Niles the next morning, he partook of one last “strawberry breakfast.” Raisins, dried figs, prunes, currants, and citron were listed in grocery store ads and could be purchased.
A variety of muffins and rolls served at Eagle Tavern, 2007. Photograph by Michelle Andonian. / THF54331
Breadstuffs contributed substantially to tavern meals, mentioned often in travel accounts as a meal accompaniment—but not always with approval! For example, Cyrus Bradley, dining in a tavern between Detroit and Pontiac in 1835, remarked: “The milk was sweet, but the bread was dry and stale and as it began to saturate, the little red bugs rose, kicking most lustily, to the surface, where they were immediately skimmed off and most barbarously committed to the flames.”
Wheat flour and cornmeal were processed at local mills and could be used for baking breads, rolls, biscuits. Charles Hoffman, in 1833, remarked that Michigan had the “best wheat bread in the world.”
Creating the Menus
From all of these accounts, I created a master list of dishes and ingredients. Then I perused every historic cookbook I could find. Fortunately, the number of printed cookbooks was on the rise by the mid-19th century, although measurements, cooking times, and temperatures were not precise—which is why so much recipe testing had to be done. Within the pages of these cookbooks, I searched for recipes that were specifically referenced in historic accounts, those that seemed regional, and those that included ingredients on my researched ingredients list.
The Good Housekeeper, from 1841, was one of several cookbooks perused for possible recipes. / THF120853
I organized my collected recipes by type—for instance, entrees, pastries, soups, vegetables—and then spent innumerable hours with the food service managers at Eagle Tavern debating and selecting the final recipes. The managers brought up constraints that I would never have considered as a curator—including modern cost and availability of ingredients as well as the durability of certain dishes on the steam table that was still being used from the old cafeteria setup. Probably our most animated conversations related to how adventurous we thought modern visitors would be in trying things that were different and unusual—like mock turtle soup and beef tongue! Once determined, the agreed-upon recipes were tested by food service cooks (this predated having chefs on staff) who, after weeks of testing, invited us to a grand two-day food tasting.
Elaborate Bill of Fare for Thanksgiving Day, 1847, at the Adams House in Boston, Massachusetts. / THF147797
At the same time, I searched for examples of historic menus from the era to see what constituted a tavern meal. As it turned out, most tavern meals started with soup and ended with a dessert course of dried fruit and nuts. (The phrase “from soup to nuts” must have originated at this time!) The Eagle Tavern menu, or “Bill of Fare,” was laid out much like the historic menus of the time but included a simpler selection of dishes that were regionally and seasonally appropriate. Today, the Eagle Tavern Bills of Fare still follow these guidelines.
Eagle Tavern’s first Bill of Fare, Spring 1982. / THF123845
The Dining Experience
According to travel narratives of the era, tavern dining was fast and furious. For example, one traveler in Chicago in 1836 wrote: “…every man for himself, and none for his neighbor; hurrying, snatching, gulping, like famished wildcats; victuals disappearing as if by magic.” Partly, this was because there were often more patrons than space at the one “common table” in an inn. To resolve this, diners often took turns eating, as James Logan described in a hotel in Detroit in 1838: “Very little conversation took place, each individual seemed to hurry on as fast as possible, and the moment one finished he rose and went away. There was not change of plates, knives, or forks, every thing being eaten off the same plate, excepting pudding, which was taken in saucers.”
For the Eagle Tavern dining experience, we knew we were not about to recreate James Logan’s experience! But how, we wondered, could we simulate the concept of the “common table” for modern visitors? Fortunately, because of the spacious cafeteria area that Henry Ford had added to the building back in the 1920s, we found that we could furnish the space with not one but several tables that simulated communal dining. It also gave us the option of seating people at separate tables if additional privacy were desired.
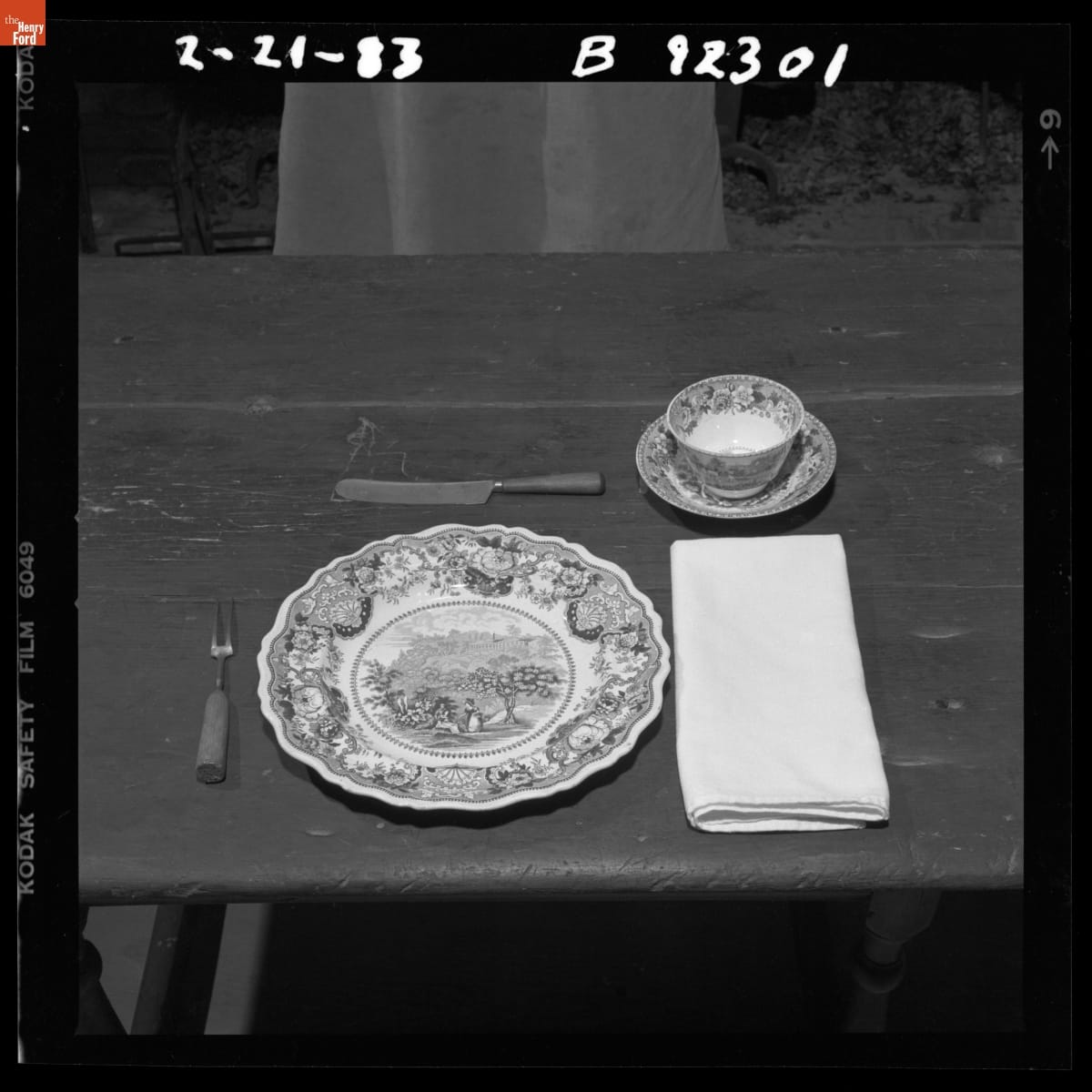

The Eagle Tavern table setting was also the result of historical research, found in Catherine Beecher’s 1850 Domestic Receipt Book. / THF147807
Today’s dining experience at Eagle Tavern is much like it was back when we first created this experience almost 40 years ago. To me, Eagle Tavern was—and still is—one of the best historic dining experiences around!
Donna R. Braden is Senior Curator and Curator of Public Life at The Henry Ford.
Additional Readings:
- Eagle Tavern at its Original Site, Clinton, Michigan, February 2, 1925
- Behind the Bar at Eagle Tavern
- Eagle Tavern Inspiration to Enjoy at Home
- Menu from Clinton Inn (now Eagle Tavern), Greenfield Village, 1952
19th century, 1850s, Dearborn, 20th century, 1980s, restaurants, research, Michigan, Greenfield Village history, Greenfield Village buildings, Greenfield Village, food, Eagle Tavern, by Donna R. Braden, #Behind The Scenes @ The Henry Ford
Welcome New Board of Trustees Members
What is your personal connection to The Henry Ford? For many, it’s the memories that have been made during visits to the museum and village. Others, it’s the stories told, artifacts observed, or the people who paved the way for future generations. For Linda Apsey, it was Thomas Alva Edison—his commitment to the utility industry, collaboration with Henry Ford, and future electrification of our society. For Carla Walker-Miller, it is the outreach that The Henry Ford is doing with Detroit Public Schools, the Rosa Parks Bus, and the story that sheds light on the importance of equality, diversity, and inclusion.
While each connection is different, they both share a common theme—access to education, history, and innovation for all, regardless of background or barrier. At this time in our institution’s history, we believe that both leaders will bring invaluable knowledge and perspective based on their experiences. These women are truly remarkable individuals who value our mission and will inspire others for generations to come.
Linda Apsey is currently the President and CEO of ITC Holdings Corp. and is responsible for the company’s strategic vision, business operations, and all subsidiaries. She has held many roles throughout her career that have shaped her into the successful businesswoman she is today. Before she was President and CEO, she served as Executive Vice President and Chief Unit Officer at ITC Holdings Corp.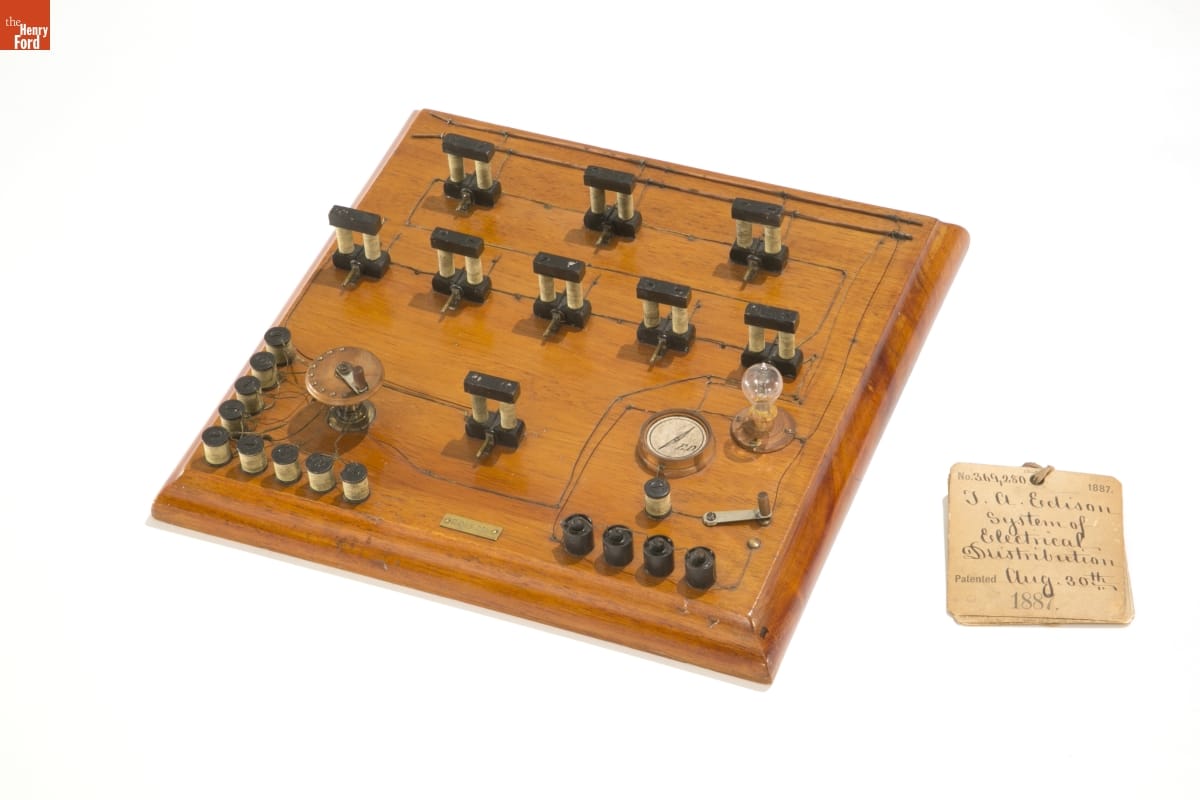
Linda Apsey is inspired by the stories The Henry Ford can tell with its collections related to Thomas Edison, including his patent model for the electrical distribution system. / THF154126
Apsey is most looking forward to Invention Convention Worldwide. “Invention Convention provides kids across the country with a space and place for imagination to come to life. And that is amazing to observe and be part of!” This program at The Henry Ford allows young minds to tap into their can-do spirit and engage with other students and professionals throughout the world. Invention Convention is one of the unique, educational programs and initiatives that The Henry Ford is using to emphasize the importance of learning and access to education. “THF has developed many exciting programs to tap into the energy, passion, and creative minds of our future generations through teaching, experimentation, and competitions, all of which provides opportunity, access, and collaboration for growing minds.”
Carla Walker-Miller is the founder and CEO of Walker-Miller Energy Services. She is a changemaker in the energy industry and strives to inspire those she encounters. Walker-Miller Energy Services is one of the largest energy waste reduction companies in the country founded and owned by an African American woman.
Walker-Miller is greatly inspired by the community outreach The Henry Ford (THF) is doing in metro Detroit, particularly Detroit Public Schools. “Like most people, I had no idea before I joined the board the amount of work this institution is doing and the commitment The Henry Ford has made in educating our children. The work THF is doing with Detroit Public Schools is so thoughtful and intentional and I’m amazed at the impact The Henry Ford is having.”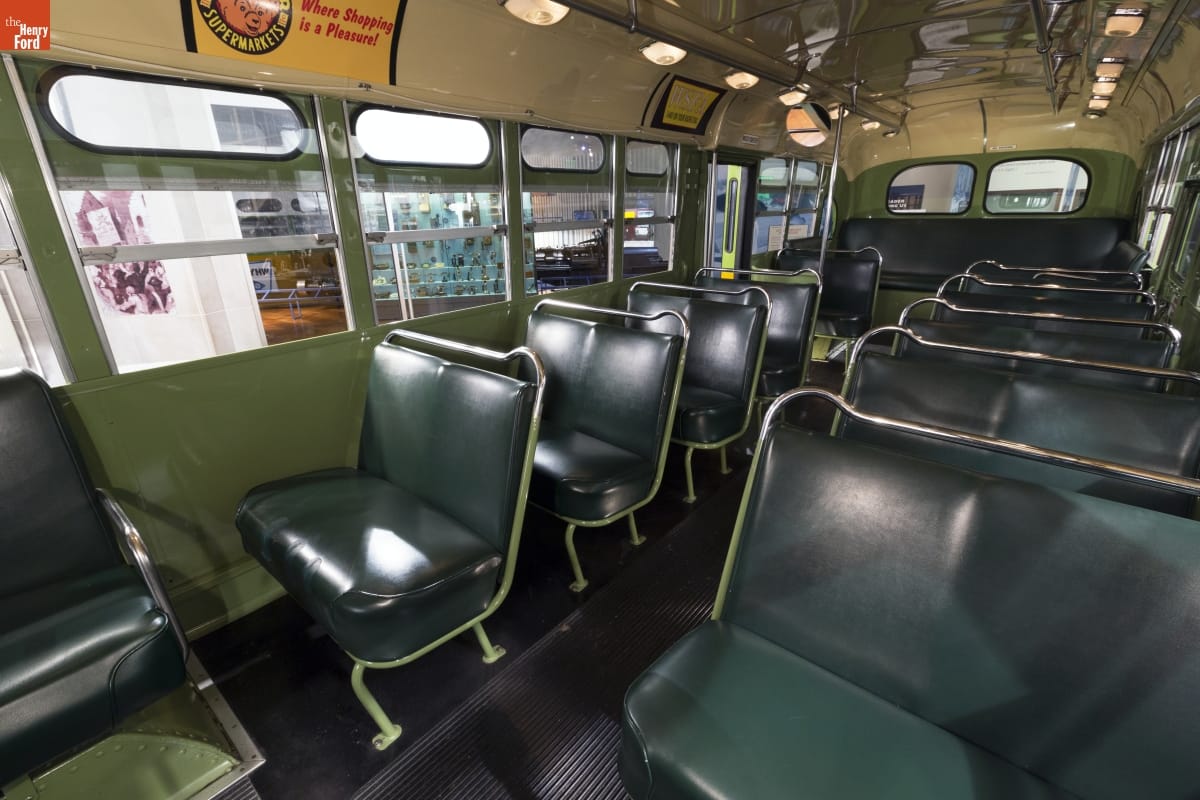
Carla Walker-Miller feels welcomed by the presence of the Rosa Parks Bus in Henry Ford Museum of American Innovation. / THF167250
Being able to inform and educate others about the many different stories and lessons we have learned throughout American history is very important. The Henry Ford is committed to telling the stories of the brave men and women who were the catalysts for change in racial equity. Carla Walker-Miller agrees that the acquisition of the Rosa Parks Bus in the early 2000s was a monumental step for The Henry Ford. “In my heart, that acquisition felt like an acknowledgement that Black history is American history. It may as well have been a bridge, because it felt like a welcome, like a personal invitation to visit. I will never forget the photo of President Barack Obama on that bus. It spoke to me and so many other people of many races.”
Linda Apsey and Carla Walker-Miller both agree that The Henry Ford is a place that is meant to be treasured. To our current donors who believe in the mission and value of The Henry Ford, thank you! For those who may be new to The Henry Ford and are still learning about the institution, we invite you to dive deeper into our mission. For Apsey, “Investing in THF is not only an investment in our rich industrial history of innovation and automation, but more importantly an opportunity to invest in the hearts, souls, and minds of future generations. THF is a world-class institution whose history has just begun!” To Carla Walker-Miller, “The Henry Ford offers a warm introduction to this country’s history. They are committed to making the institution inclusive and accessible to all and to say, ‘Everyone is welcome here.’” We are very lucky to have these two passionate executives help take The Henry Ford to new levels and reach the hearts and minds of future generations.
Caroline Heise is Annual Fund Specialist at The Henry Ford.
Michigan, Detroit, education, entrepreneurship, Invention Convention Worldwide, The Henry Ford Effect, by Caroline Heise, African American history, women's history, #Behind The Scenes @ The Henry Ford
The Crafty Sport of Paper Wigs
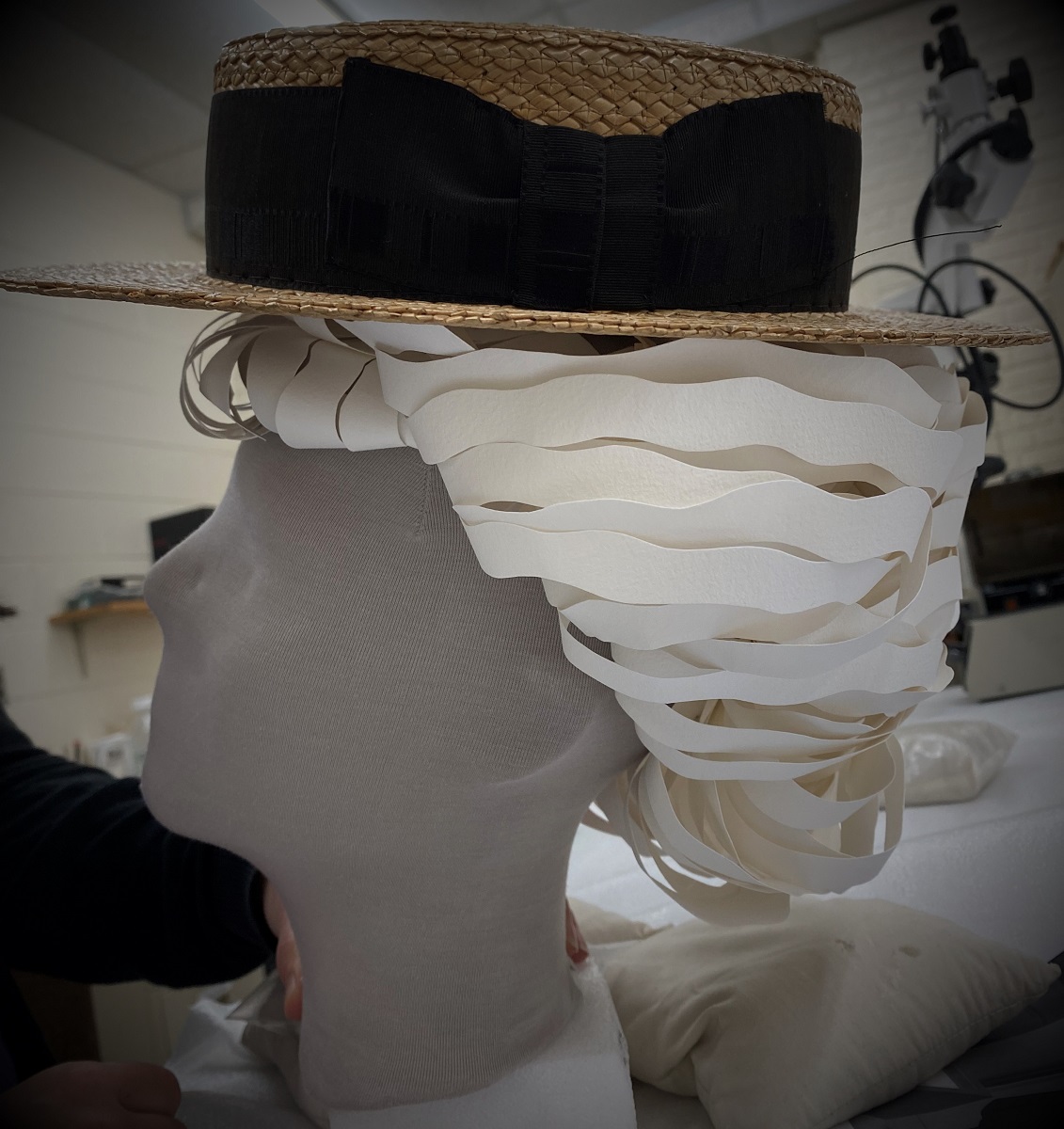

For a museum professional who takes care of collection objects, it isn’t often that the opportunity to be crafty comes along. When it does, however, those random skills you never thought would be useful come in handy.
Case in point was a mannequin for our latest What We Wore display, featuring clothing and accessories related to sports, that needed a fresh hairstyle. Paper wigs are useful in creating a simple look, but can also give a “wow” factor that regular wigs cannot. For our cycling mannequin, we attempted the windswept, curly style of the early 20th century. What follows is the process it took to make this paper wig. May it inspire you to try crafting your own!
The useful tips and tricks detailed by the FIDM Museum & Galleries and the Museum of Applied Arts & Sciences were invaluable resources to start the process. First, the search for suitable paper was a challenge, based on the recommendation of a 70 lb. watercolor paper. The art store had a wide selection of papers, but nothing that fit that description perfectly. We tried two samples: a 74 lb. smooth, waterproof synthetic paper made of polypropylene, and a textured 90 lb. cotton fiber watercolor paper. Both had their strengths and weaknesses, based on dyeability, strength, and size. Trial and error with curling the papers determined that the cotton fiber paper was best for this project because it was a bit more durable and gave us the option for coloring the paper.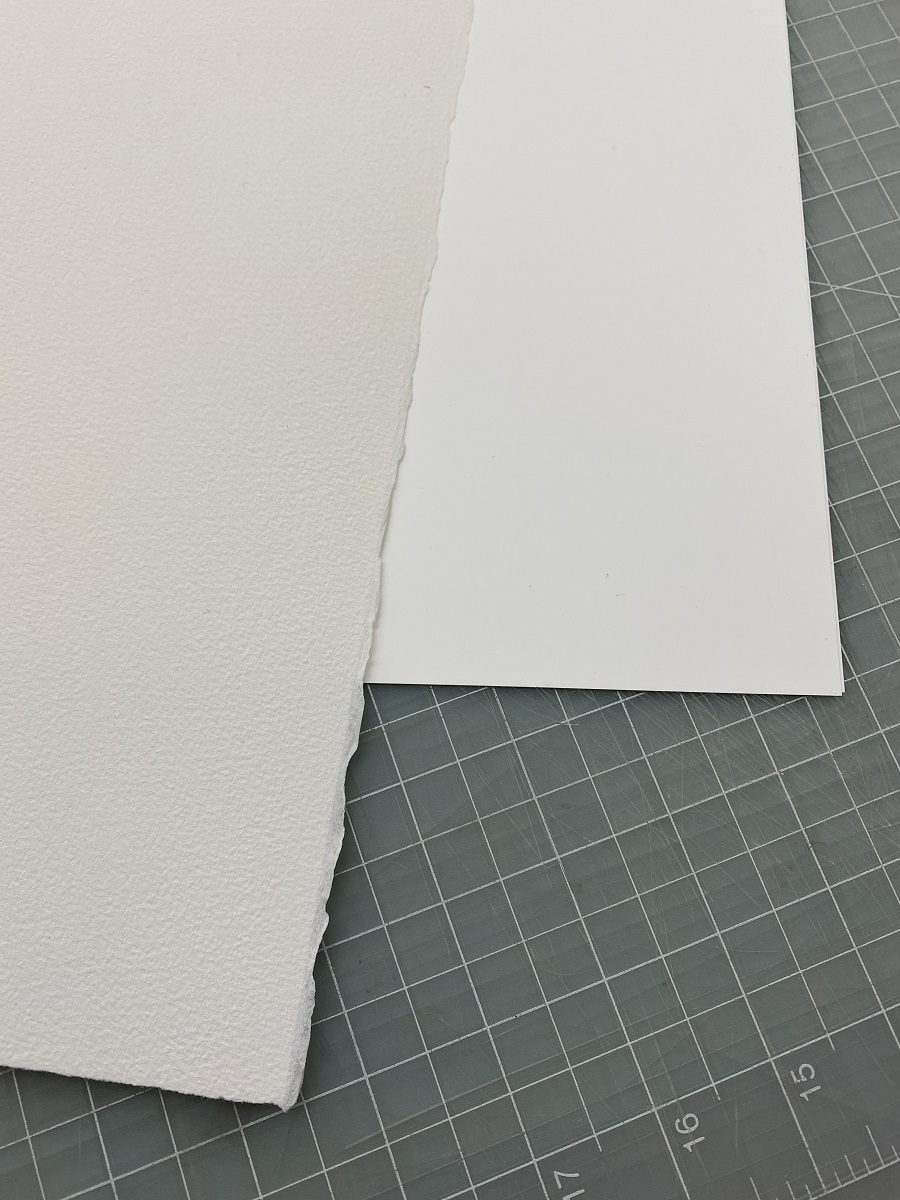
Comparison of the synthetic paper on top and the cotton fiber watercolor paper on bottom.
The next step was deciding how to cut the paper into strips. We tried straight, long “hairs,” and a half-rainbow segment, but ultimately went with a wavy rainbow that created the perfect curly appearance.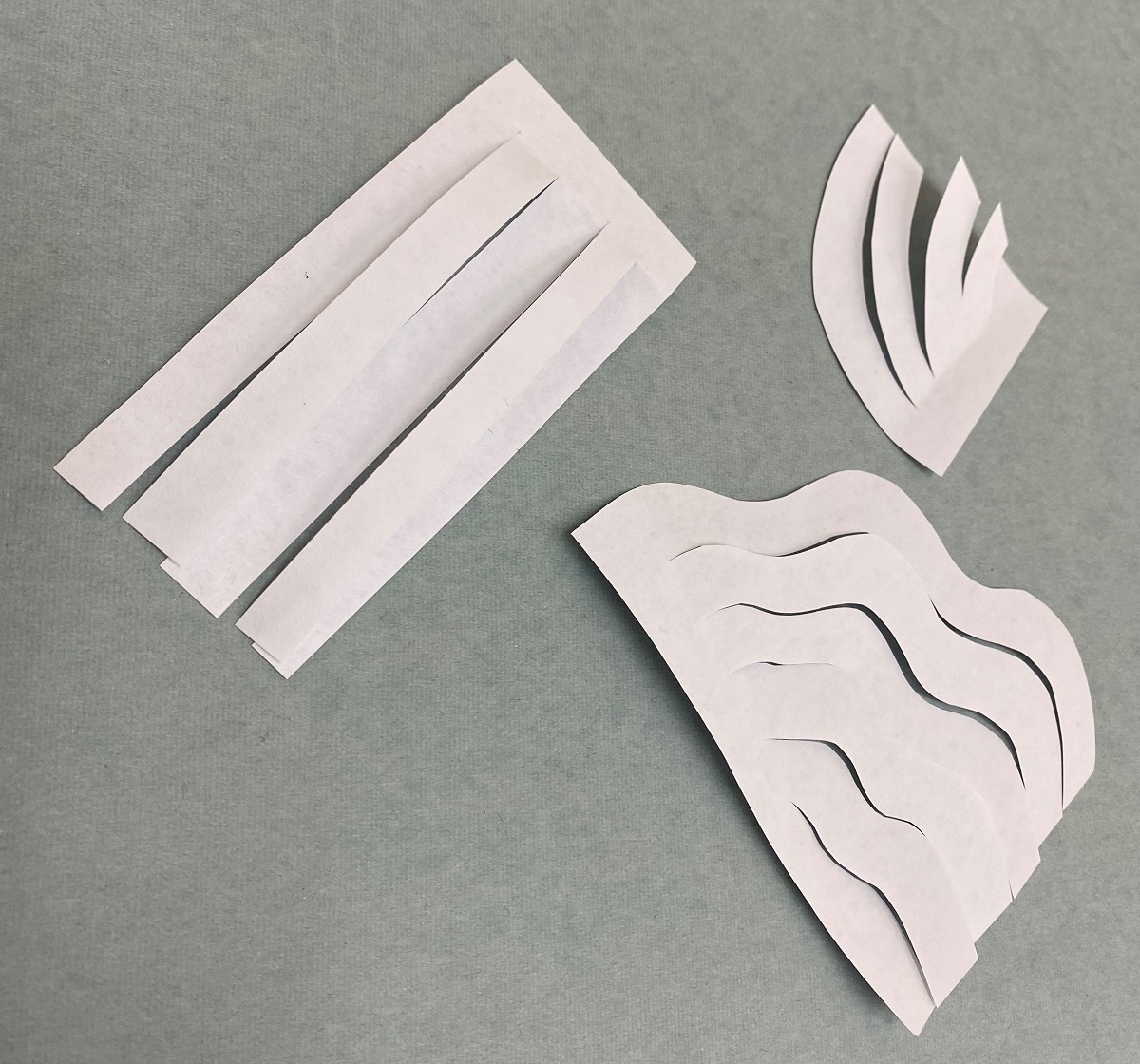
Leave a ½-inch edge at the top of the hair sections, as this will be the “roots” that attach to the mannequin head.
As for curling the strands, here is where those random skills help! The suggestion was to wrap the paper strands around a #2 pencil or the end of a paintbrush to create the waves. However, we found that pulling the paper with scissors, a technique used for curling balloon ribbons, was most effective in getting the result we wanted.
We then took our fabric-covered foam head and decided where the hairline should start and in which direction to start attaching the strand sections. We used straight pins to keep the “hair” in place, but you could also use double-sided tape or glue, depending on the material of the mannequin head and its intended use afterwards. For us, since the hair is pinned in place, it is easily removable for the next exhibit.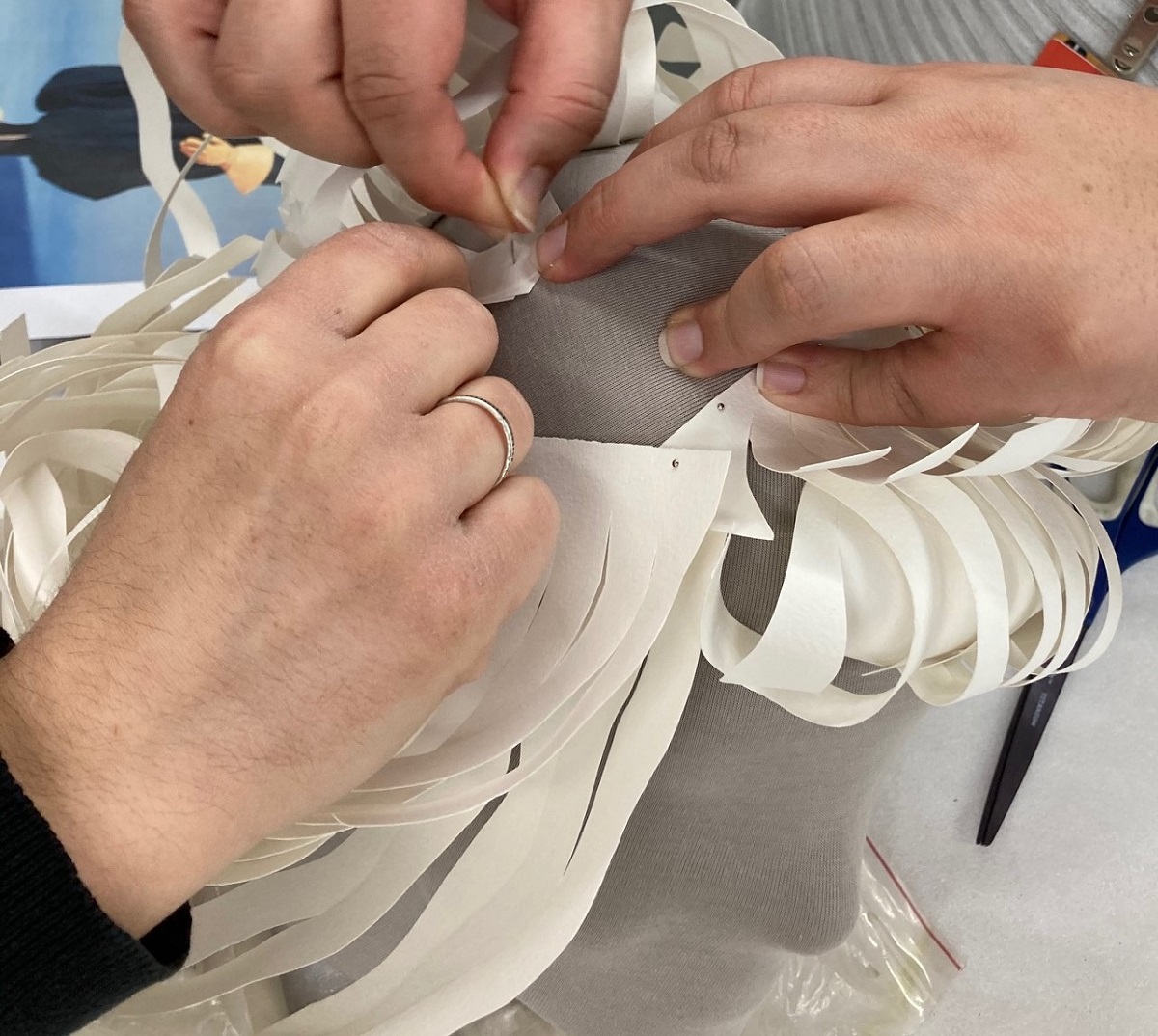
A hat would be placed on top, so we pulled the sections of hair back around a ball of tissue paper for volume and extra support. These sections were taped, because the pins would slide out from such a thick amount of paper to secure. A circular piece of foam was placed on top of the head so that the hat could be secured in place with long pins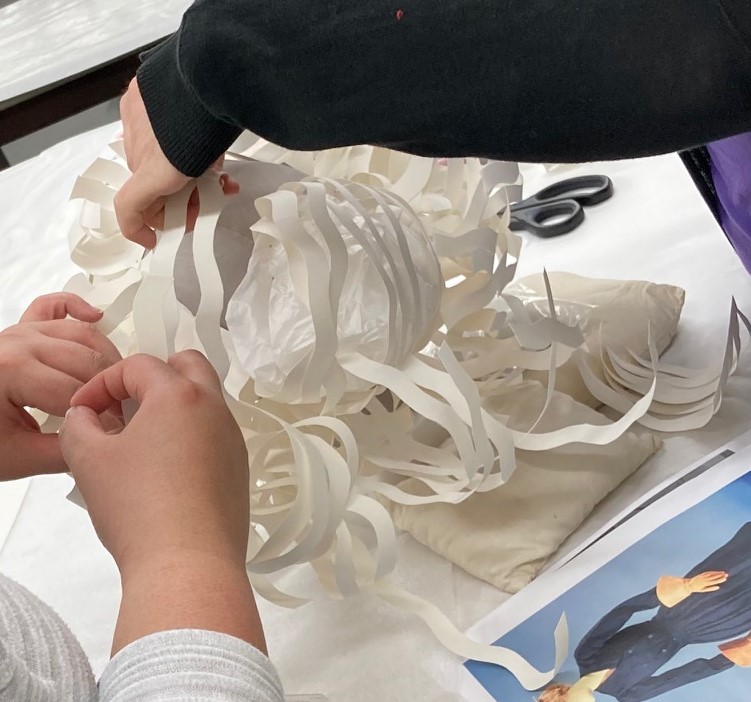
Ball of tissue inside the first layers of “hair.”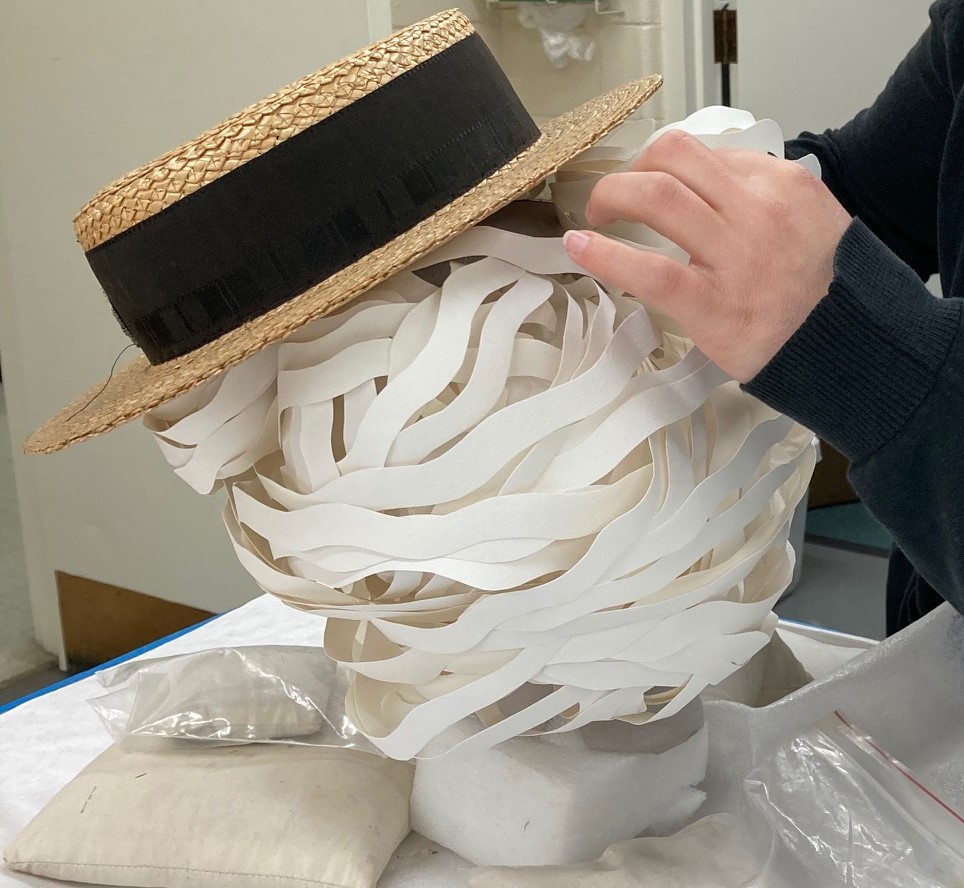
Attaching the final strands to the head.
The great thing about paper wigs is that you are limited only by your own creativity! Ribbons, feathers, and hairpins can all be added to create even more style. Depending on the paper used, colorful looks are also an option.
And voila! Here we have our cycling fashionista enjoying some time with her other athletic friends. Be sure to come to the museum and see our new What We Wore exhibit, featuring sports, on display all summer.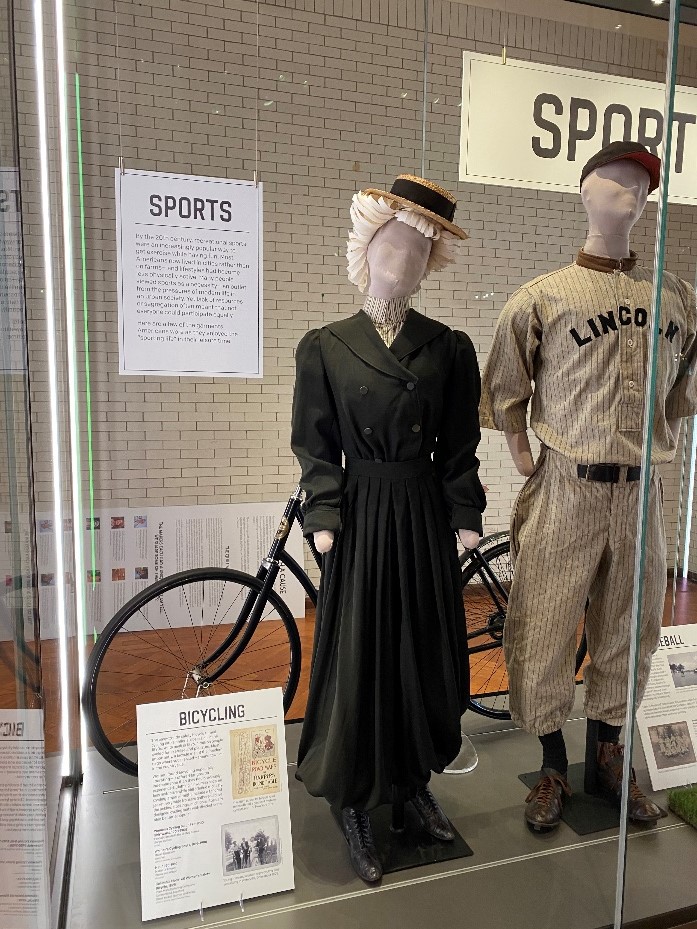
The cyclist, with her paper wig, in the What We Wore sports display, currently on exhibit in Henry Ford Museum of American Innovation.
Marlene Gray is Senior Conservator at The Henry Ford.
by Marlene Gray, #Behind The Scenes @ The Henry Ford, making, fashion, What We Wore, Henry Ford Museum, collections care
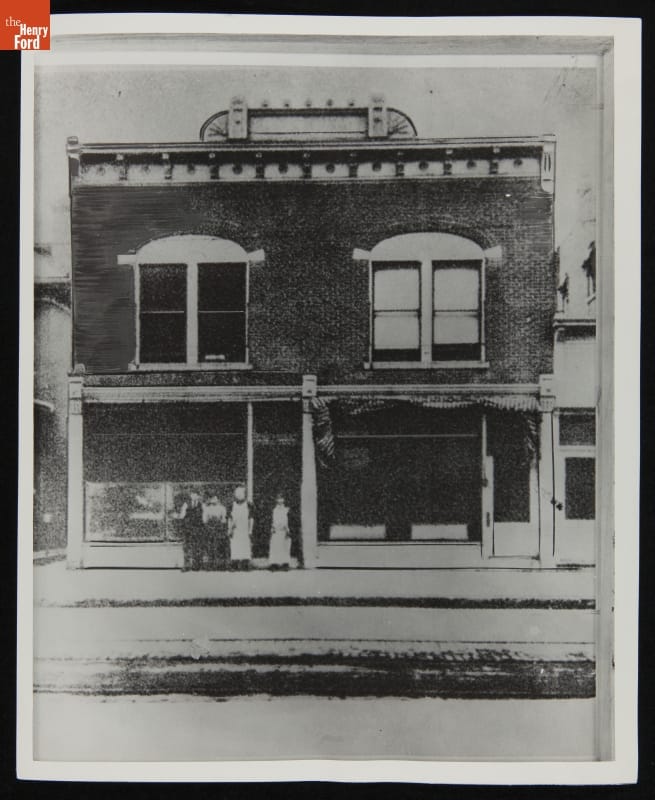

This photograph was taken some time between 1905 and 1911. Why? The sign in the front window of the storefront adjacent to the Wright Cycle Shop shows an undertaker’s business run by L.G. Keller. City of Dayton business directories of this period show Mr. Keller in business at 1127 West Third Street during this span of time. Clearly shown is the C .Webbert Block sign on top of the building and the Wright Cycle sign as well. Bicycle production and sales had ceased by 1905, but until 1909, airplanes and airplane engines were being built and partially assembled here. / THF236870
In 1903, the building that houses the Wright Cycle Shop and the undertakers’ establishment of Fetters & Shank was collectively known as the C. Webbert Block. The building was moved to and restored in Greenfield Village in 1937. It’s a very faithful representation of the two-story, two-storefront building that stood at 1125-1127 West Third Street in Dayton, Ohio, restored to appear as it did at the time of the Wright Brothers' first flight. There was one exception, though—the decoratively lettered sign that graced the top of the bracketed cornice spanning the front façade of the building was missing for over 100 years.
Charles Webbert, a relative by marriage to Charles Taylor, the Wright Brothers' mechanic, purchased the building in 1896. Mr. Webbert did an extensive addition to the front that created the double storefront we see in historic photographs. The Wright Brothers were his first tenants. Mr. Webbert was a plumbing supplier, a bicycle enthusiast, and, later, a great supporter of the brothers’ flying efforts. He was friends with Orville and Wilbur, and purchased and bartered both bicycles and bicycle repairs. Rent payments were dependent on what bicycle services were provided.
Between 1897 and 1916, the building saw a variety of uses by the Wright Brothers. Initially, the focus was on bicycles, including two lines of hand-built enameled finished bicycles, the Saint Clair and the Van Cleve. In the late 1890s, bicycles were a lucrative business and the proceeds from the Wrights' successful business became the funding source for everything that would eventually allow the Wright Brothers to fly.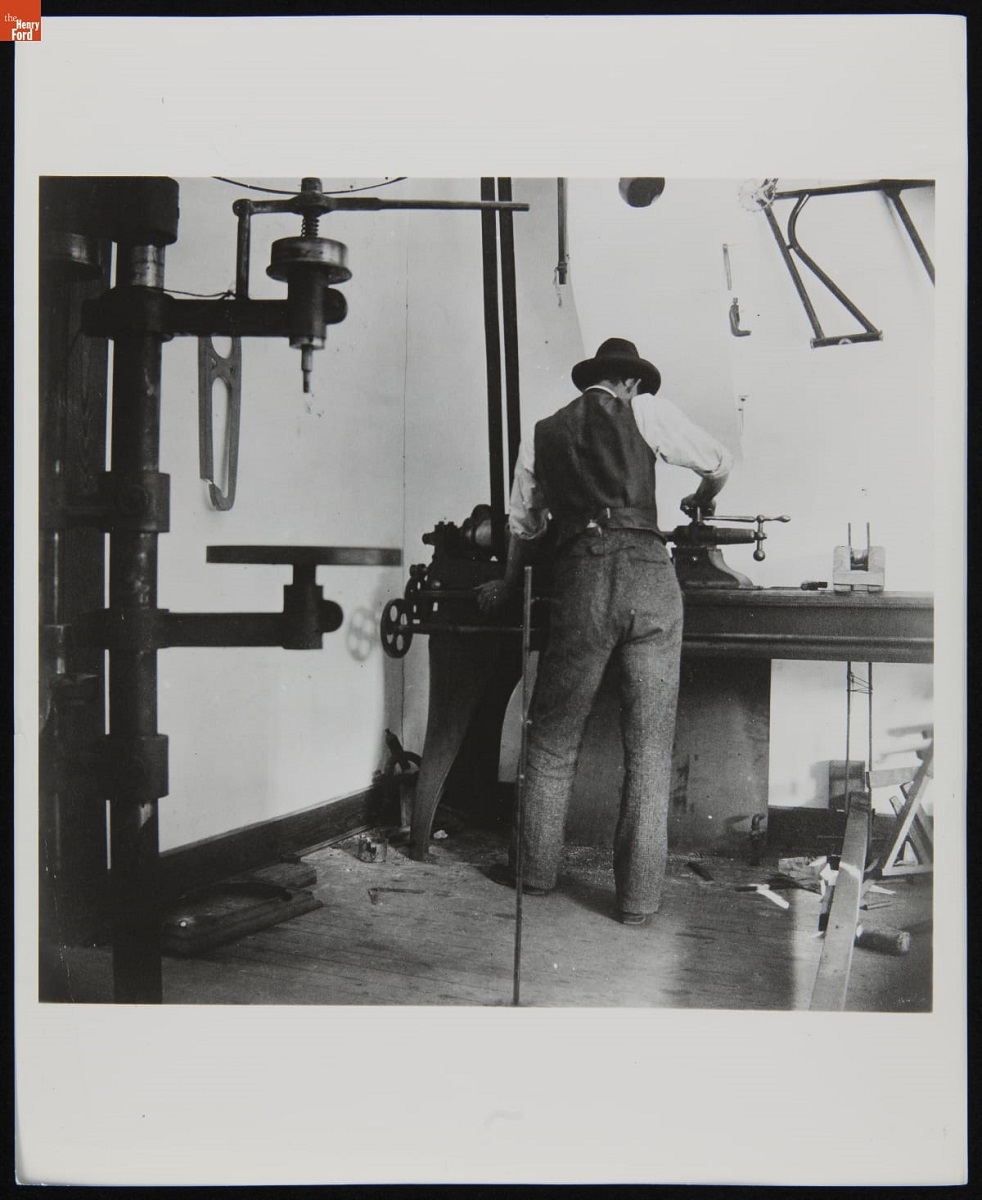
Man Working at a Lathe in the Wright Cycle Shop, Dayton, Ohio, 1897 / THF236804
From 1899 until 1909, the building served as the brothers' first experimental laboratory and design studio, dedicated to creating that first flying machine. The first gliders, as well as the first Wright Flyer, were built in sections in the back machine shop, along with the gasoline engines that powered the first flight. For a time, the Wright Cycle Shop was one of the world’s first airplane factories. Following the sale of their first airplane to the U.S. Army Signal Corps in 1908, Orville and Wilbur attracted the attention of New York investors and the Wright Company was formed in 1909. The airplane business quickly outgrew the space, and the assembly of airplanes consequently took place in a rented space in the Speedwell Motor Car Company while awaiting completion of a new factory building. The Wrights broke ground on this new facility on Home Road in Dayton in 1910.
After 1909, though manufacturing and final assembly moved elsewhere, the gasoline-powered engines continued to be machined and assembled in the Wright Cycle Shop. Both brothers also kept offices on the second floor, along with their company files and archives.
Following Wilbur’s death from typhoid fever in May of 1912, Orville took over as president of the company and ran the business alone. In 1915, he sold his interests and retired from the Wright Company. He continued to work on aviation design with his own firm but gave up the lease at the Cycle Shop in November of 1916, permanently moving to 15 North Broadway, a few blocks away.
Based on photographic evidence, the C. Webbert sign remained in place from 1897 until 1919, when significant structural changes took place. These included the addition of another bay and a third storefront, later to become 1123 West Third Street. Historic images show the building in its final iteration, as Henry Ford would have first seen it. By the time of the 1919 renovations, the building needed significant repairs, in part due to a huge flood that ravaged downtown Dayton and its neighborhoods in the spring of 1913. Water levels reached nearly to the second floor of the building. By this time, it’s very likely that the sign had deteriorated to the point where it was not practical to redesign it to fit with the new façade, and so it was likely removed.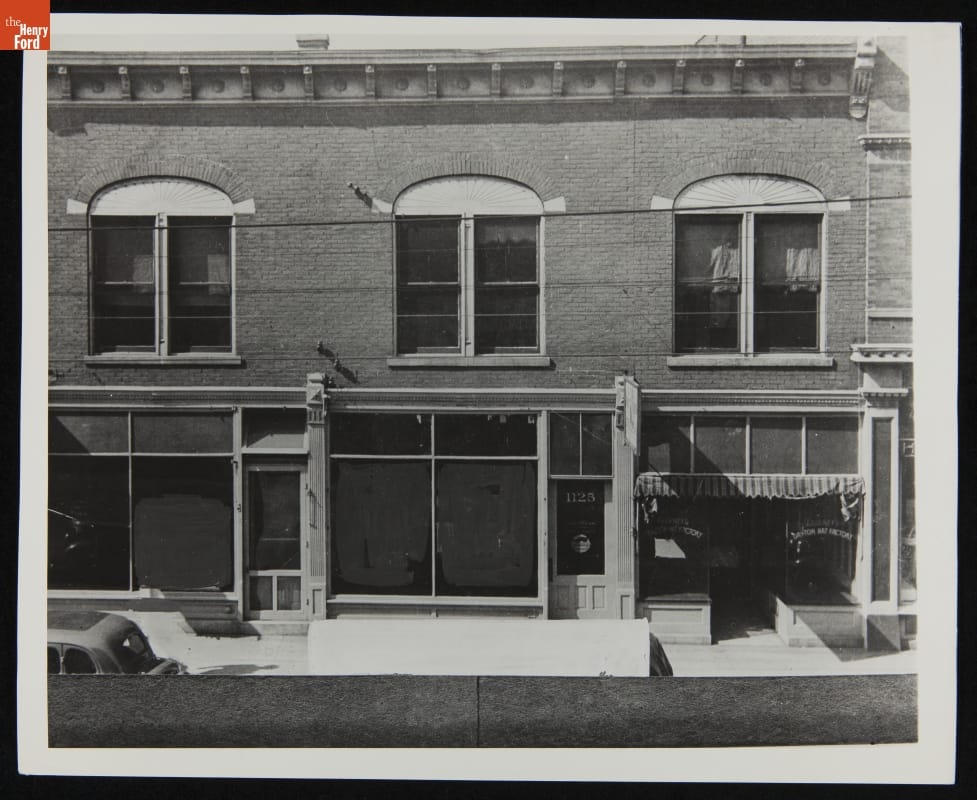
This photograph of the vacant building taken in October of 1936 is part of a series taken after Henry Ford purchased the building from Charles Webber, in preparation for dismantling the building and shipping it to Dearborn, Michigan. Its reconstruction in Greenfield Village, without the C. Webbert sign, was completed in the Spring of 1938 with the dedication taking place on April 16, which would have been Wilbur Wright’s 71st birthday. / THF236872
Henry Ford purchased the building from Charles Webbert in 1936 with the understanding that it would be dismantled and moved to Dearborn, where it would be reconstructed in Greenfield Village. For reasons unknown, the sign was never added to the Wright Cycle Shop when it was restored in Greenfield Village in 1937. This is surprising, as it is such a significant architectural element. In 1991, another major restoration of the building took place in the Village, and again, the sign was not included in the project.
As they say, the third time’s the charm.
In 2018, research work began, focused on recreating the sign to more accurately represent the building’s appearance in 1903. In 2019, Mose Nowland, one of our talented conservation department volunteers, created detailed construction drawings based on high resolution scans of original photographs showing the sign still in place. Mose had only a few photographs, taken several years apart, to work with. True to form with his decades of experience, his finished drawings were works of art themselves, and brought to life the exquisite details included in what was the finial crest for the newly-designed façade of the building.
Mose Nowland poses with one of his detailed architectural drawings, which allowed the C. Webbert sign to come to life again after being missing for 100 years. / Photo by Jim Johnson
Using these wonderful drawings, combined with Mose’s sound advice and suggestions, Mike Zemney, one of our talented carpentry staff, began the construction of the sign. The sign was built in sections, with each decorative element individually hand-crafted, just as it would have been in 1897. Mike used a wide range of techniques and materials, with the ultimate goal of making the sign as weather-proof as possible, with a minimal amount of maintenance required. The sign is a combination of several kinds of water-resistant wood species, copper flashing, and cladding, all carefully sealed. The decorative elements are all three-dimensional, and the sign reaches nearly four feet high and over seven feet long, in perfect proportion to the height and width of the building.
Carpenter Mike Zemney with the nearly completed sign he built. In this photograph, the sign has been painted and dry fitted together, with final assembly, sealing, and final painting to take place once it was lifted up onto the building.
Using high-resolution versions of historic photographs, we carefully studied and analyzed these images to determine the color combination to use in painting the sign, along with the rest of the building. What appear to be different colors in some of the photos are actually shadows, as the photographs were taken a few years apart, at different times of the year, and at different times of the day. Based on our analysis, it appears that the building and the entire sign were monochromatic, painted all one color. This was not an uncommon practice for commercial and industrial buildings in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The sign, therefore, was completely covered in many coats of a high-quality paint by Jeff Serwa, one of our dedicated painters.
There were great hopes of completing this project and having everything installed for the opening of Greenfield Village in April of 2020. As we all know, 2020 took a very different direction, and the actual installation of the sign was delayed.
However, I am very happy to announce that over 100 years later, the Wright Cycle Shop is now complete once again, proudly claiming its rightful place as part of the C. Webbert Block.
The sign is lifted onto the top of the building.
The sign is carefully installed and secured.
The C. Webbert Block sign atop Wright Cycle Shop in Greenfield Village.
Jim Johnson is Director of Greenfield Village at The Henry Ford. Special thanks to the staff and volunteers of The Henry Ford that made this project possible: Mose Nowland, Mary Fahey, Ben Kiehl, Dennis Morrison, Robert Smythe, Mike Zemney, and Jeff Serwa.
2010s, 2020s, 19th century, 21st century, 20th century, Michigan, Dearborn, Ohio, Wright Brothers, research, making, Greenfield Village history, Greenfield Village buildings, Greenfield Village, collections care, by Jim Johnson, #Behind The Scenes @ The Henry Ford
Staff Favorites from the IMLS Grant
Now that we are getting close to wrapping up our Institute of Museum and Library Services (IMLS) Museums for America grant to conserve, photograph, catalog, and rehouse artifacts from our collection, some of the staff who have worked on this grant would like to share interesting objects they’ve encountered over the course of the grant.
Marlene Gray, IMLS Project Conservator, has three objects she would like to share.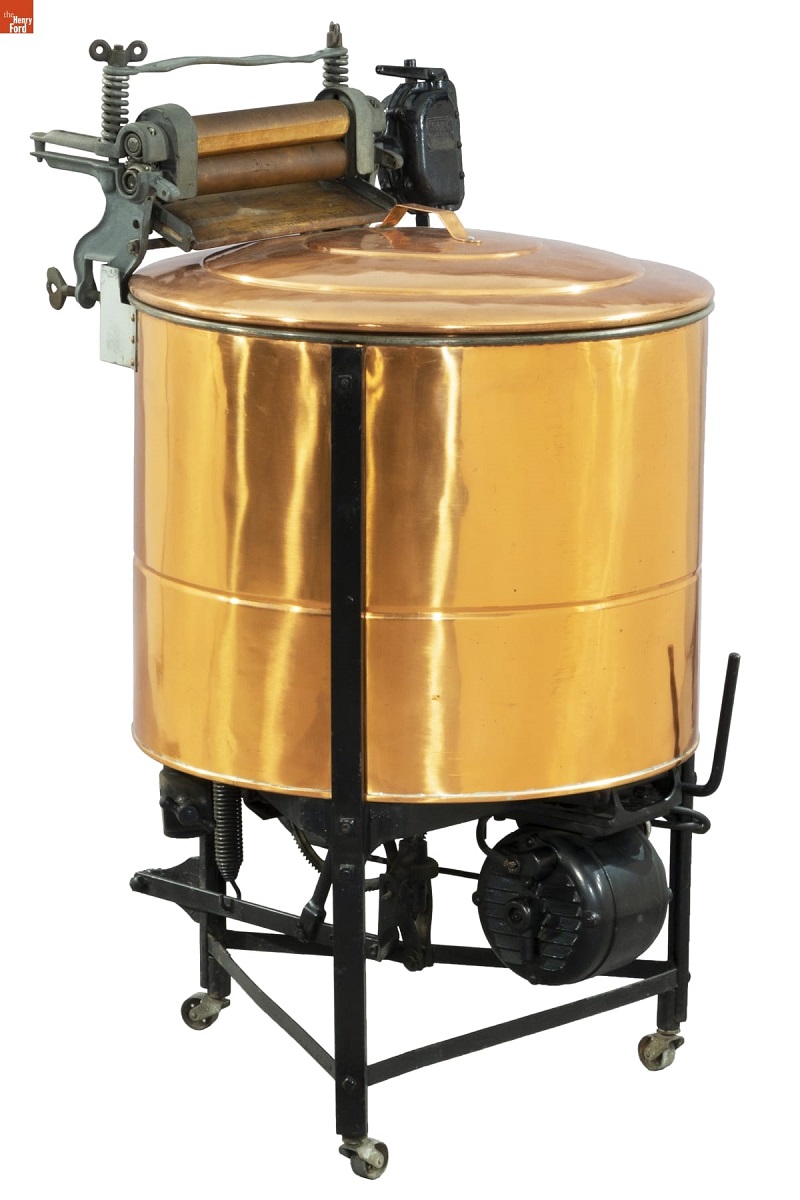
Dodge & Zuill Easy Model C Washing Machine, circa 1912 / THF186088
As the IMLS Project Conservator for the last year of the grant, clearing space for larger objects in storage was our main priority. However, there were chances to conserve some interesting objects, one of which was a copper electric washing machine from the early 20th century. The dazzling copper tub was a sight to behold while in the conservation lab. While cleaning it, I remember thinking how grateful I am that technology has come such a long way in making tasks simpler!
Next is this footwarmer from the mid-19th century: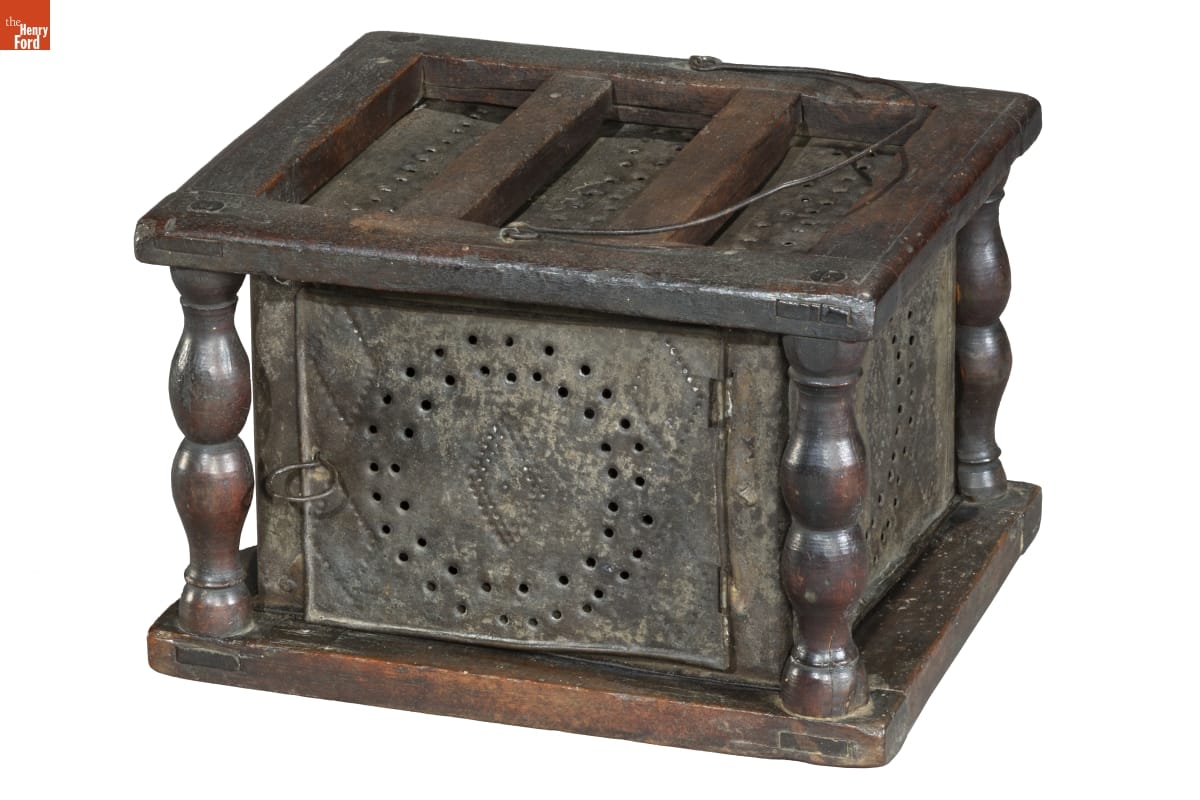
Footwarmer, 1830-1860 / THF185807
This footwarmer was a cute object to conserve because of the decorative elements in the wood frame and pierced tin stove box. One of the wooden columns had separated from the rest of the object. The opportunity to completely reassemble the object and give it a thorough cleaning made it feel as though the little stove could still be heated for the approaching cold months.
And finally, this lubricator cup assembly: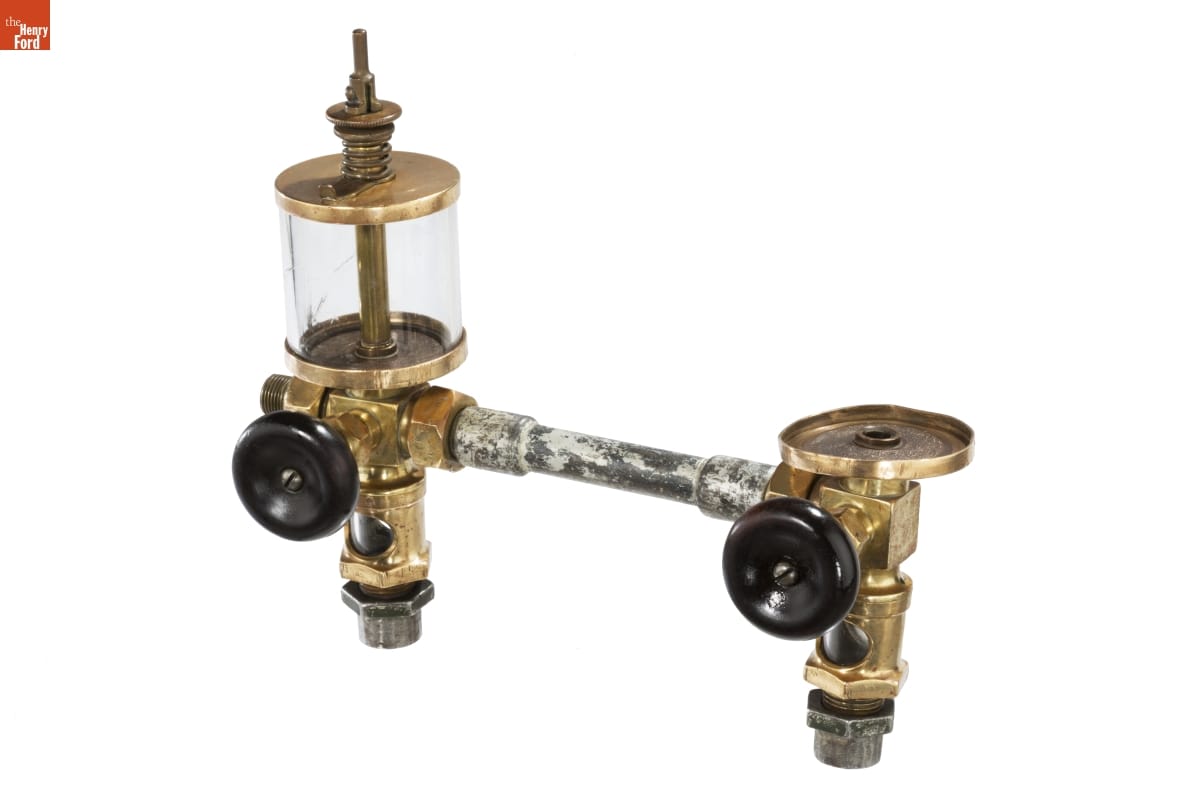
Lubricator Cup Assembly / THF181364
The great thing about conservation is that you are always learning about history through ordinary objects. While the conservation treatment of this object involved relatively simple metal polishing and glass repair, learning about the inventor of the lubricator cup, Elijah McCoy, and his connection to Detroit was fascinating. I highly recommend exploring his story, like I did!
For more information about the conservation process, as well as other milestones that we reached during this grant funded project check out Behind the Scenes with IMLS: Cleaning Objects, Behind the Scenes with IMLS: “Extra Large” Objects, and Exposing the Collections Storage Building.
Next up are Susan Bartholomew and me, Laura Myles, Collections Specialists in the Registrars’ Office. We have worked closely cataloging and researching the objects that have been selected for the grant. It was hard to narrow down our favorite objects, or at least the ones we think are the most interesting, but here is a brief overview of some of the objects we enjoyed working with the most.
My name is Susan Bartholomew. I am a Collections Documentation Specialist and simply put, my role in this project was to update or revise catalog records for objects selected for the grant. This included identifying and applying accession numbers, which allow us to track an object both physically and digitally using our database, as well as conducting provenance research, and creating or modifying existing records in our database using cataloguing standards.
My personal highlights for this grant include the following.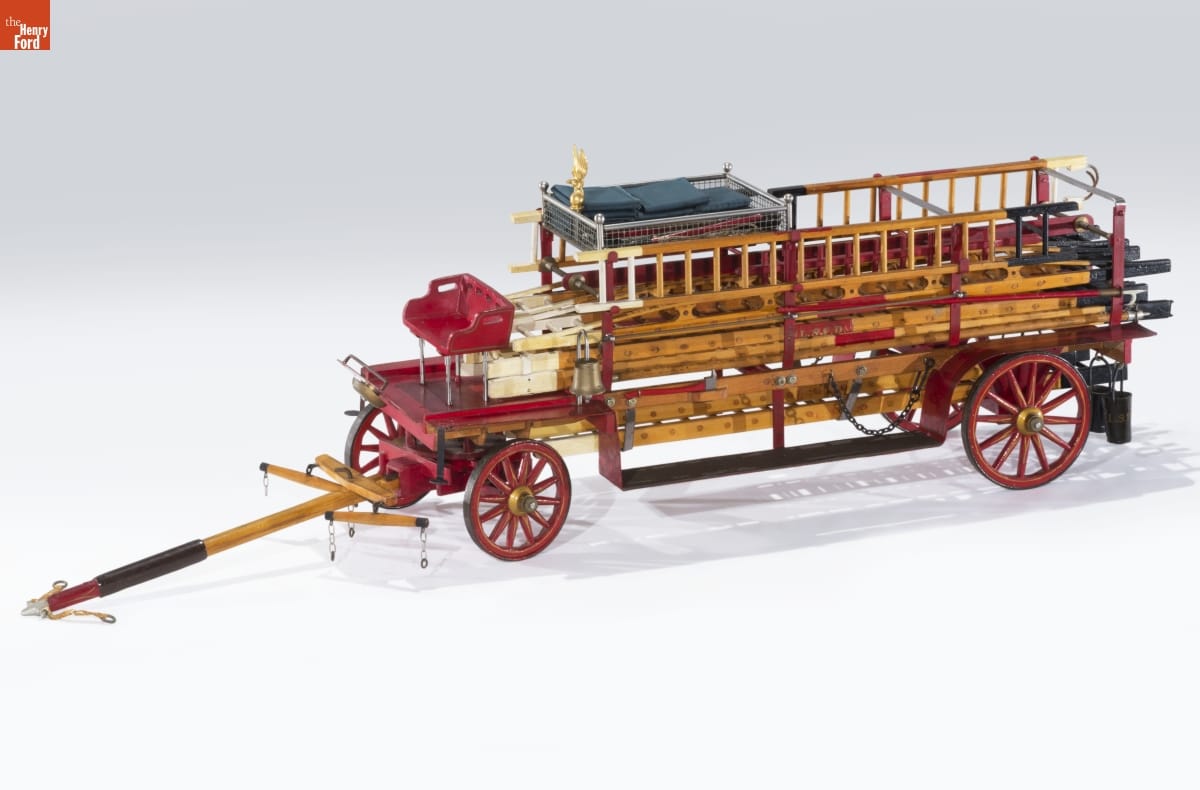
Model of a Hook and Ladder Truck, circa 1900 / THF170406
This incredibly detailed handmade model of a turn-of-the-century fire truck is complete with removable ladders, firemen’s tools, and what are possibly the world’s tiniest leather fire buckets.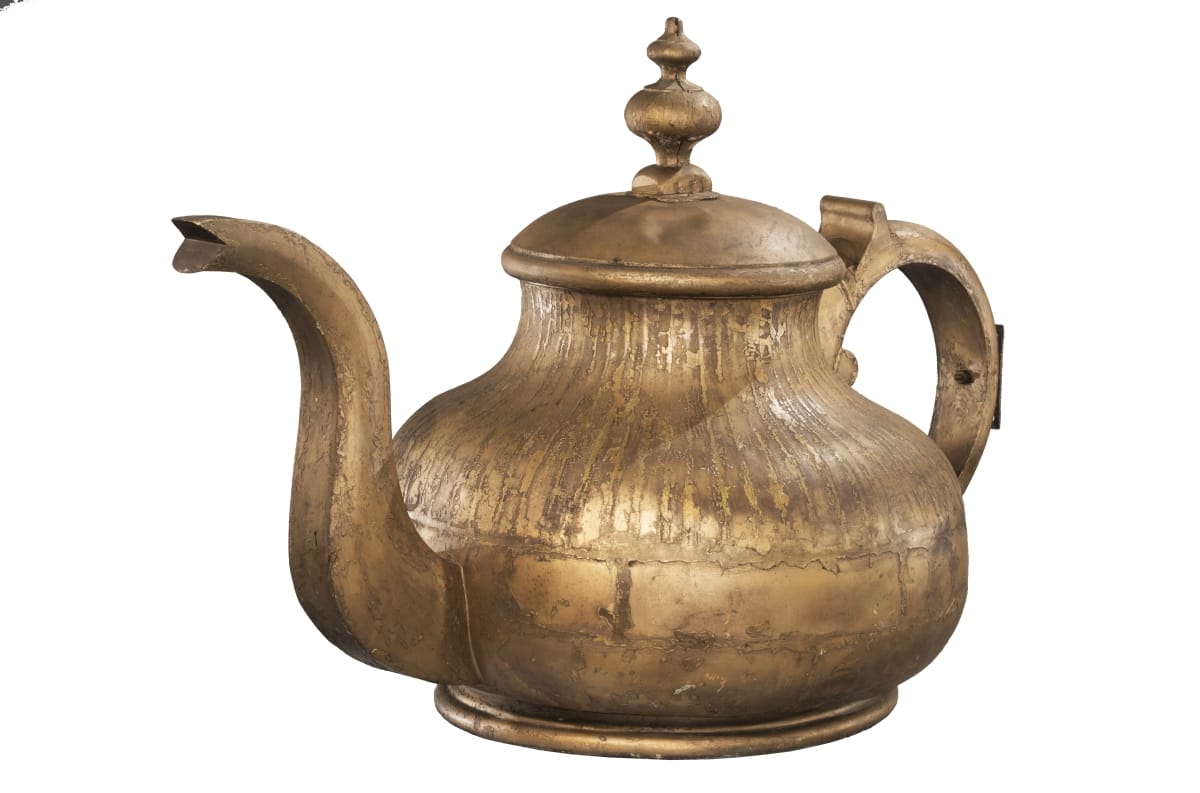
Shop Sign, 1870-1920 / THF175572
From the tiny to the huge, this is a shop sign in the form of a giant gold-painted tin teapot. It stands over three feet tall and four feet long from spout tip to handle. For more information about this unique giant teapot, check out this blog post Senior Conservator Louise Beck wrote about its surprising discovery.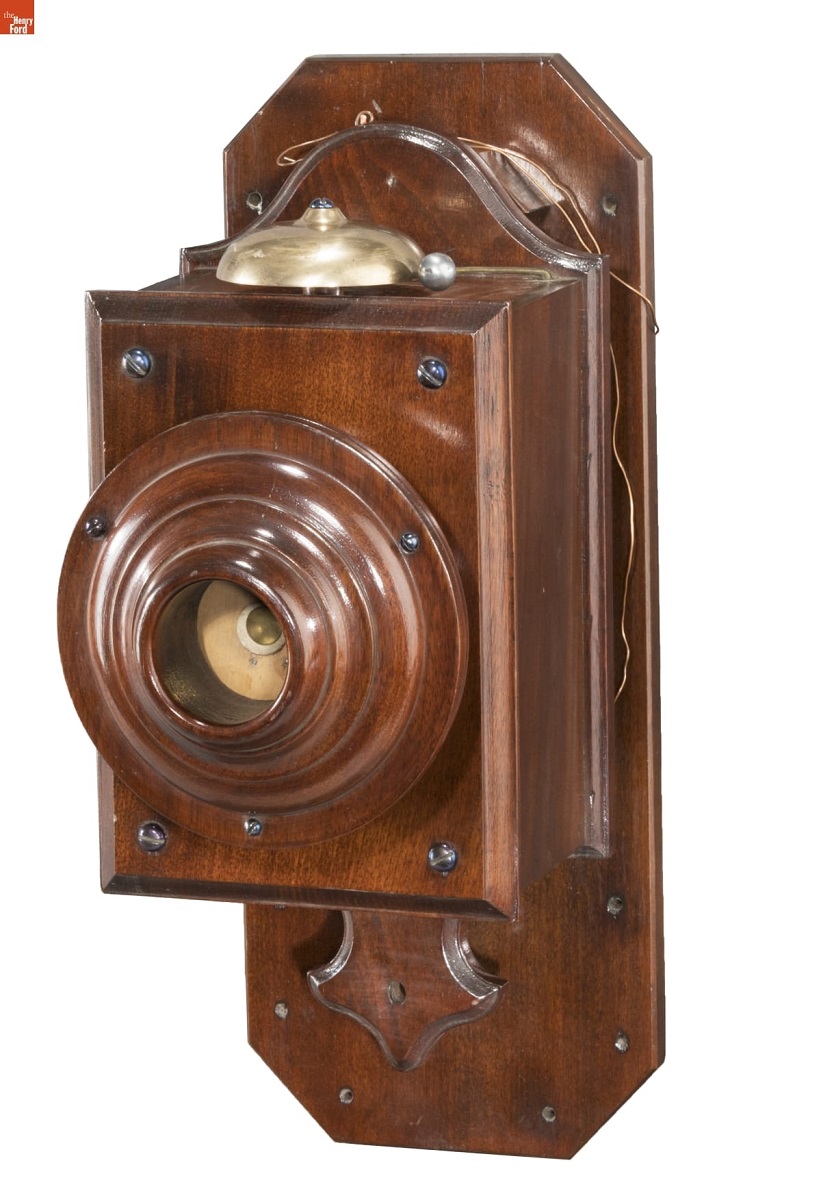
Acoustic Telephone, circa 1878 / THF176648
A very early example of a type of telephone that had no batteries, this device operated on the same principle as two tin cans connected by a string, an idea that had been around for centuries. They were used in pairs and were connected over a short distance by a tightly stretched wire. With no dependence on electricity, they were advertised as being more reliable than battery-operated telephones. This unit was one of a pair used by the father of the donor to connect the flour mill he operated to the boats he used to ship his flour. One set would be at the mill and the other was placed on the wharf boat half a mile away.
And now, Laura Myles shares her favorites.
Like Susan, I have assisted with cataloging, but I also research objects more in depth to uncover missing dates and/or manufacturers, as well as approving records to go online into our Digital Collections. Working on the grant over the last three years has been a wonderful learning experience, as the objects are so varied you really have no idea what to expect.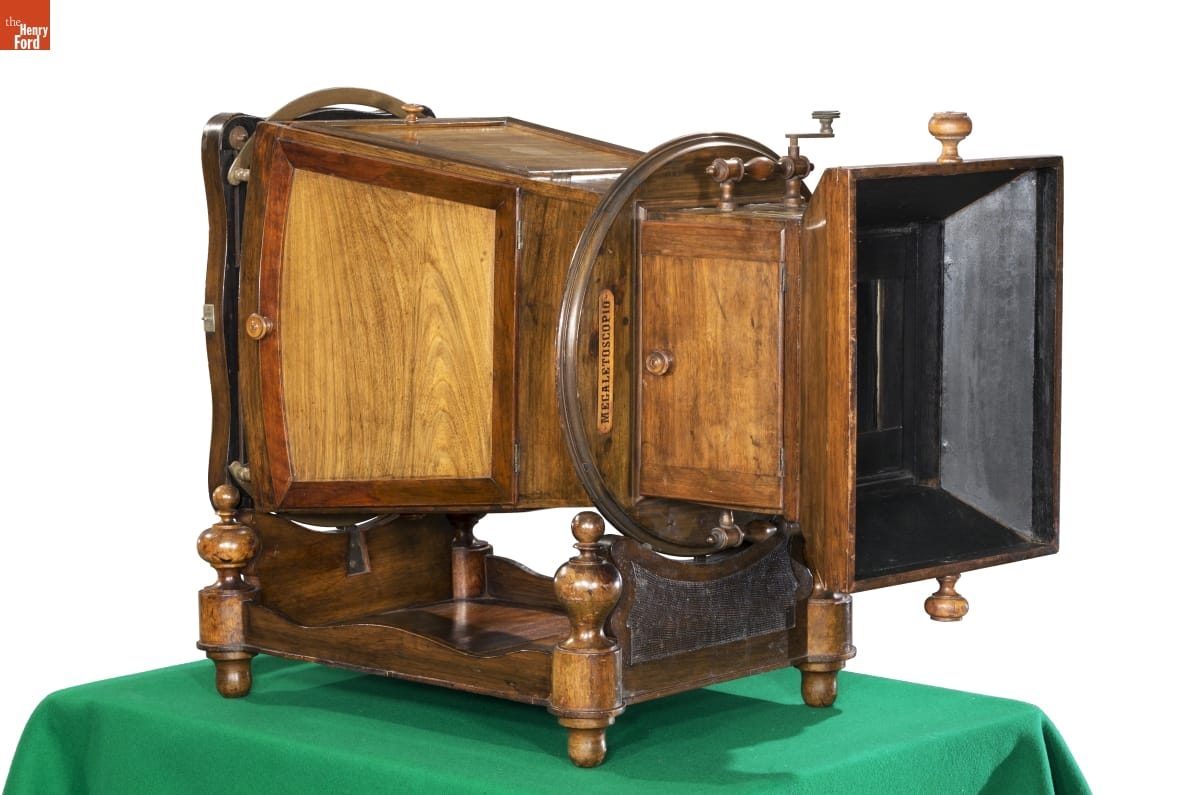
Charles Ponti Megalethoscope, 1862 / THF179318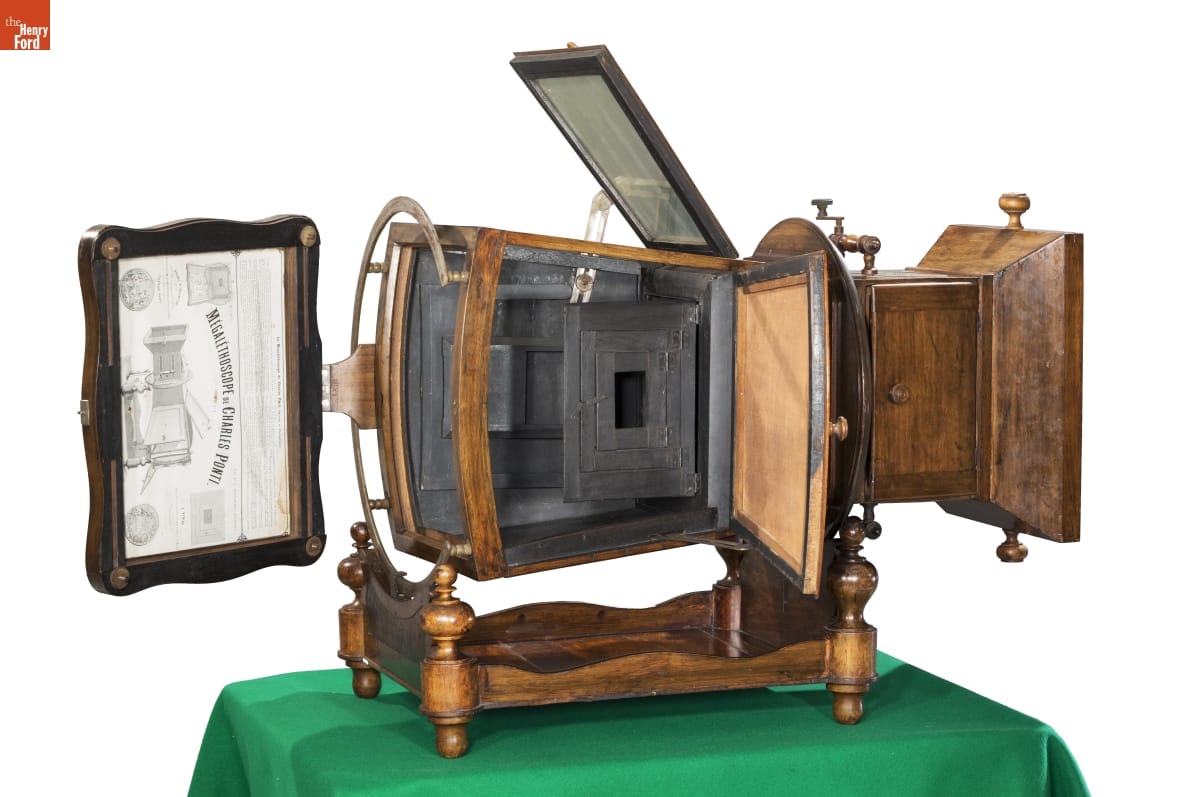
Charles Ponti Megalethoscope, 1862 / THF179324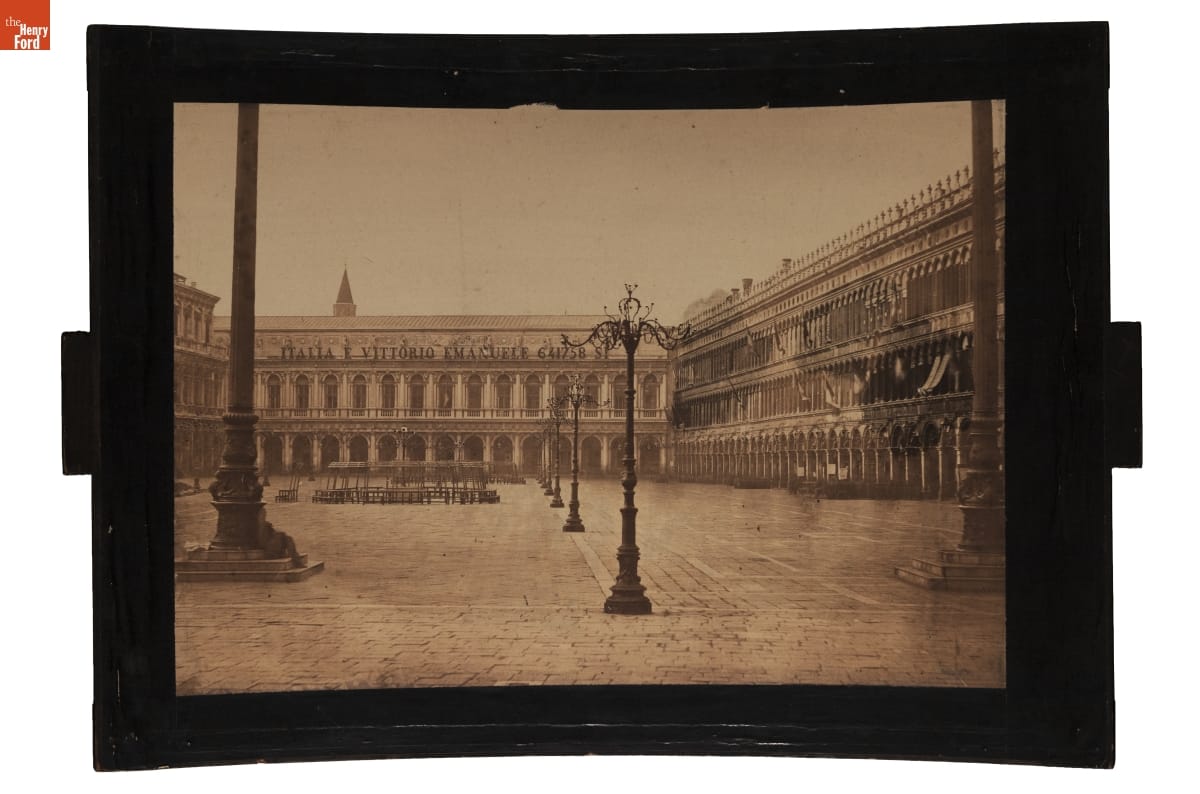
Megalethoscope Slide, "St. Mark's Square," unlit / THF179345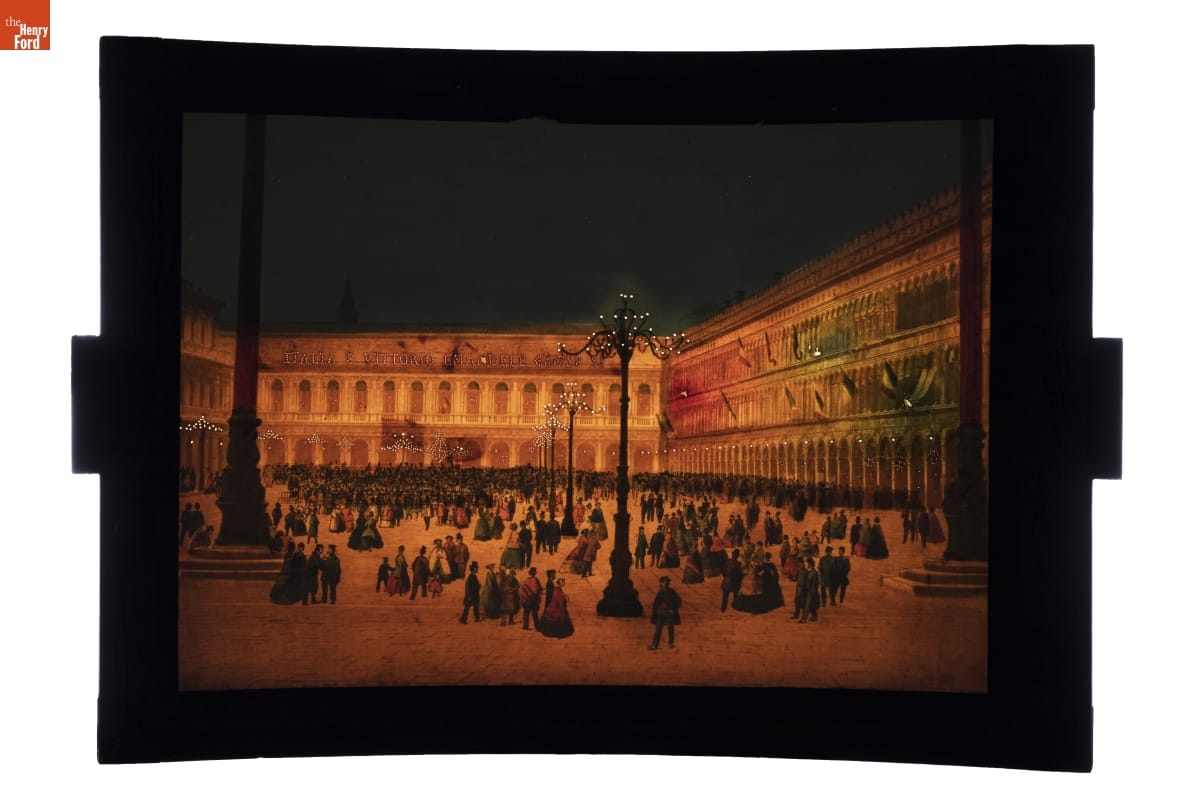
Megalethoscope Slide, "St. Mark's Square," lit up / THF179346
Perhaps my most favorite object is the megalethoscope and its slides. One of the best parts of my job is rediscovering hidden treasures in the collection. While we knew this was something special by looking at it, it was not until we were working on the slides that we knew how truly special it was.
At first glance, it looks like the megalethoscope is a fancy magic lantern device—merely projecting the images on slides. The megalethoscope was designed by Charles Ponti while he was living in Venice, Italy circa 1862. Ponti photographed his travels through France, Switzerland, Italy, and Egypt, and it was these photographs that he turned into transparencies for his megalethoscope, costing five francs each at the time. These transparencies look like normal slides until they are inserted into the megalethoscope and manipulated to show night views painted onto the backs of the images but hidden by a dustcover. One of the 22 slides can be seen above. For even more information about the megalethoscope, here is a blog post written about its conservation and photography.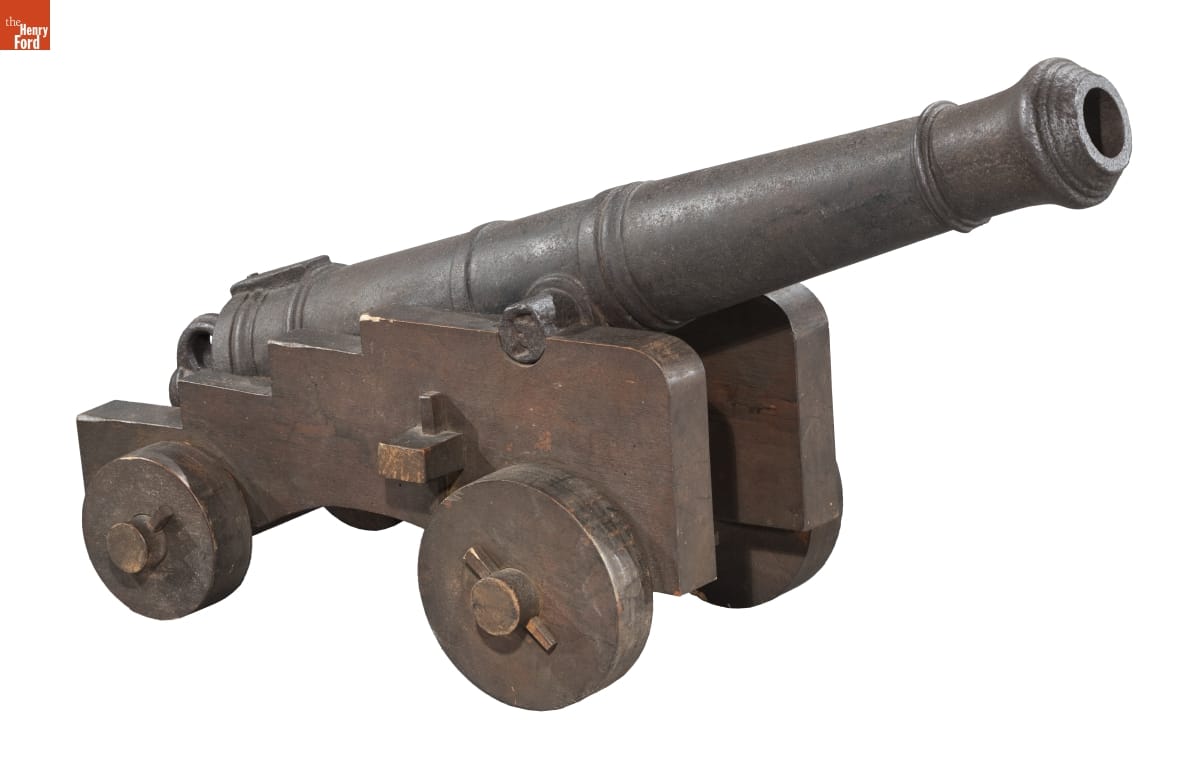
Naval Cannon, circa 1780 / THF179510
Another object that I enjoyed researching was this naval cannon. While we know this cannon was accessioned in 1929, we do not have information about who made it or where it was used. Based on its estimated manufacture date, circa 1780, and similar design to British artillery, I reached out to the Royal Armouries, which helped eliminate the possibility of it being British in origin. Unfortunately, we do not know its history, but at least we know it was very likely made in the United States to be used on a merchant marine vessel.
Sign / THF172438
This sign advertising the O. H. Perry Inne is one of my favorites just for its connection to the War of 1812 and Oliver Hazard Perry. On the front of the sign is a portrait of Perry, there is an eagle with seventeen stars above (although there were eighteen states by 1813, further adding to the mystery), and the words “Lake Erie” below on the reverse. Perry was regarded as a hero after defeating a British squadron in Lake Erie, which led to Detroit being freed from British control. Unfortunately, this sign’s history has been lost to time, although there are similar signs that have come up for auction. It seems likely that some local establishment capitalized on Perry’s name, probably along Lake Erie. We can only imagine the building it adorned.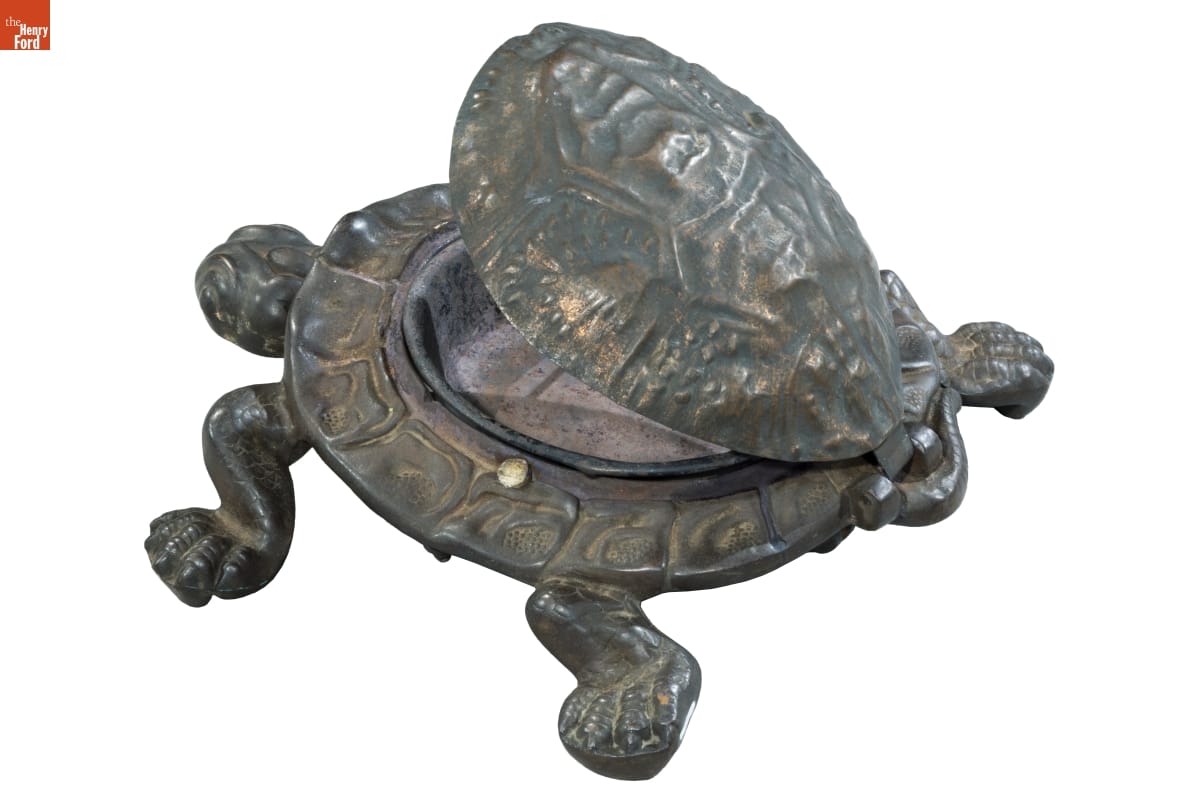
Spittoon / THF186256
One of the more recent objects to make my short list, and Susan’s as well, is this turtle spittoon. We think it is one of the cutest objects to have come through the IMLS pipeline, especially since spittoons themselves are not the most elegant of objects. Apparently turtle designs for spittoons were quite popular in their time, as well as remaining popular among collectors. The one in our collection is functional: pressing the turtle’s head flips open the shell to reveal the bowl.
If you would like to know more about the cataloging process, you can read more about that here (and see a few more interesting objects we have worked on as a result of this and a previous IMLS grant), and if you would like to know more about the provenance research Susan refers to, check out Associate Registrar Aimee Burpee’s blog post.
This is but a small sampling of some of our favorite objects from this grant. Over the course of the grant so far, we've digitized nearly 3,000 objects, and cataloged and conserved over 4,300 total objects. Unfortunately, this means that we had to be a little bit picky in what we shared here, but hopefully you will discover more of the treasures from our Collections Storage Building yourself while searching our Digital Collections.
Marlene Gray is IMLS Project Conservator, Susan Bartholomew is Collections Documentation Specialist, and Laura Myles is Collections Specialist, all at The Henry Ford.
by Marlene Gray, by Susan Bartholomew, by Laura Myles, digitization, research, conservation, collections care, #Behind The Scenes @ The Henry Ford, IMLS grant
The Making of “Fueled by Passion”: Behind the Scenes of Driven to Win
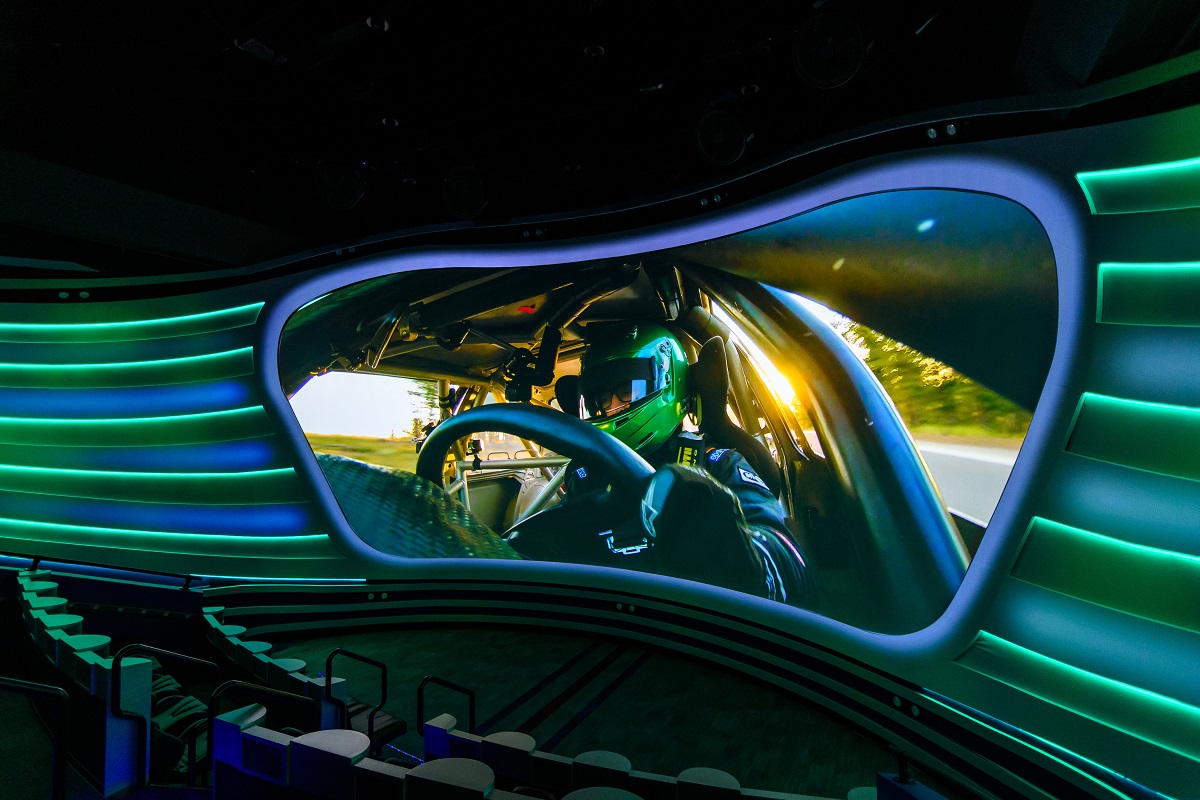

The multisensory theater in Driven to Win at The Henry Ford.
American innovation knows no bounds, and racing, which combines technical excellence with the human endeavor, speaks to our constant need to push the limits of what’s possible. That’s why Henry Ford Museum of American Innovation has gathered one of the finest collections of innovative, powerful, record-busting race cars and automotive artifacts in the world.
Building on this unparalleled collection, The Henry Ford’s newest exhibition, Driven to Win: Racing in America presented by General Motors, gives guests a visceral sense of just how thrilling it is to “go faster and push the limits of racing.” BRC Imagination Arts partnered with The Henry Ford to help bring its incredible collection to life through emotional storytelling, and to get guests excited about “the lives of those who invented their way into the winner's circle and often changed the world in the process.”
The result: Fueled by Passion, the exhilarating, immersive experience at the heart of the new exhibition. The 15-minute sensory-filled experience shares the stories of five people who have empowered themselves to push their personal limits, and ignites the drive we all have to power our passions.
Continue Reading
2010s, 2020s, 21st century, racing, race cars, race car drivers, movies, Henry Ford Museum, Driven to Win, cars, #Behind The Scenes @ The Henry Ford
Restoring Sir John Bennett's Giants
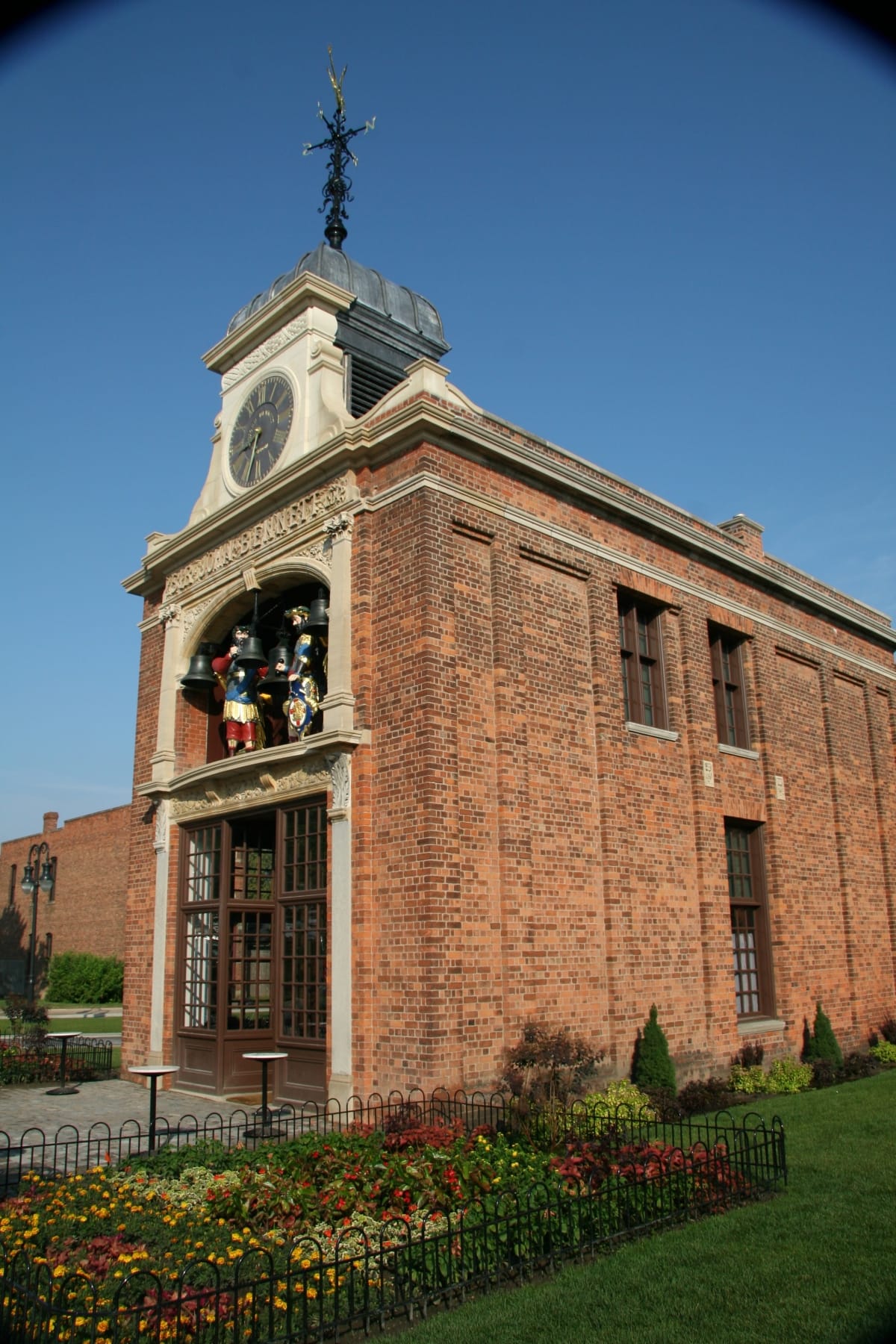

Sir John Bennett. / THF17783
For decades, Sir John Bennett's shop—with its figures of mythological giants Gog and Magog—has intrigued and enthralled Greenfield Village's visitors. Prior to 1930, the jewelry and clock shop was a popular presence many thousands of miles away in London, where its animated giants chimed the quarter-hours above the busy thoroughfare of Cheapside.
While London and Dearborn would seem to have little in common, Gog and Magog—if they could talk, as well as chime—might disagree. Exposure to the weather has been a continuous element in their over 125 years of timekeeping in both England and America. Climate has taken its toll on the figures. So, during the winter of 2005–2006, The Henry Ford undertook an extensive restoration of the Sir John Bennett figures.
Clock Figures
This was not the first time that the figures, or "jacks," as they are known in the world of clocks, had been given a thorough restoration. When Henry Ford originally brought them to the United States in 1931, he had them repaired and repainted. A second restoration and repainting took place in the 1970s.
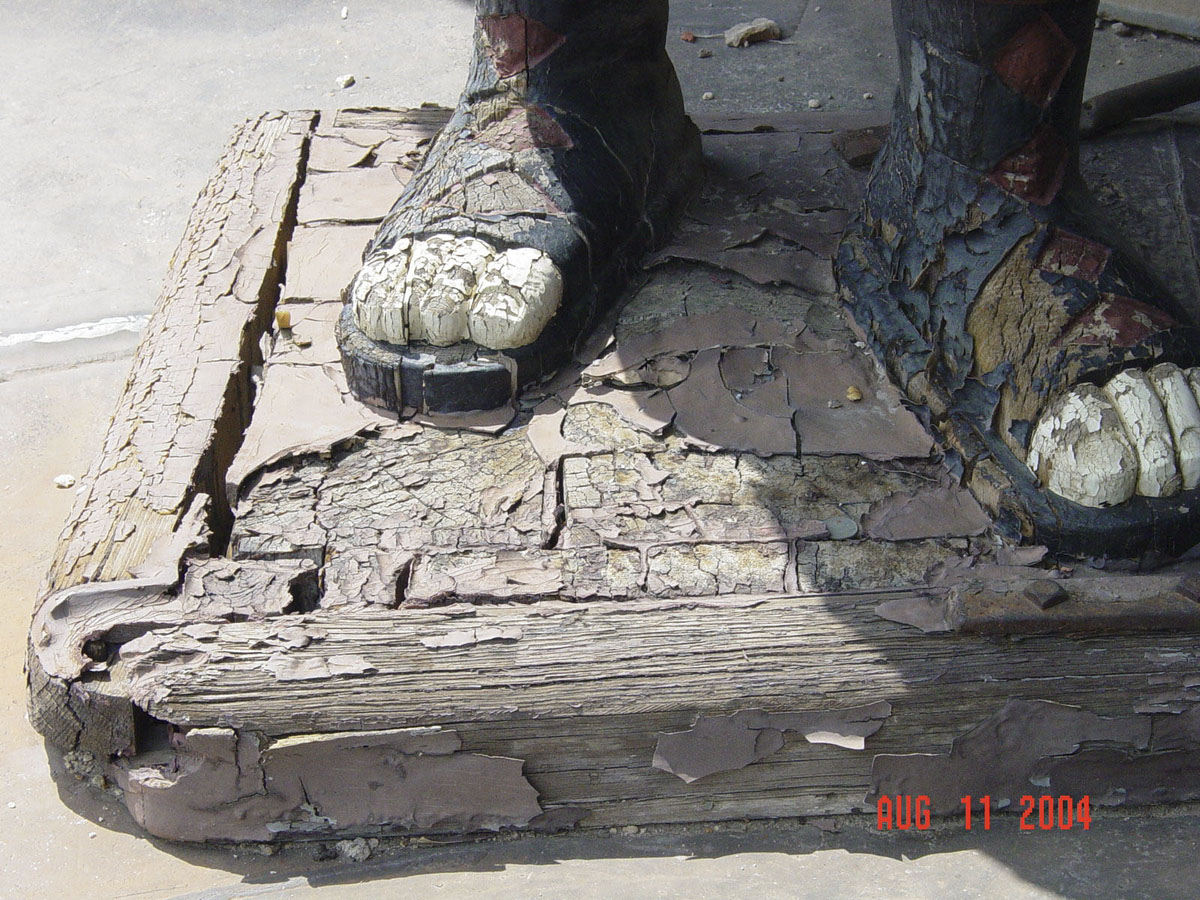

Pre-restoration deterioration on the feet of one of the carved wooden figures.
The 2005–2006 restoration, in addition to reversing damage and safeguarding Gog and Magog for future generations, also offered an opportunity to attempt to determine what the wooden figures originally looked like. Deeply carved recesses were carefully excavated in order to discover clues to the original color scheme. Conservators also studied a similar set of Gog and Magog figures in London's Guildhall; a set in Melbourne, Australia; and many historical prints and illustrations to compare our paint analysis with other known examples.
One finding was that the giants' chain mail had, at some point, been painted the color of their clothing. The chain mail is now painted to look like metal rather than cloth. Areas of the giants' armor were found to have traces of gold leaf in the recesses. Also, successive paint layers and weathering had obscured a number of decorative elements in the giants' armor. Previous restorations had used gold-colored paint on the armor, which eventually oxidized and turned brown. In 2005–2006, all the decorative armor components were coated with gold leaf.
The figures themselves were in poor structural condition, with many breaks and numerous large cracks. With a view to preserving as much of the original figures as possible, the decision was made to inject a deep penetrating resin into the porous wood, rather than cut out and replace damaged sections.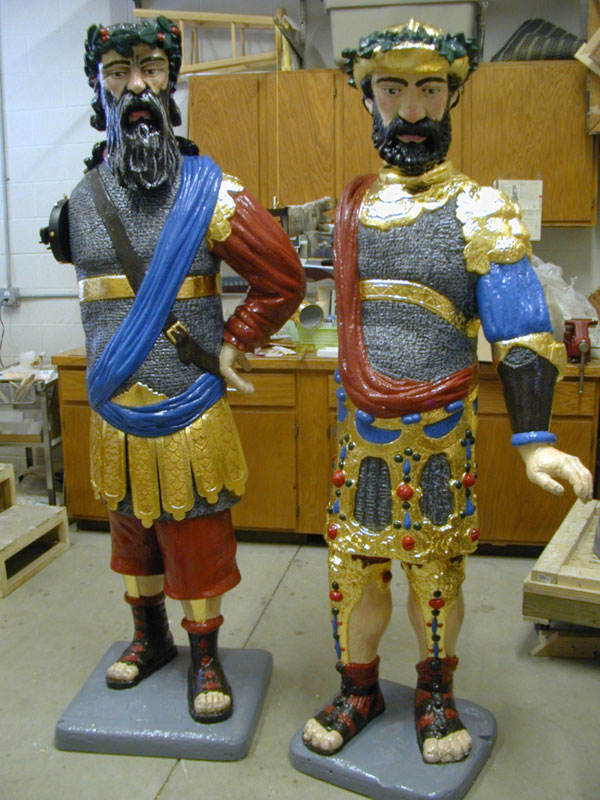
Newly restored Gog and Magog await their return to the Sir John Bennett shop.
Of course, Gog and Magog are not the only figures in the facade of the building—Father Time and a Muse are also in attendance to assist in the job of chiming. Made of plaster rather than wood, these figures were given structural repairs and then gilded with 1,400 sheets of gold leaf. During the repair work on the Muse, decorative elements were discovered on the harp under layers of paint and filler. The decoration was carefully restored, and can be seen on the front vertical post of the harp. A maker's name, "Brogiotti," was also revealed during the restoration.
Finally, the internal mechanisms for all four figures were repaired, and additional lubrication points were added to help minimize future wear.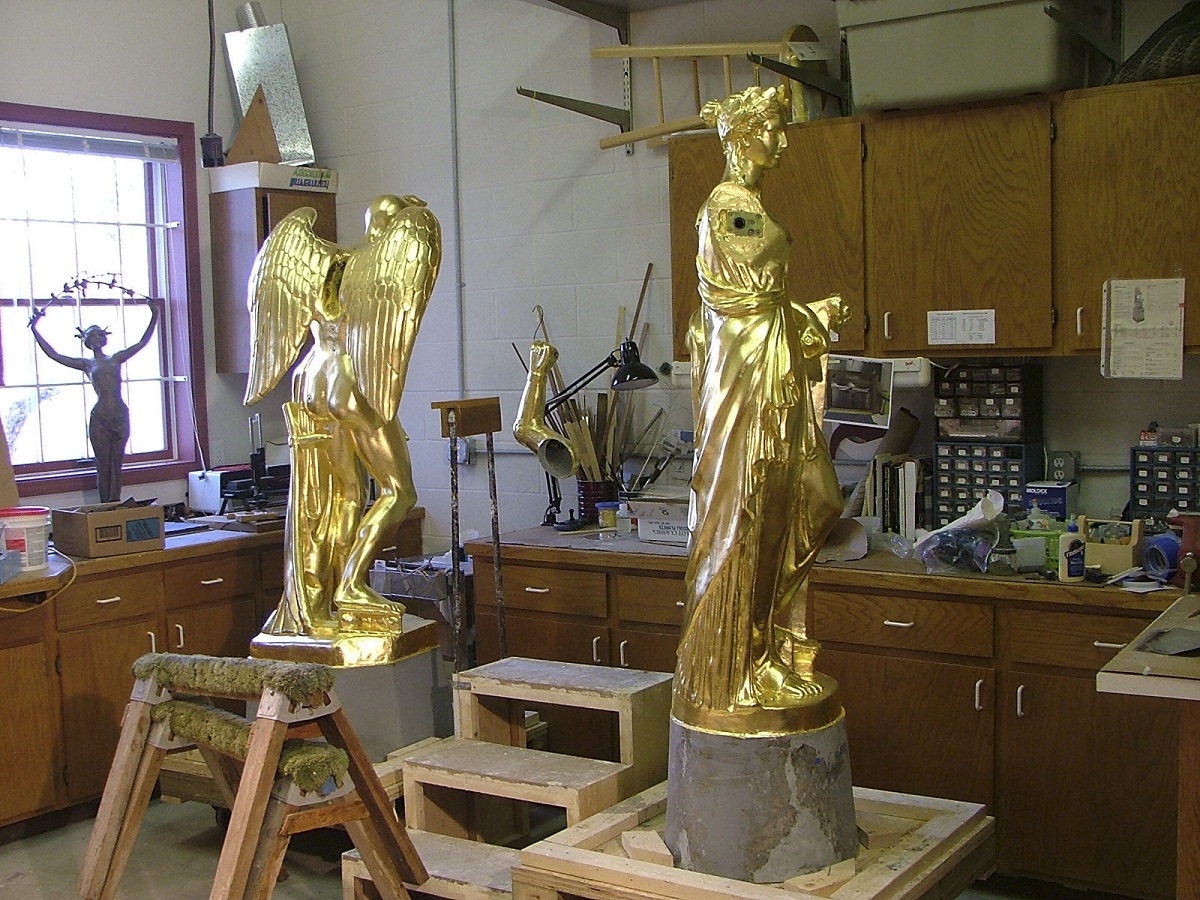
Father Time and the Muse show off their new coats of gold leaf.
The Clock
The clock mechanism was in need of a complete overhaul. Many of the bronze bearings—separate components fitted into the clock movement's large cast iron frame—had become worn and needed to be "re-bushed" to bring the mechanism back to its original operating specifications. During cleaning, conservators discovered that all of the cast iron framing was originally painted a blue-green with white pin striping. All of this original paint was carefully cleaned and preserved.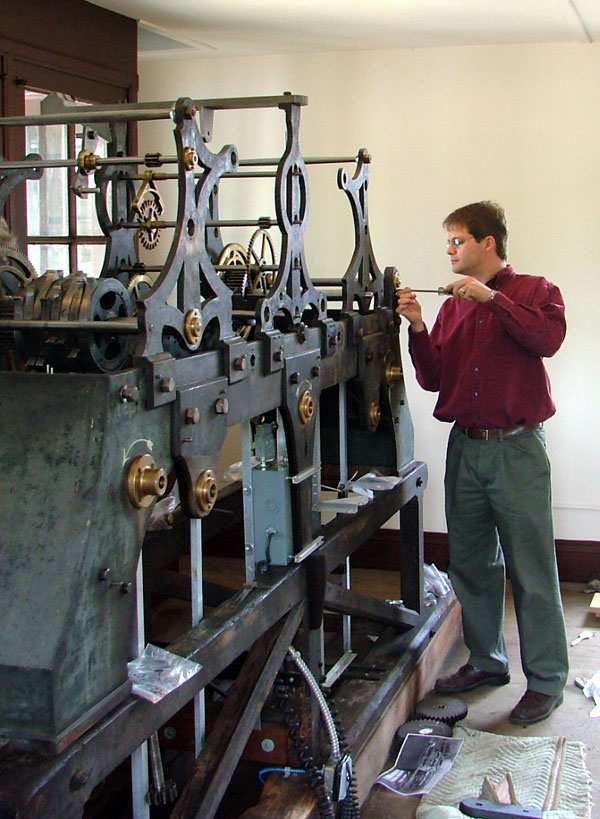
Conservator Malcolm Collum reassembles the restored Sir John Bennett clock movement.
During the 1931 reconstruction of the building and clock in Greenfield Village, a number of components were replaced. Cleaning the mechanism helped us gain a better understanding of the extent of Henry Ford's restoration: the modern steel components lack the dark graining found in the original wrought iron pieces. These dark lines are called "slag inclusions," remnants of a glass-like material that gets worked into the iron during the smelting and production processes.
Weathervane
Gog and Magog receive the most attention from visitors—understandably, given their size, character, and animation—but higher up, fully exposed to everything the Michigan climate has to offer, is one of the most vivid elements of Sir John Bennett's shop: the dragon weathervane. The dragon—made of hammered copper and detailed with sharp claws, taut bat-like wings and a fiery tongue—is a quiet masterpiece of design, craftsmanship, and balance. Its swept-back wings and extended tail are designed to catch even the slightest breeze; its head is weighted with lead in order to balance the body and allow for free pivoting.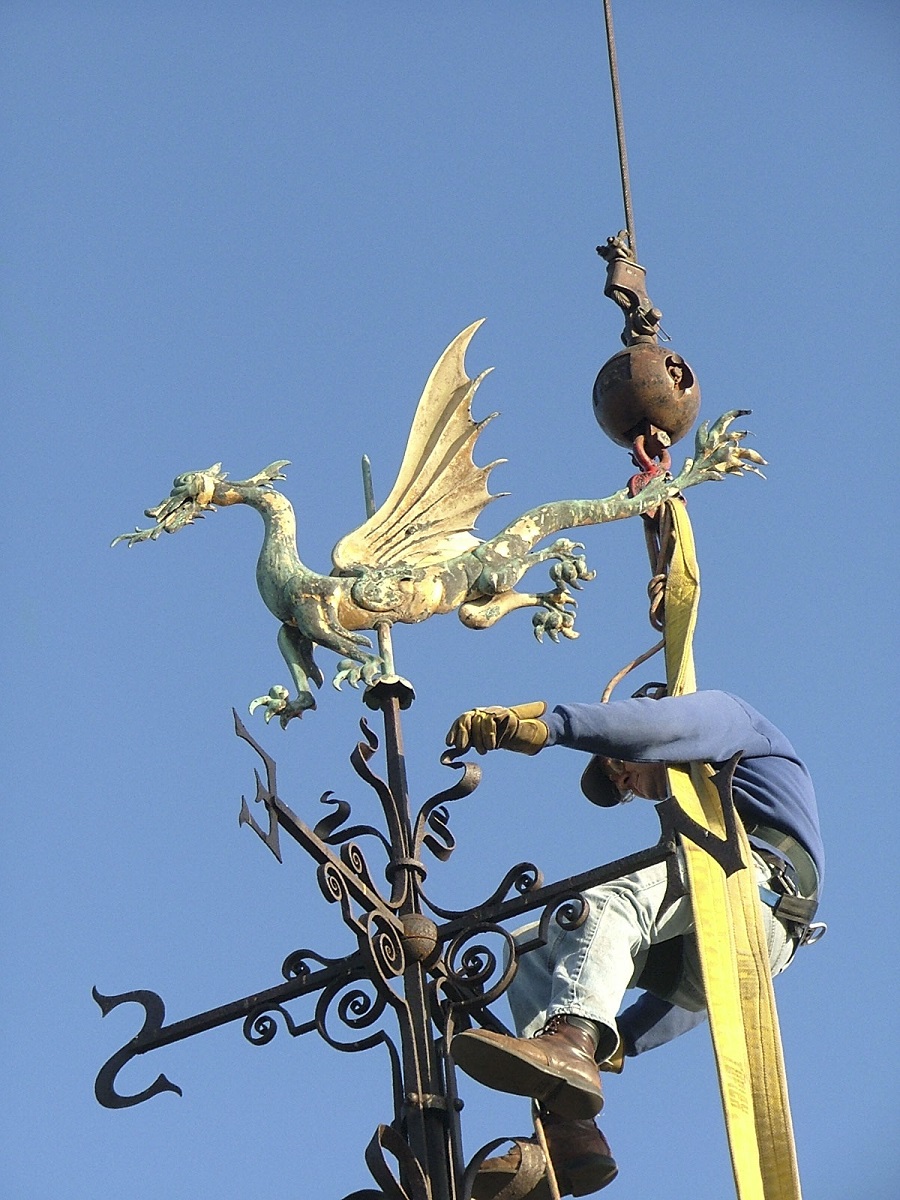
The dragon weathervane is readied for removal from its perch.
When the dragon was removed from its perch in late 2005, it was found to be in stable condition. Structural repairs were followed by a thorough cleaning to remove corrosion and degraded metallic paint. Finally, rather than simply repaint the dragon, we returned it to its original splendor with a coat of gold leaf.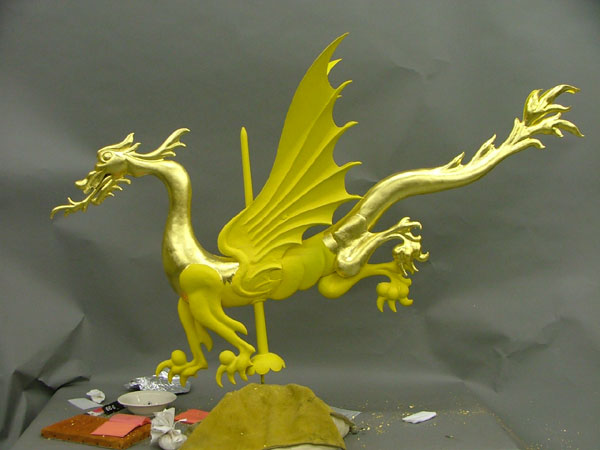
Dragon weathervane during gilding.
Repaired and resplendent, silhouetted against a Dearborn rather than a London sky, the dragon once again watches over the visitors who gather to watch Gog and Magog.
Malcolm Collum is former Conservator at The Henry Ford and Marc Greuther is Chief Curator and Vice President, Historical Resources, at The Henry Ford. This post originally ran as part of our Pic of the Month series in May 2006.
Michigan, Dearborn, Europe, 21st century, 2000s, Sir John Bennett, research, Greenfield Village buildings, Greenfield Village, conservation, collections care, by Marc Greuther, by Malcolm Collum, art, #Behind The Scenes @ The Henry Ford
The Webster Dining Room Reimagined: An Informal Family Dinner
 THF1882
THF1882With Greenfield Village reopening soon, you’ll find something new at the Noah Webster Home!
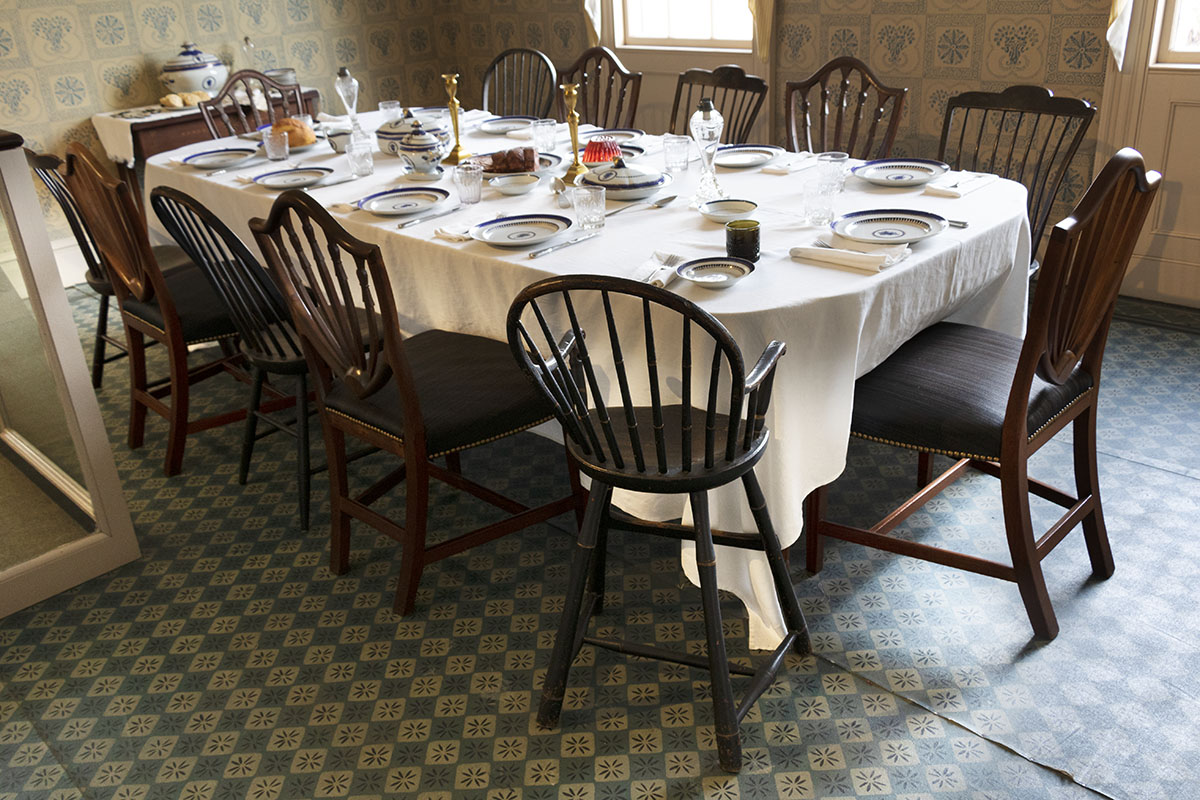

THF186494
We have reinstalled the formerly sparsely furnished Webster dining room to better reflect a more active family life that took place in the Webster household at the time of our interpretation: 1835.
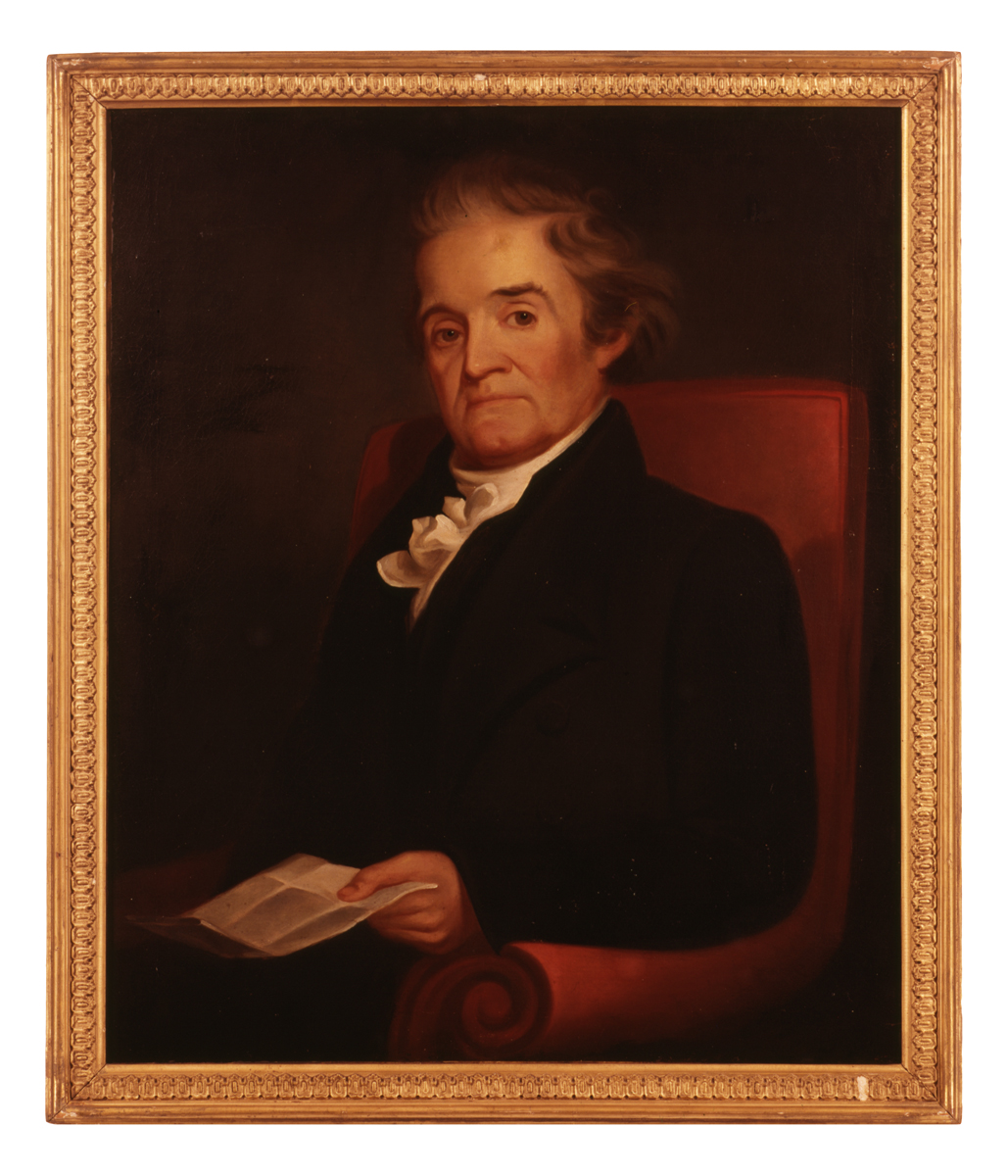

THF107986
Noah and Rebecca Webster moved to their New Haven, Connecticut, home in their later years to be near family and friends, as well as the library at nearby Yale College. This painting of Noah dates from about this time.

THF119510
The Websters moved into their comfortable, newly-built home on Temple Street in New Haven in 1823. This portrait shows Rebecca Webster from about this time as well.
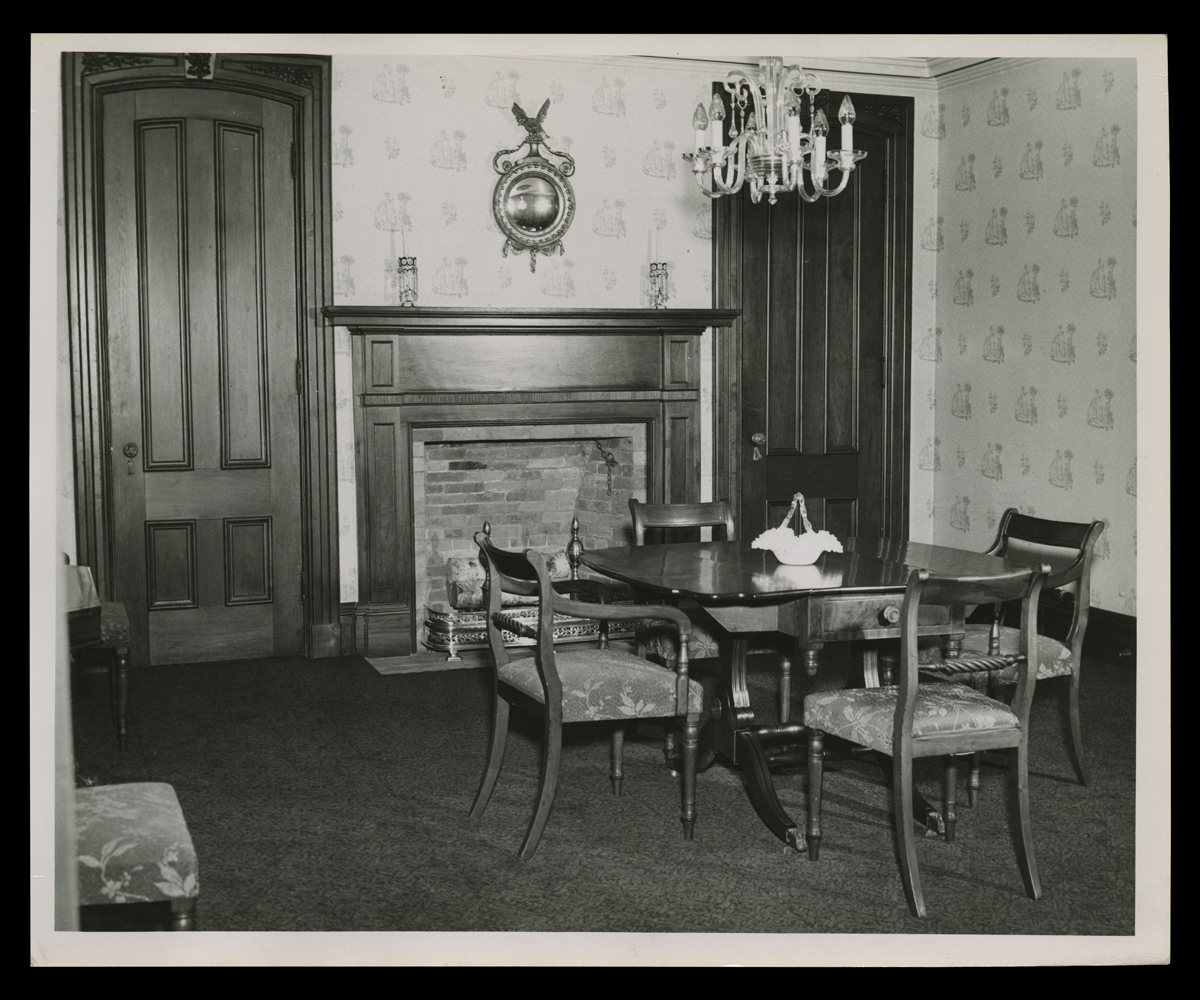

THF147812
New research and evolving historical perspective often lead us to reinterpret Greenfield Village buildings. So, furnishings change to reflect these richer or more accurate stories. This is what the Webster dining room looked like in 1947.
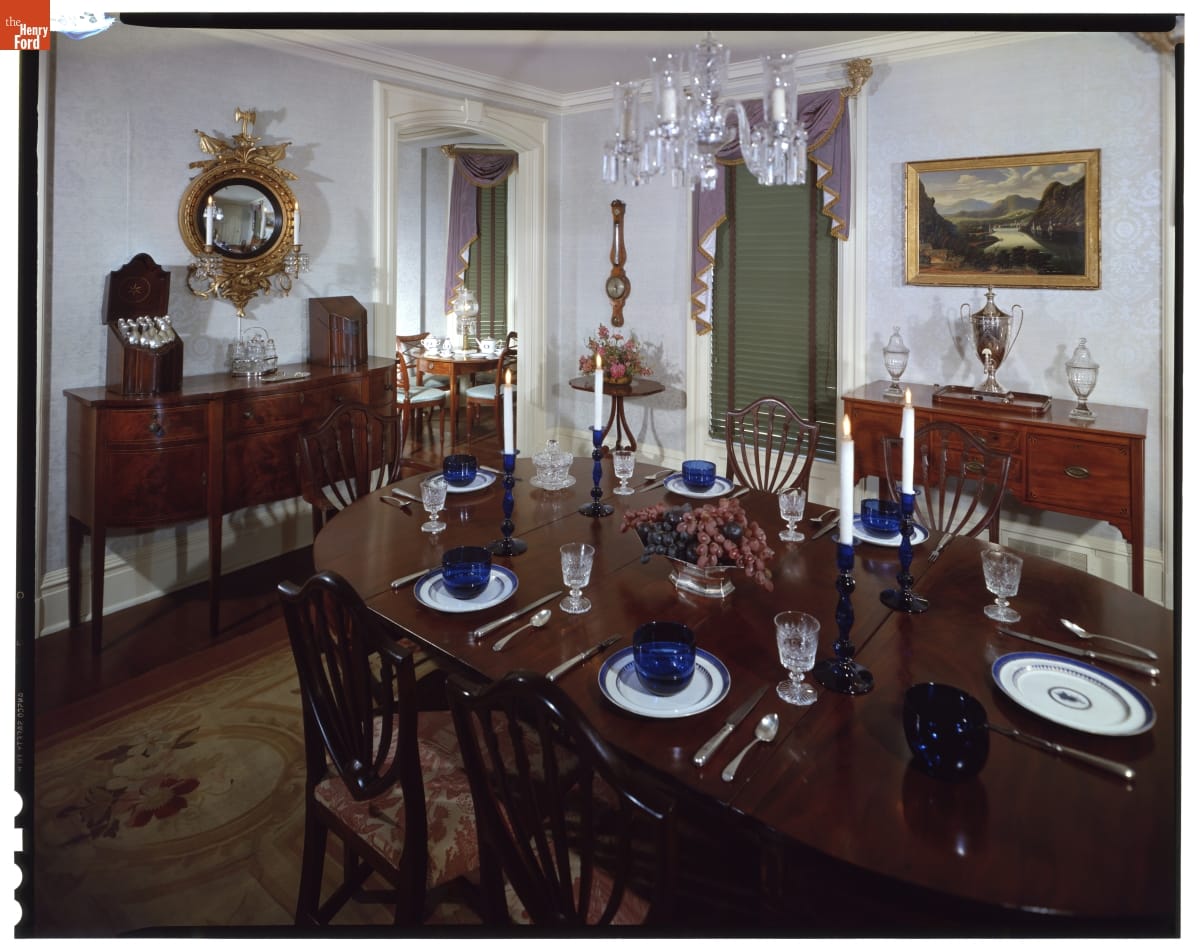

THF147776
In 1962, the Webster house was refurnished to showcase fine furnishings in period room-like settings—rather than reflecting a household whose elderly inhabitants started housekeeping decades before.
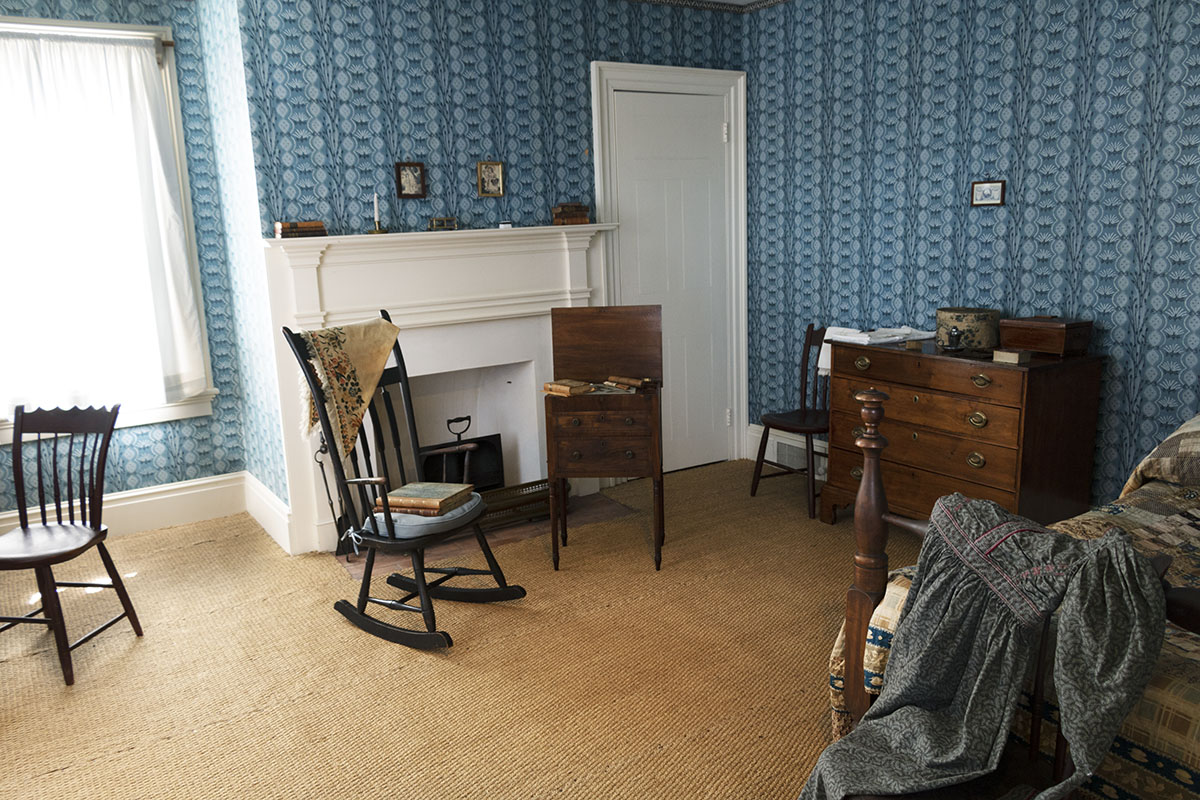

THF186507
In 1989, after meticulous research on the house and on the Webster family, the home was beautifully transformed, and its furnishings more closely reflected the Webster family’s lives.
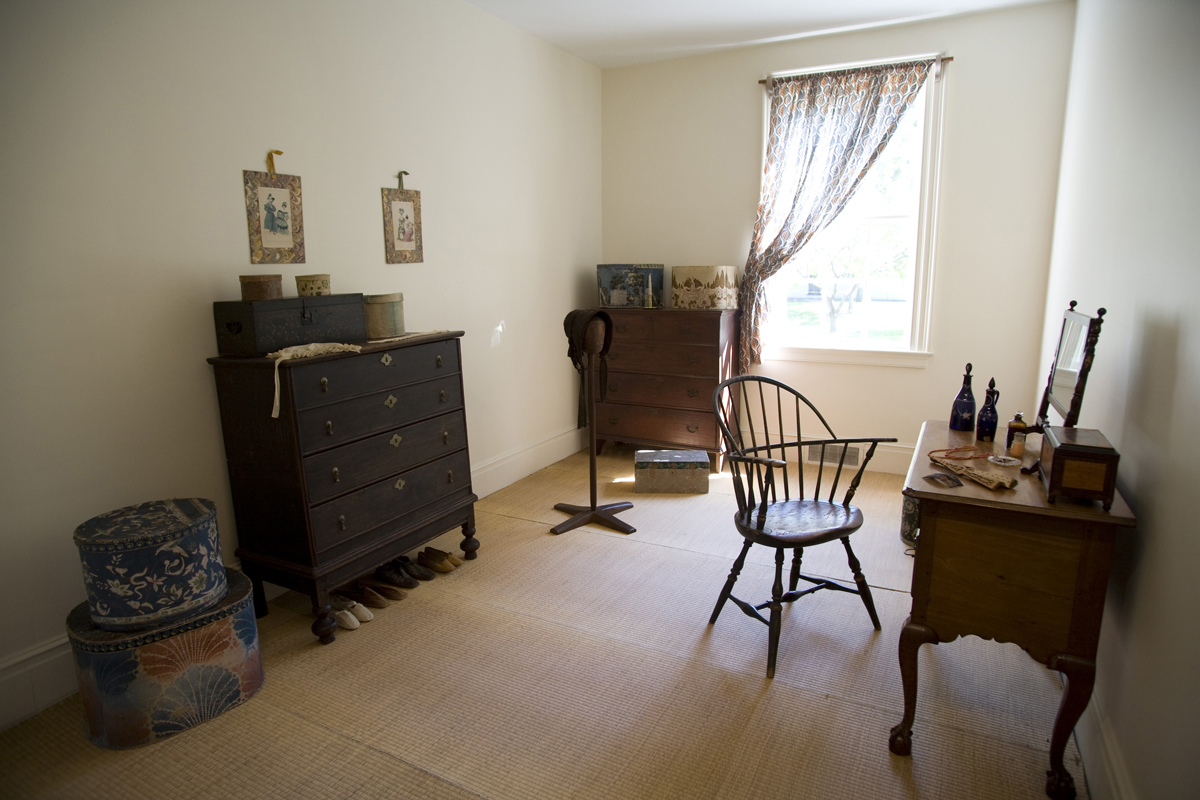

THF53248
You could imagine the Websters living there. This is Rebecca Webster’s dressing room.
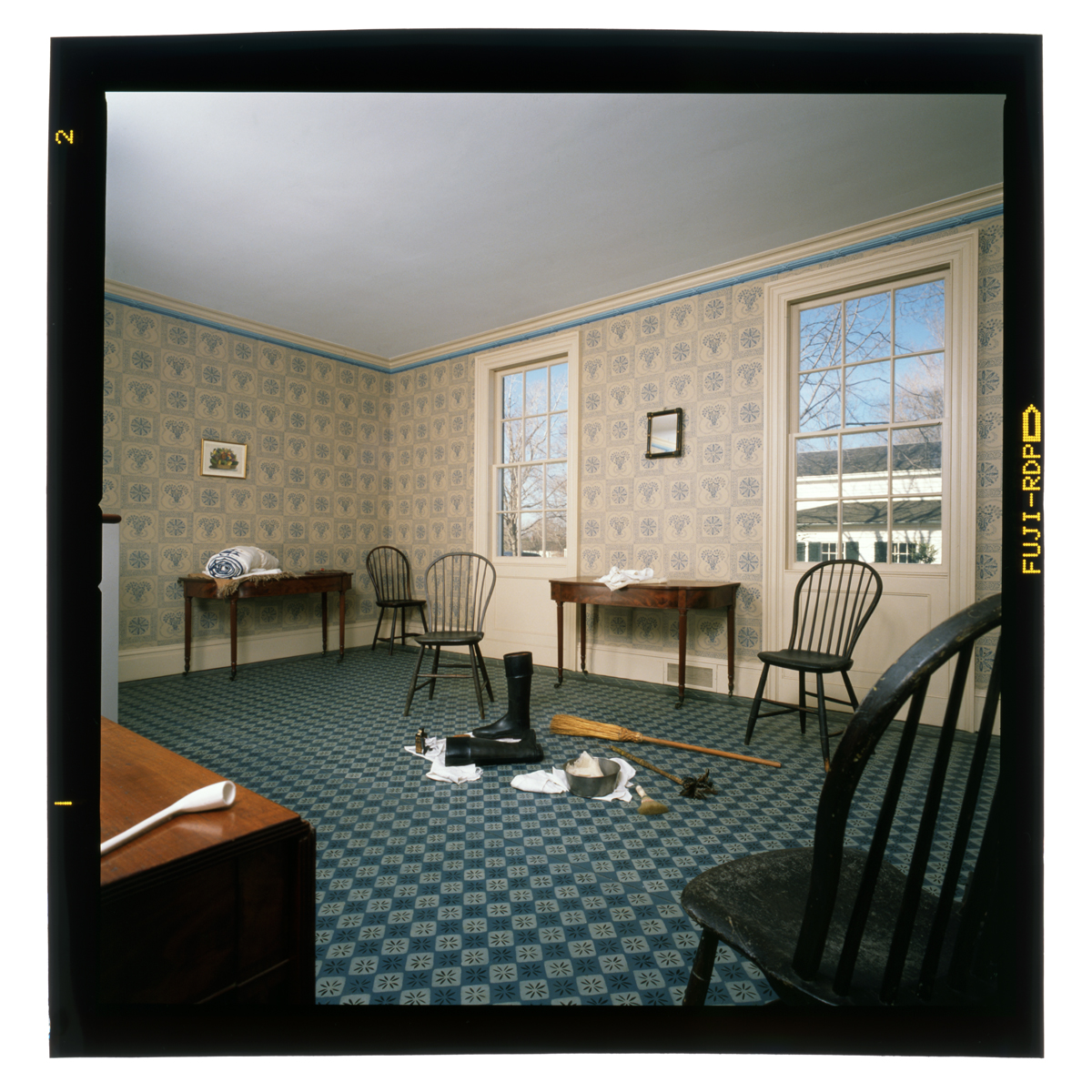

THF147817
Yet the dining room was sparsely furnished. The 1989 reinstallation suggested that the Websters were “in retirement” and “withdrawn from society,” and didn’t need or use this room much.
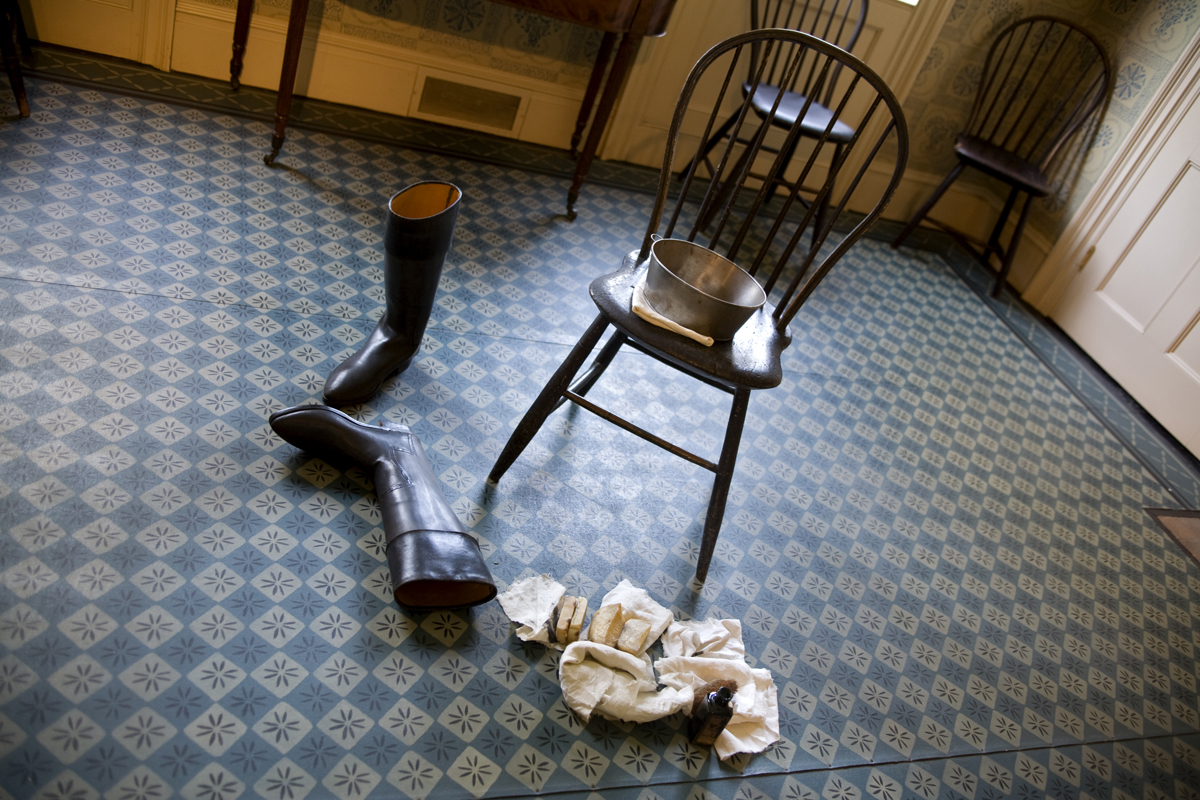

THF53258
The dining room was presented as a seldom-used space in the Webster home during the mid-1830s. This detail showed boots being cleaned in the otherwise unused room.
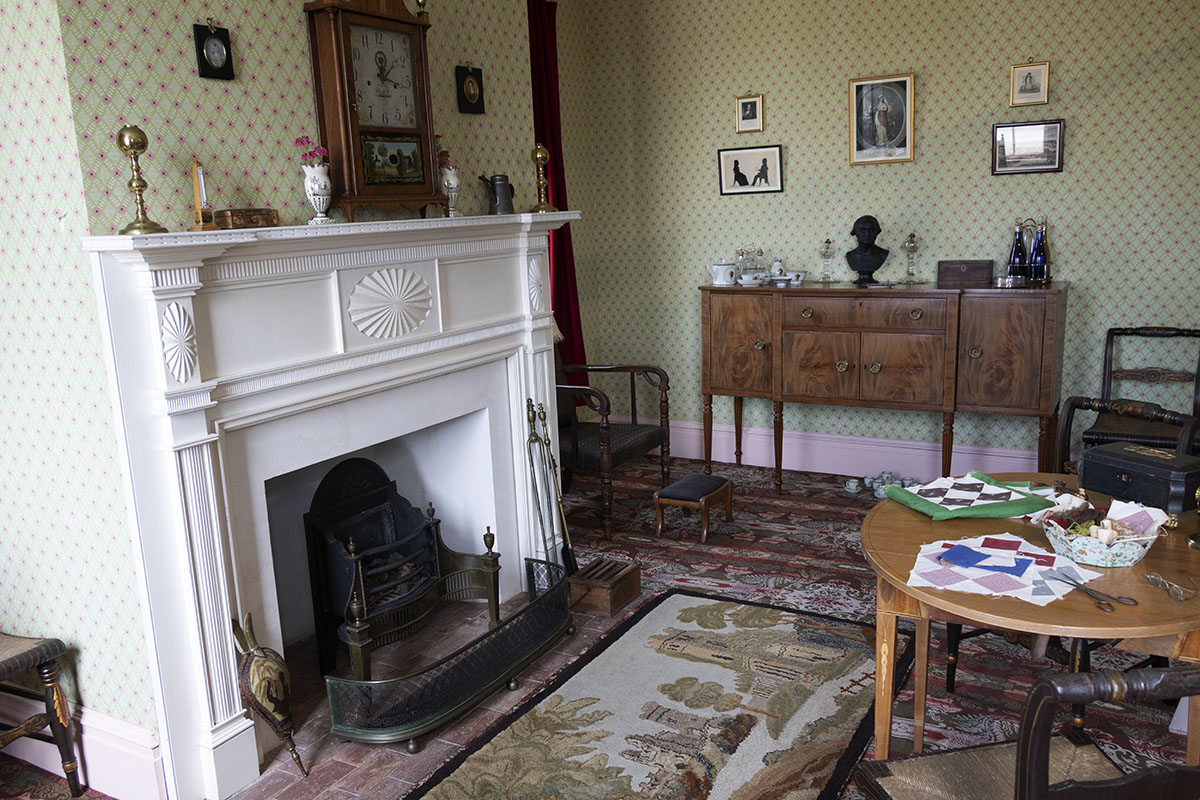

THF186509
Webster family correspondence and other documents paint a picture of a household that included not only family activities, but more public ones as well, during the 1830s and beyond.
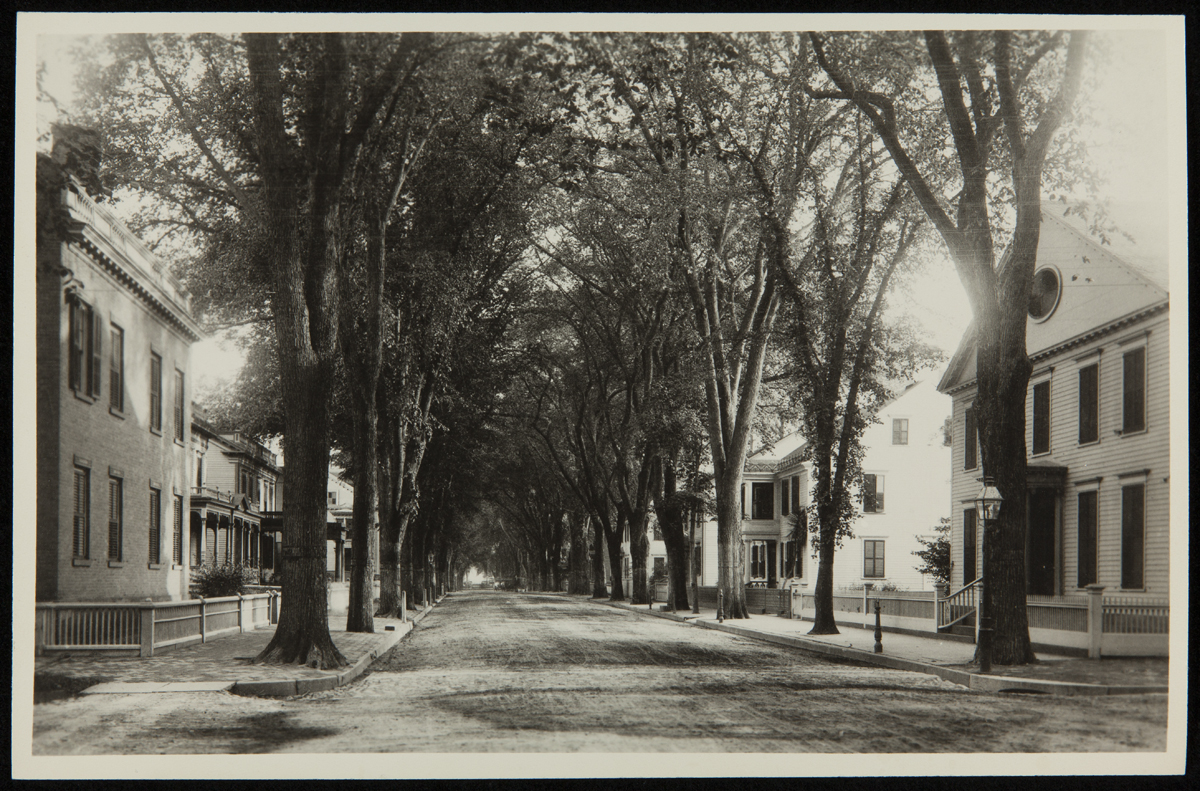

THF236367
Daughter Julia Goodrich and her family lived down the street and were frequent visitors. The Webster house appears at far right in this photo of Temple Street taken in the 1920s.
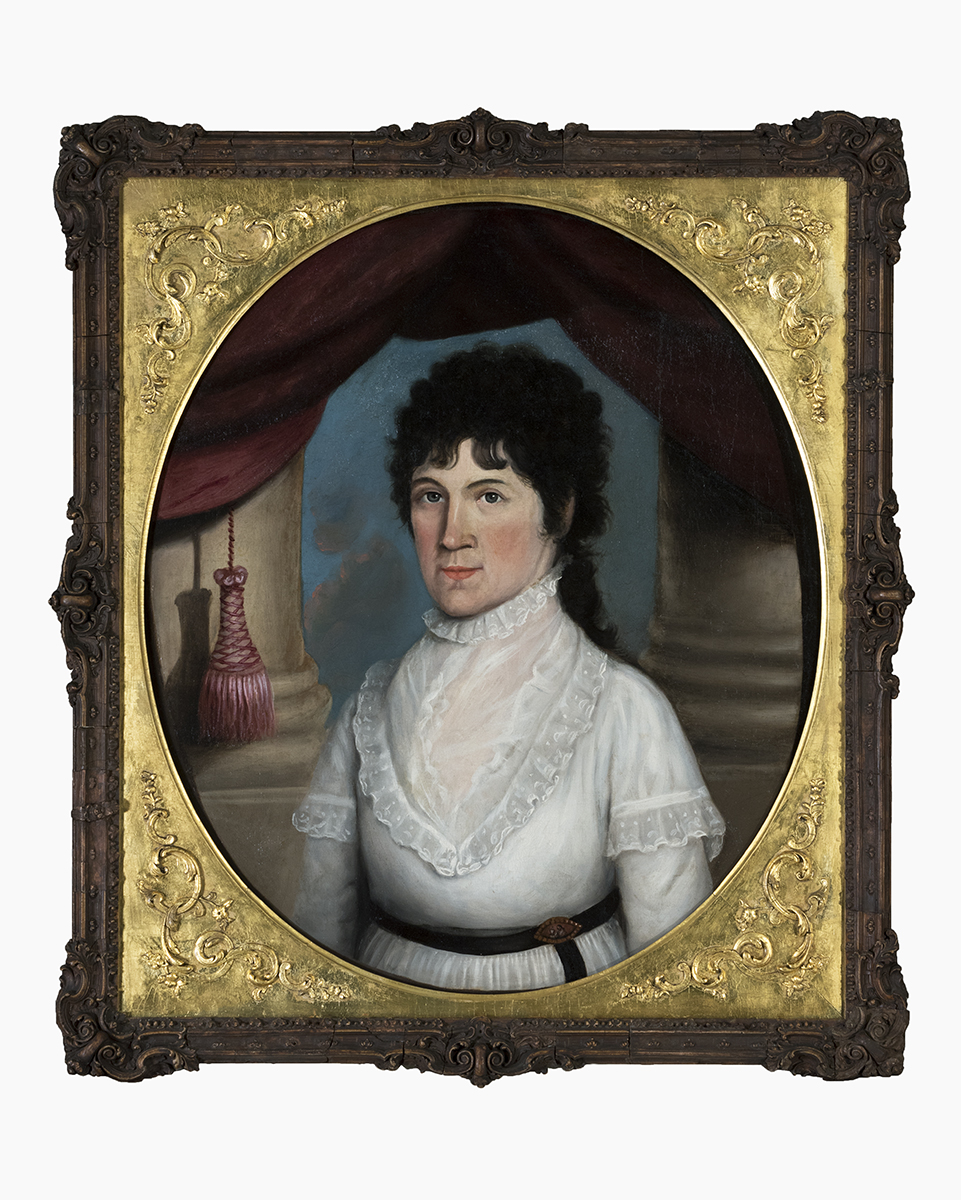

THF174984
Webster children and grandchildren who lived farther away came for extended visits. Daughter Eliza Jones and her family traveled from their Bridgeport, Connecticut, home for visits.
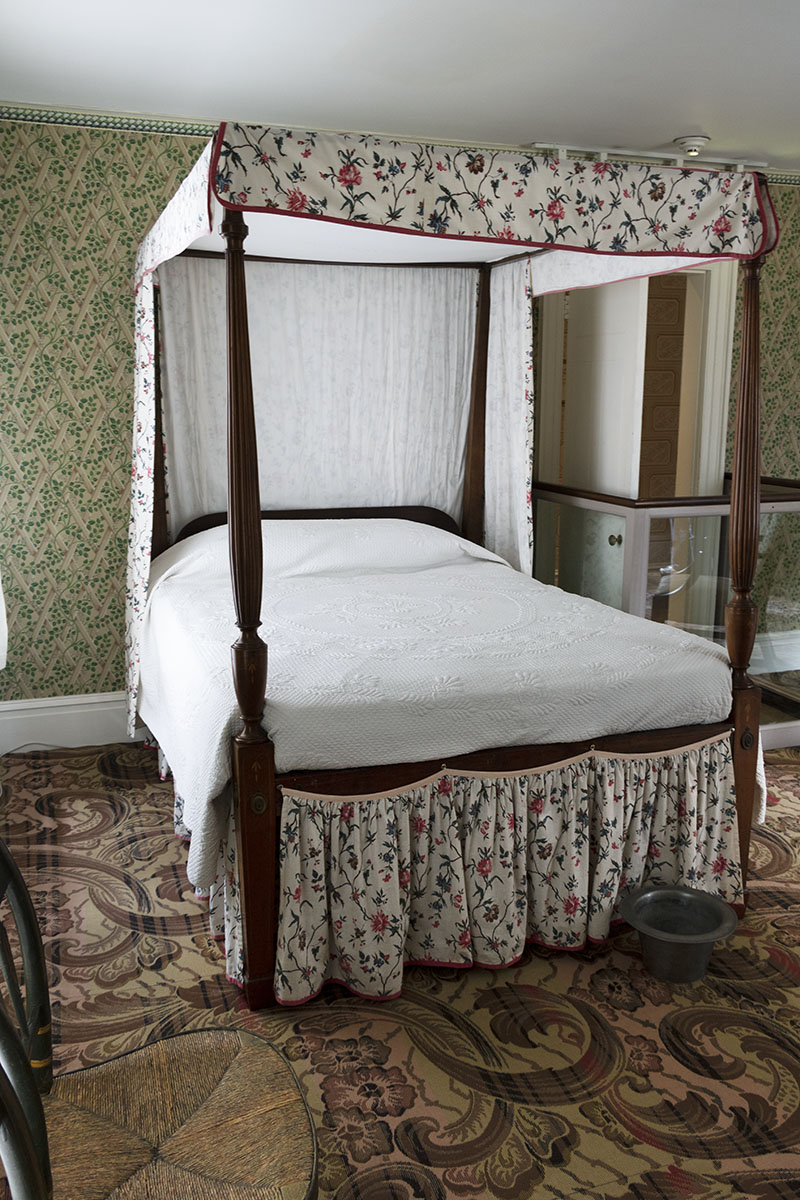

THF186515
At times, some Webster family members even joined the household temporarily. They could stay in a guest room in the Webster home.
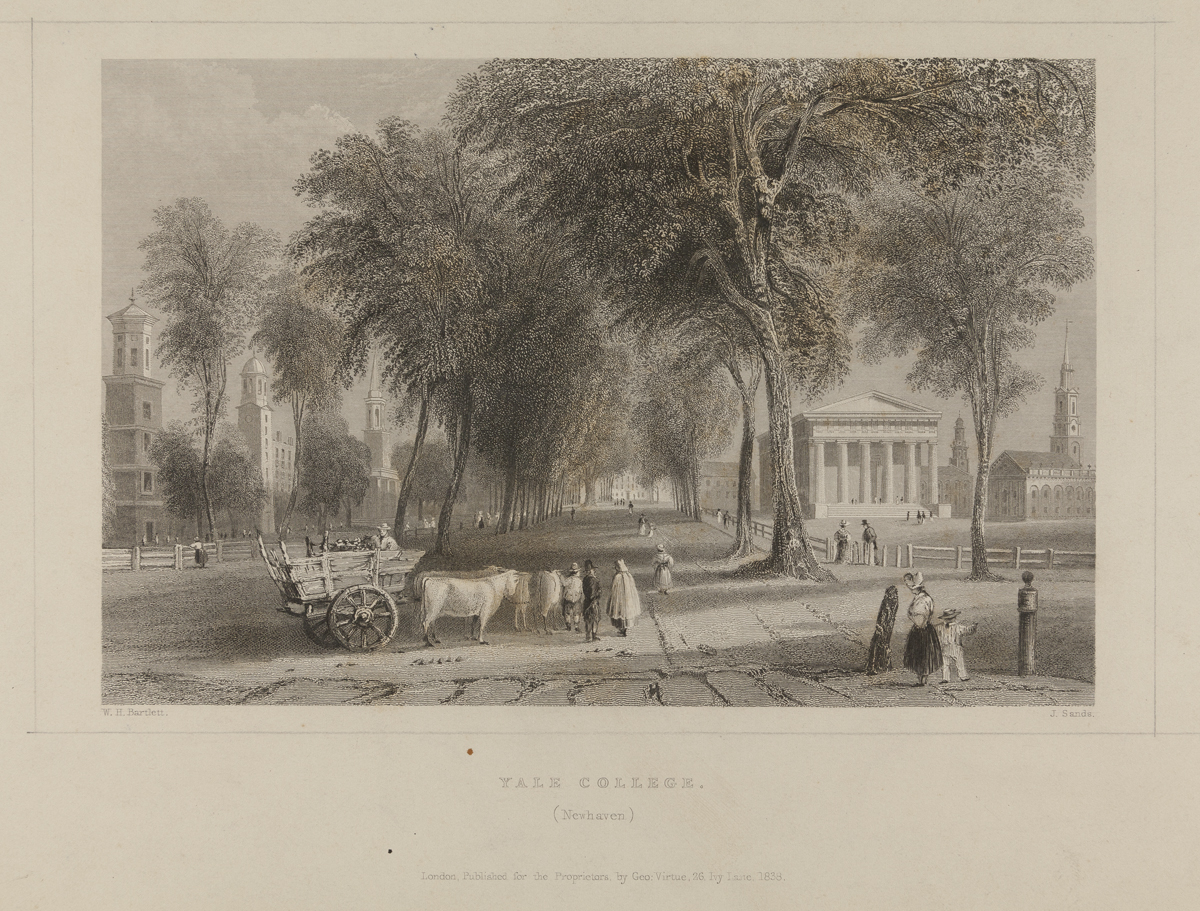
THF204255
Webster’s Yale-attending grandsons and their classmates stopped in for visits and came to gatherings. This print shows Yale College—located not far from the Webster home—during this time.
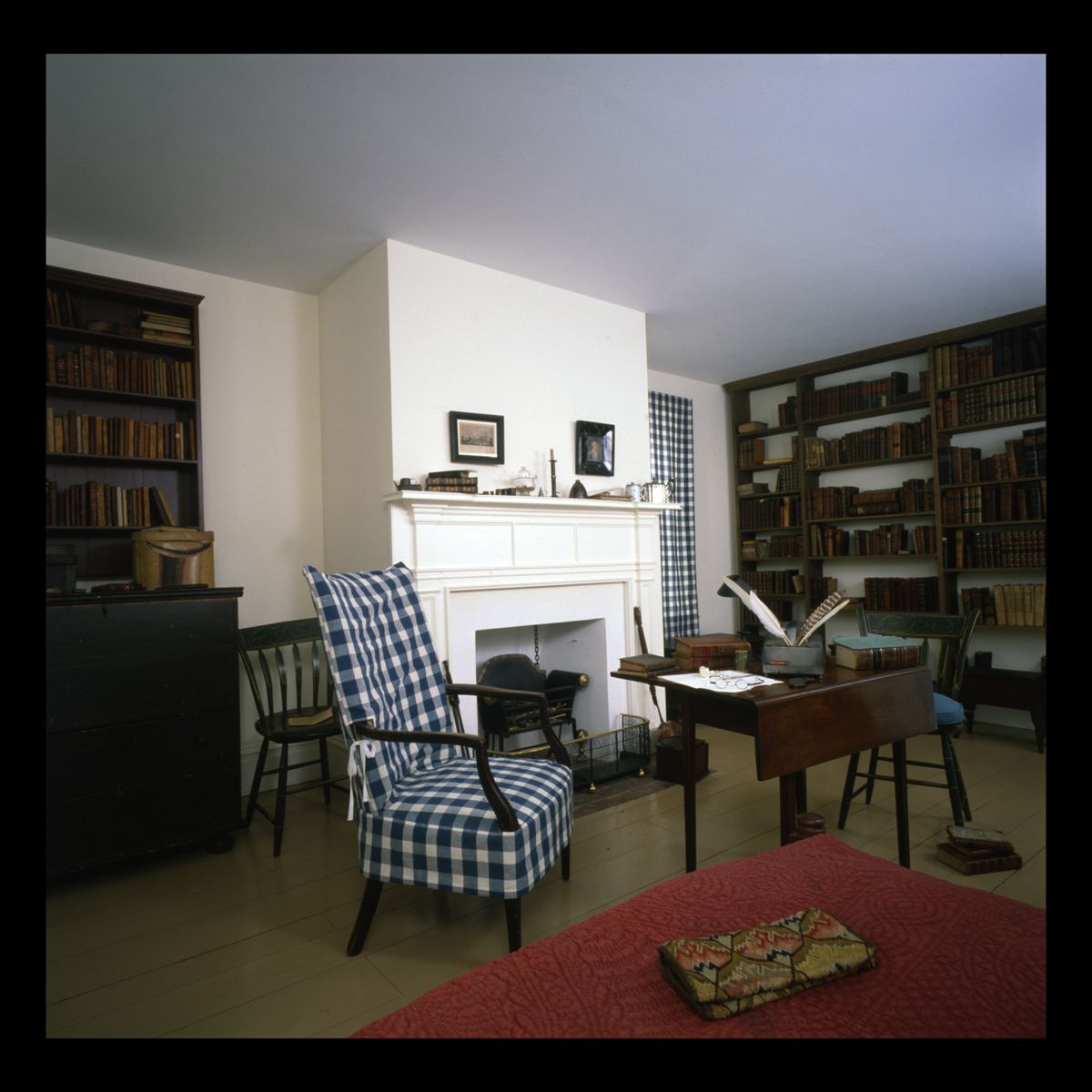

THF133637
The Webster family home was also Noah’s “office.” He had moved his study upstairs in October 1834, met there with business associates and students.
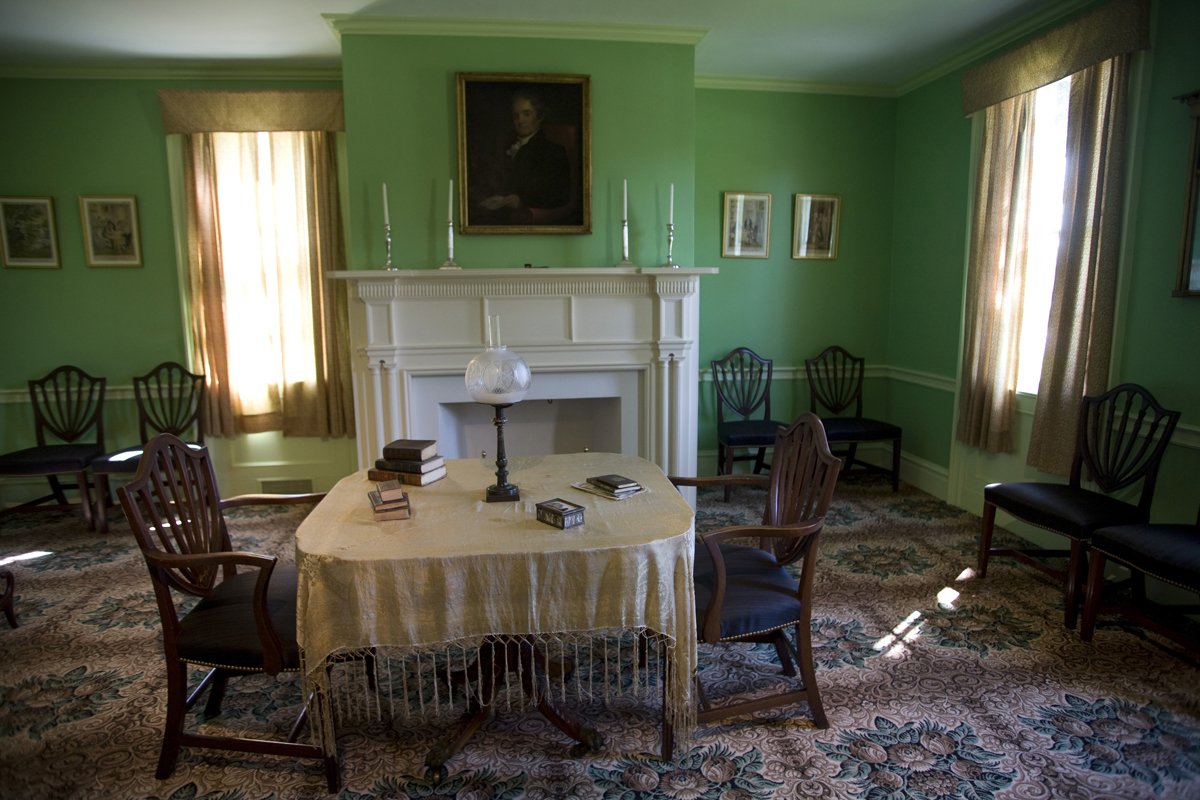

THF53243
Guests—including visiting clergymen, publishing associates, Yale faculty, and political leaders—would have called at the house or would have been invited to gatherings in the home. This is the Webster parlor.
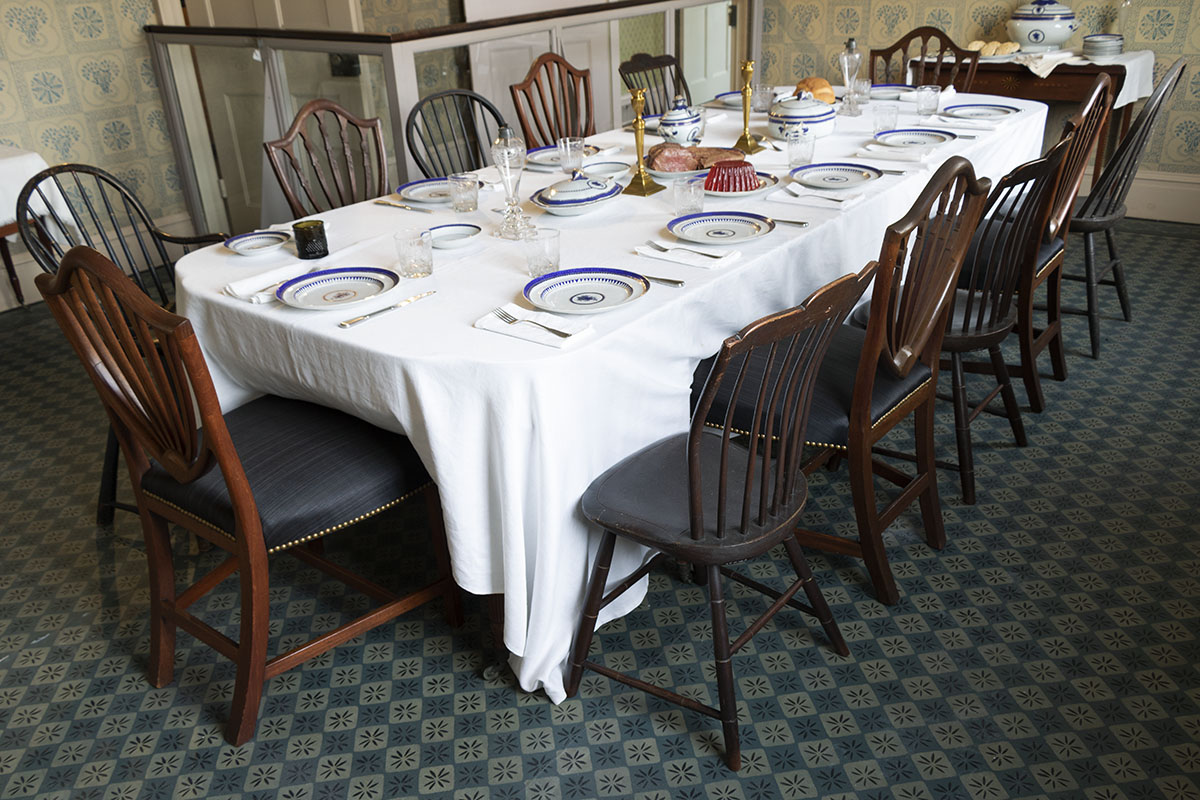

THF186495
To help reflect the active family life that took place in the Webster household in 1835, the new dining room vignette suggests members of the extended Webster family casually gathering for a meal.
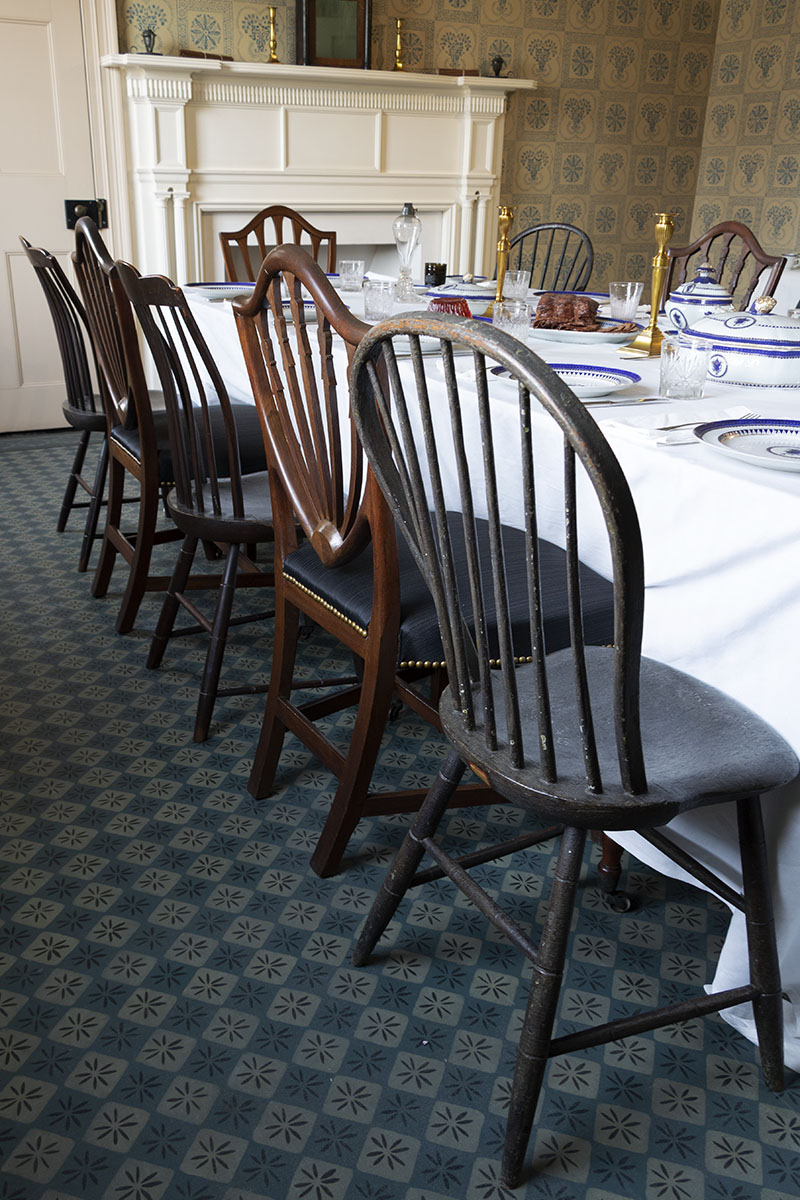

THF186496
The room’s arrangement is deliberately informal, with mismatched chairs. Hepplewhite chairs that are part of the dining room set are supplemented by others assembled for this family meal.
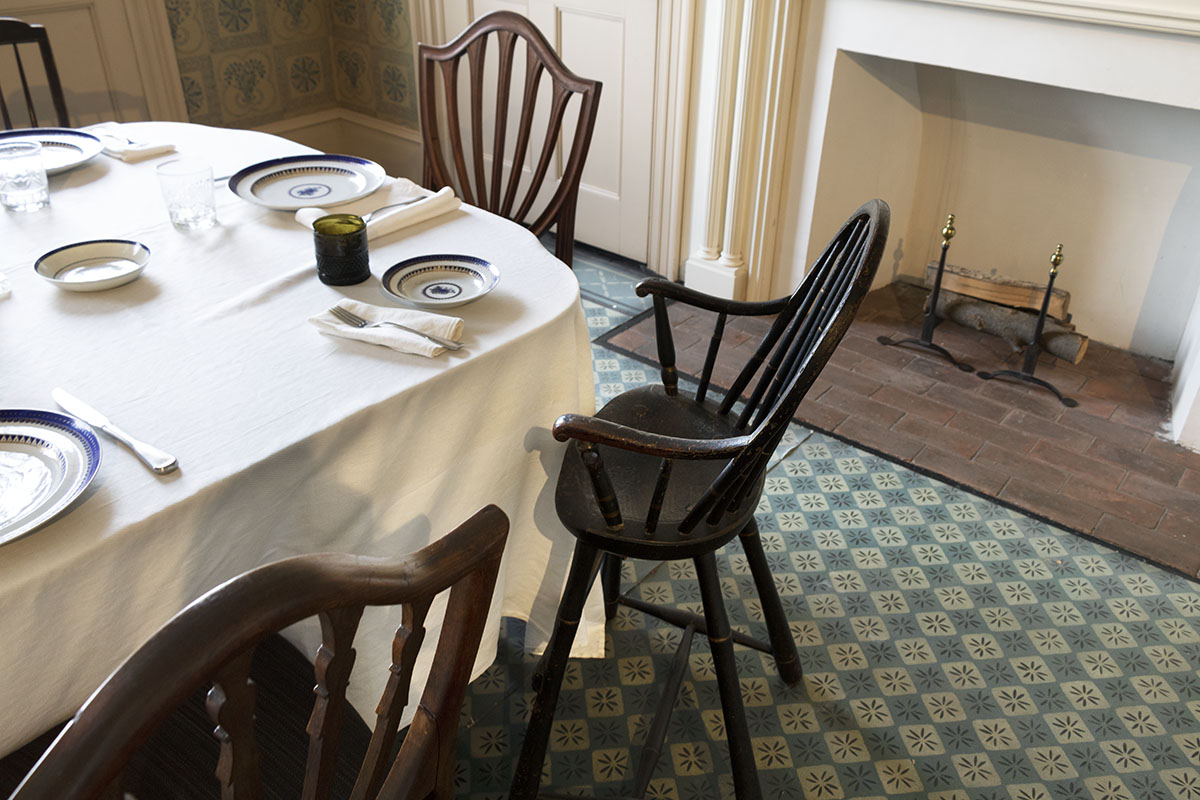

THF186497
A high chair is provided for the youngest Webster grandchild.

THF186498
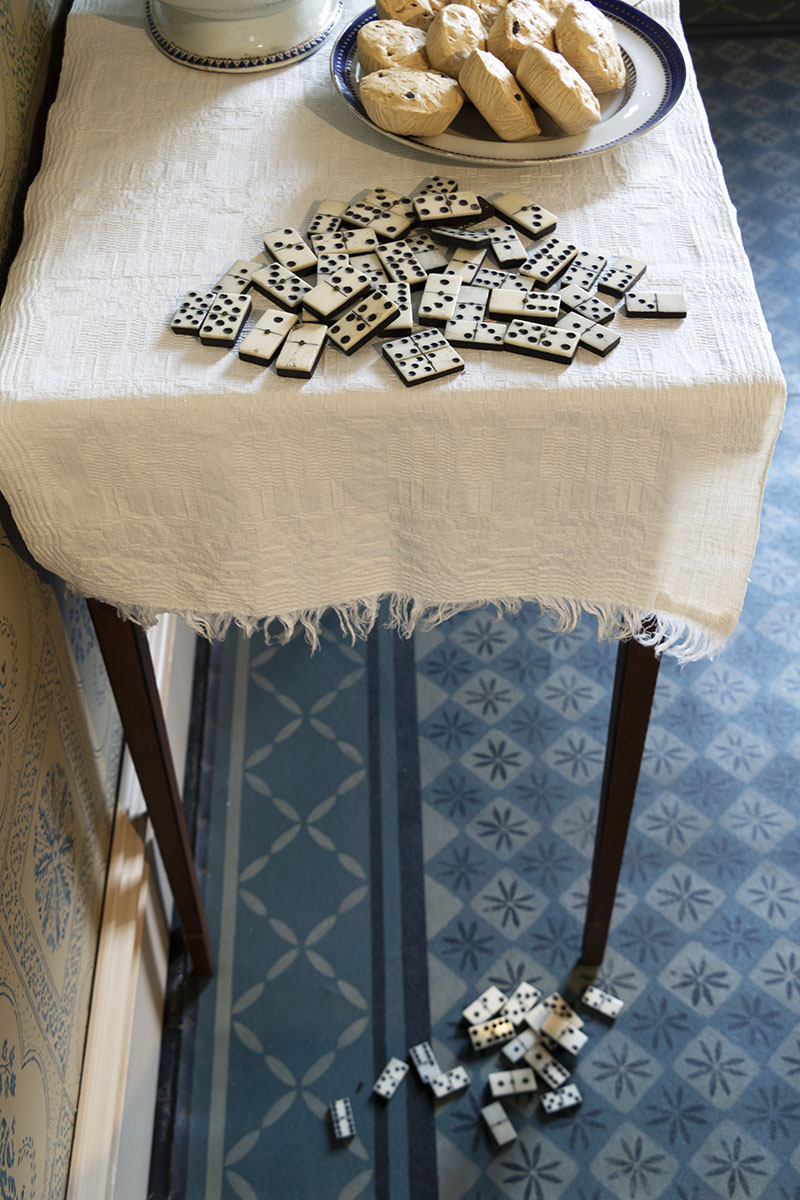
The grandchildren’s domino game was quickly set aside as the table was set and three generations of the family began to gather.

THF186500
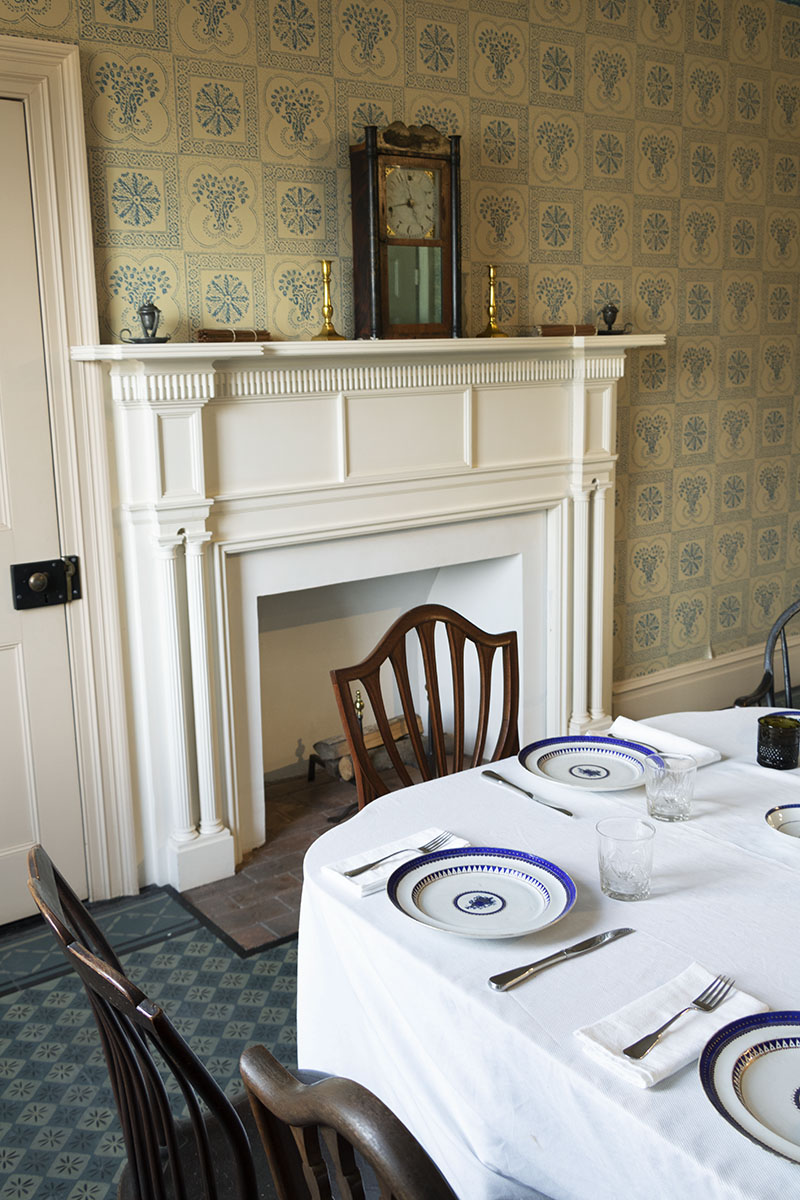
The dining room furnishings, like those in the rest of the home, reflect a household whose elderly inhabitants started housekeeping decades before. The Websters would have owned most of their furniture, tableware, candlesticks, and other items for decades. The Connecticut-made clock on the mantel would have been a bit newer, since it dates from 1825–1835.

THF186499
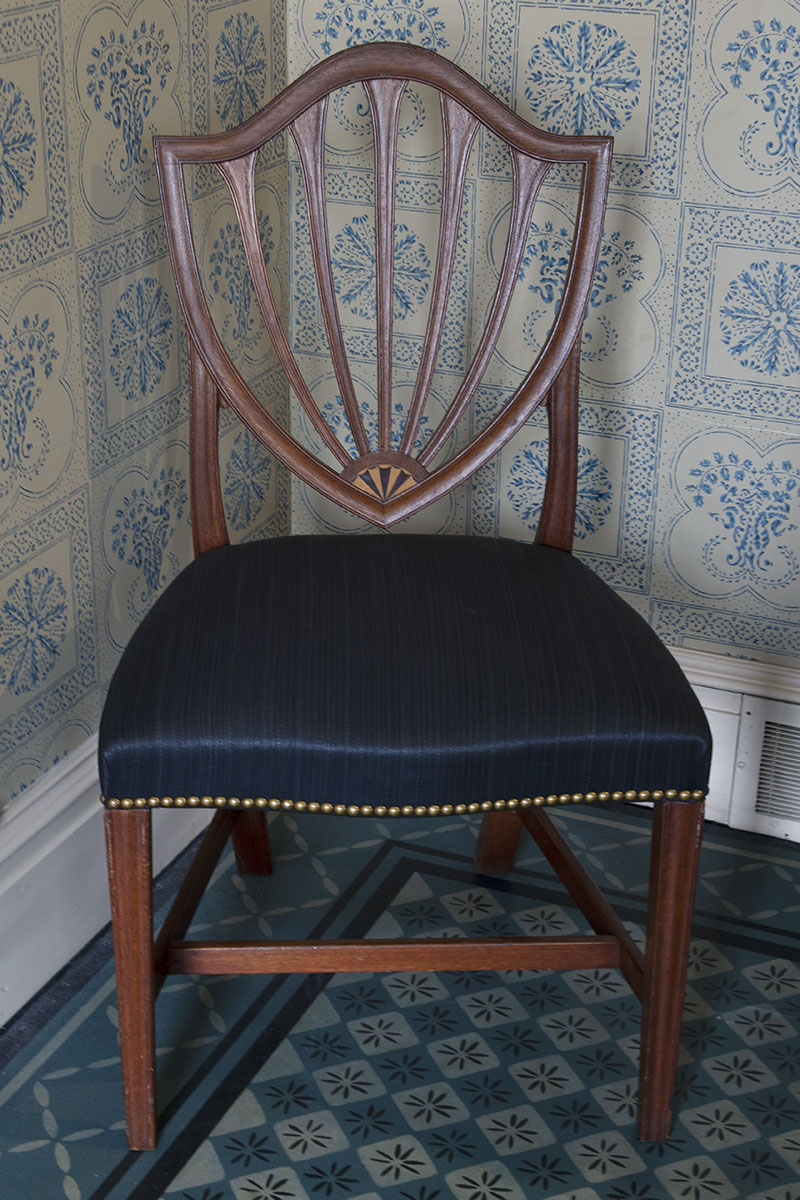
But the Hepplewhite style chairs—no longer in fashion—would have been purchased more than 30 years before.

THF186501
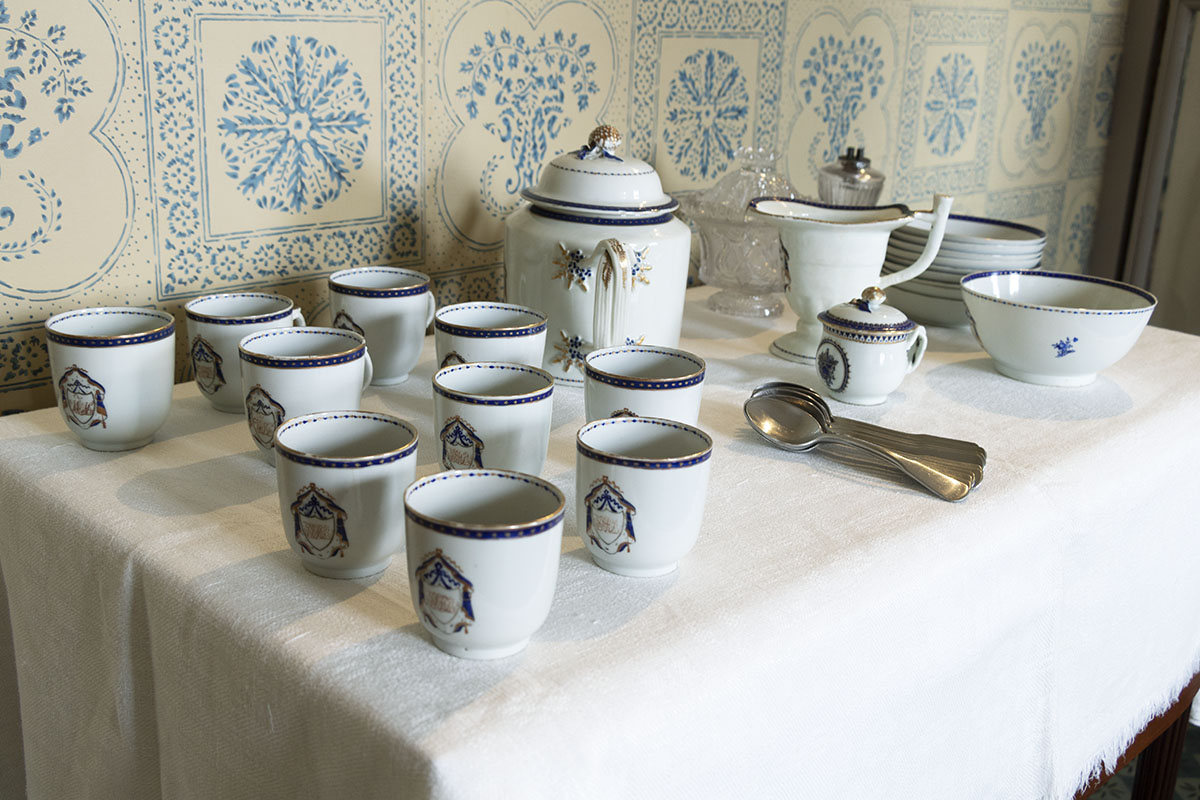
The early 1800s Chinese export dishes would have likely been bought decades before. Quite fine and fashionable when new, the sturdy dishes would have survived to be used at everyday meals and for family gatherings many years later.

THF186503
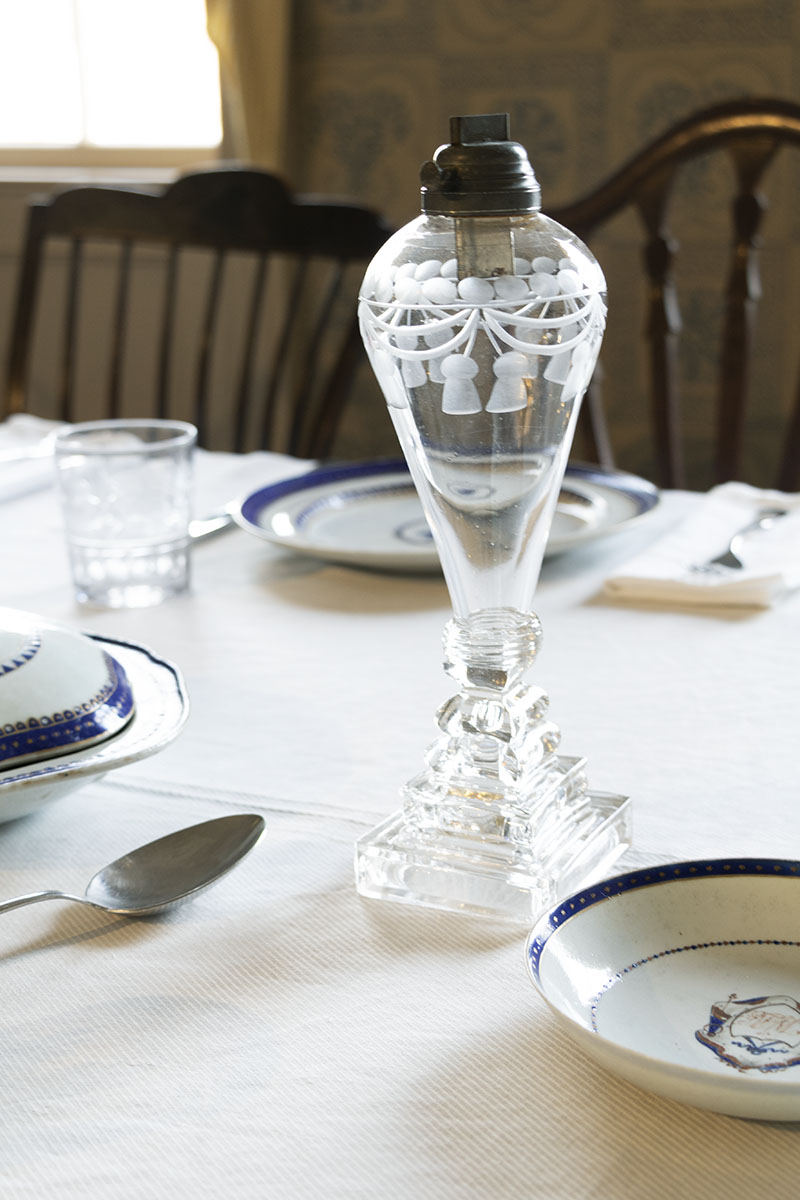
The Websters would have acquired other furnishings more recently--including newly available whale oil lamps, which provided brighter lighting than candles. In coastal New Haven, whale oil was readily available.

THF186505
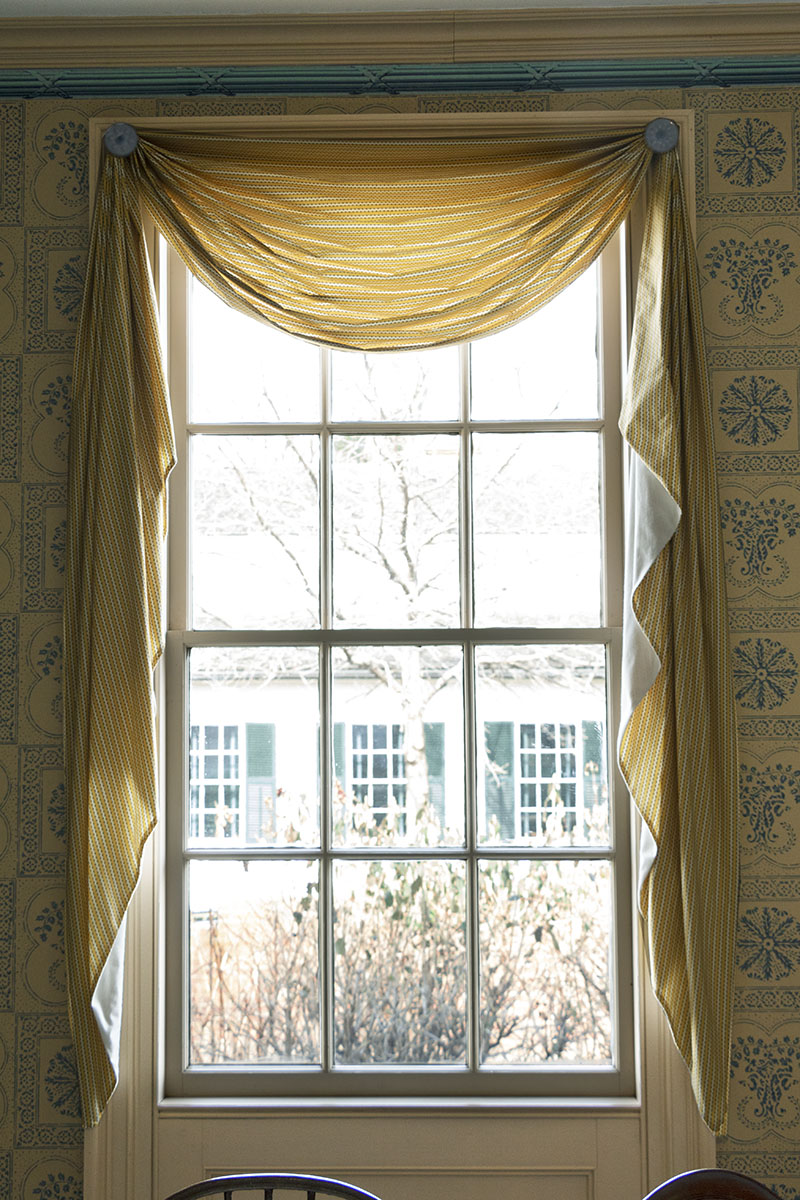
Stylish curtains of New England factory-made roller-printed cotton fabric are gracefully draped over glass curtain tiebacks and decoratively arranged.

THF186506
Do stop by the Noah Webster Home when Greenfield Village opens this spring and see what the Websters are having for dinner as they “gather” with their children and grandchildren! And for even more Village building makeover stories, see also this recent post from Senior Curator and Curator of Public Life Donna Braden.
Jeanine Head Miller is Curator of Domestic Life and Charles Sable is Curator of Decorative Arts at The Henry Ford.
Additional Readings:
- Prototype Eames Fiberglass Chair, circa 1949
- Arts and Crafts Furniture Making in West Michigan: The Charles Limbert Company of Grand Rapids and Holland
- Creatives of Clay and Wood
- Sidney Houghton: The Fair Lane Estate
Connecticut, 19th century, 1830s, 21st century, 2020s, Noah Webster Home, home life, Greenfield Village history, Greenfield Village buildings, Greenfield Village, furnishings, food, by Jeanine Head Miller, by Charles Sable, #THFCuratorChat, #Behind The Scenes @ The Henry Ford
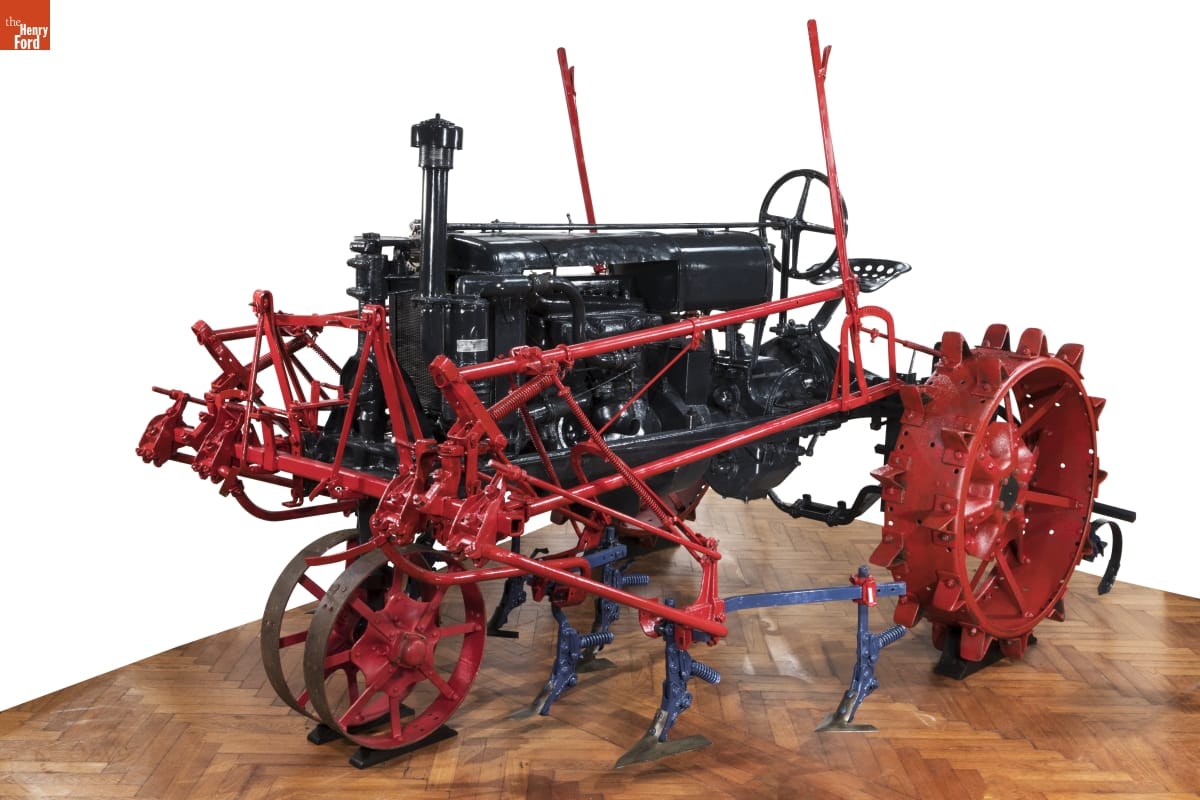

McCormick-Deering Farmall Tractor, circa 1925 / THF179719
International Harvester introduced the first commercially successful row-crop tractor, the McCormick-Deering Farmall, in 1924. It represented a whole new approach to farming. Today we think of corn, cotton, soybeans, and other crops as being planted and harvested in long rows, but before the 1920s, farmers often planted crops in a grid pattern on smaller fields, which they cultivated using draft animals and a shovel plow.
As tractor usage increased, farmers were able to reduce the amount of land dedicated to housing and feeding draft animals. On average, farmers could re-purpose five acres of land for every horse that was no longer needed. This increase in usable land for farming provided a powerful incentive for farmers to own a tractor.
The McCormick-Deering Farmall was the first tractor to incorporate small, closely spaced front wheels that could travel between rows, and a high rear axle clearance to straddle the plants. It also included a power “take-off” unit to run machinery like the New Idea corn picker. International Harvester, with its Farmall tractor, overtook Ford Motor Company to lead the nation in tractor sales.
We recently completed some conservation work on the McCormick-Deering Farmall "Regular" tractor (52.38.4), which is on display in the Agriculture and the Environment exhibit in Henry Ford Museum of American Innovation. The Farmall “Regular” has gone through a series of restorations and re-interpretations since it came into our collection in 1952.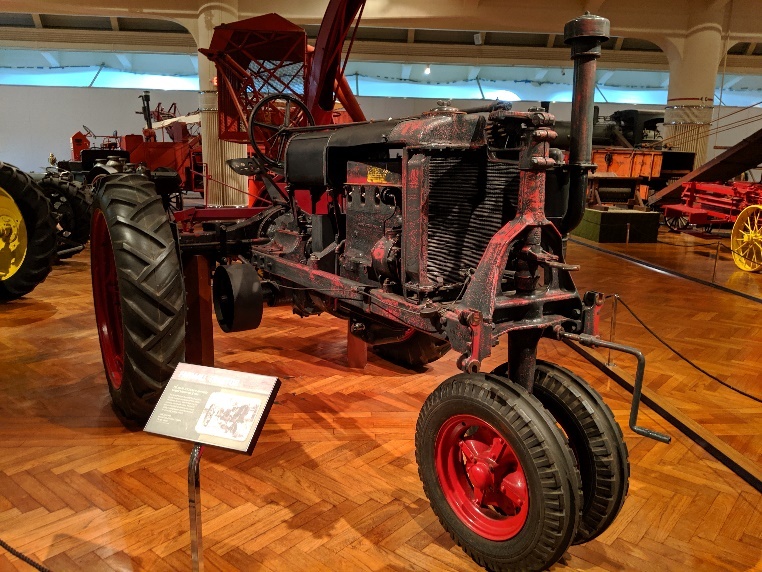
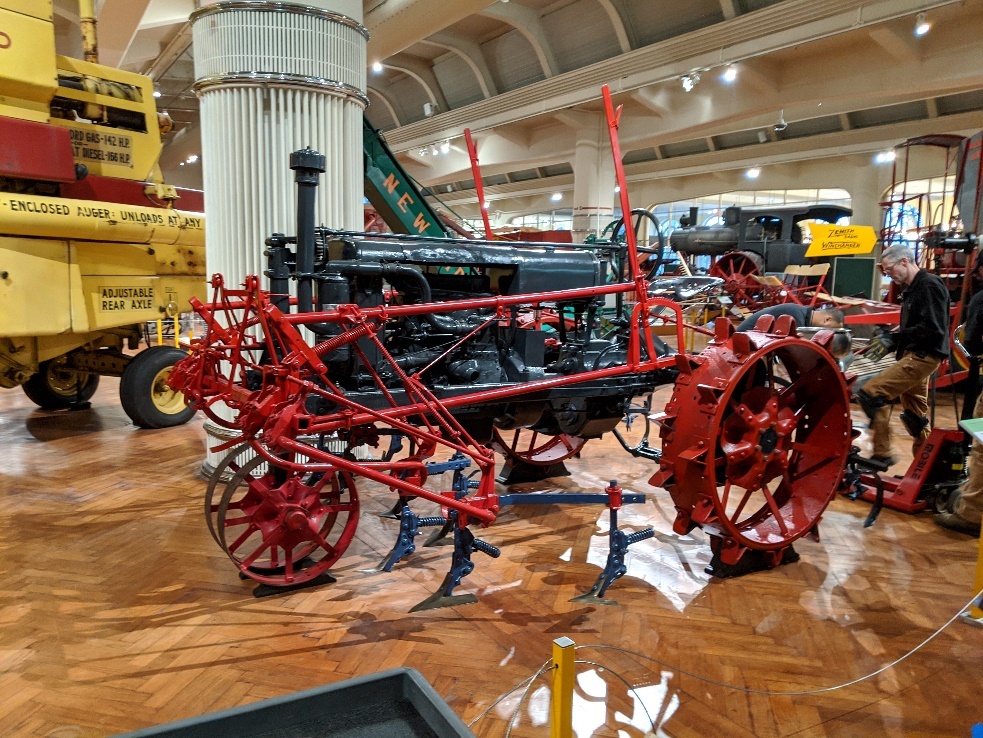

Before (above) conservation and after (below) 2019 conservation work, with the addition of the Farmall Cultivator No. HM-229 add-on kit and set of metal wheels.
In 2003, a team of volunteers, under the direction of a conservator, began the process of returning the tractor to its 1926 appearance. During this process, most of the newer Farmall red restoration paint layer was removed, as were F-20 parts that were not appropriate to the “Regular” model.
Most recently, we made the decision to retain the 1926 appearance and re-introduce the 1930s Farmall Cultivator No. HM-229 add-on kit, a compatible addition farmers could purchase. To do this, the tractor would need to be painted in appropriate colors. Luckily, our Curator of Agriculture and the Environment, Debra A. Reid, tracked down the manufacturer’s elusive colors: International Harvester Gray and Harvester Blue varnish enamel paint.
Harvester Gray was fortunately documented by Mark Stephenson at McCormick-Deering.com. The Harvester Blue was matched from residual paint on a gang beam that was hidden behind an installed cultivator part. The paint was compared with a manufacturer’s paint chart from the Wisconsin Historical Society.
The residual Harvester Blue paint on the Cultivator’s gang beam.
To aid in completion of this project, a copy of the manufacturer’s original instruction manual we obtained proved to be an invaluable resource.
Conservation volunteers Doug Beaver, Glen Lysinger, and Jim Yousman put on the cultivator rear track sweep attachment, supported by a high-lift pallet jack.
Conservation Specialist Andrew Ganem steers the tractor as it is towed by Exhibits Preparator Bernhard Wilson.
Logistics included towing the tractor to its display location at the museum and completing the rest of the assembly onsite in the museum; for ease of movement, the rubber wheels were used to maneuver the tractor into the museum.
Exhibit Preparators Ken Drogowski on the forklift and Jared Wylie on the floor remove one of the 40” x 6” rubber wheels.
The metal wheel gets mounted by Exhibits Preparators Jared Wylie and Neil Reinalda and Conservation Specialist Andrew Ganem.
The rest of the cultivator assembly, which includes gang beams, two rear spring teeth, and ten gang sweeps, was added after the tractor returned to the exhibit area. A set of 25” x 4” front metal wheels and 40” x 6” rear metal wheels replaced the rubber wheels. This process required a methodic approach to safely complete, using forklifts, straps, a watchful eye for concerns and risks, and general tools. Once removed, the set of rubber wheels were returned to collections storage.
This work could not have been completed without the help of staff from the collections management, conservation, curatorial, and exhibits teams at The Henry Ford, as well as our dedicated volunteers Glenn Lysinger, Doug Beaver, Jim Yousman, Larry Wolfe, Harvey Dean, Neil Pike, Deb Luczkowski, Maria Gramer, and Eric Bergman.
Check out the recently conserved tractor and a variety of other agricultural items in the Agriculture exhibit in Henry Ford Museum of American Innovation.
Cuong T. Nguyen is Conservator at The Henry Ford.
farming equipment, Henry Ford Museum, farms and farming, conservation, collections care, by Cuong Nguyen, agriculture, #Behind The Scenes @ The Henry Ford
In preparing for the Louis Comfort Tiffany: Treasures from the Driehaus Collection exhibit, The Henry Ford’s curatorial department expressed interest in displaying a Tiffany Studios early floor lamp, circa 1900, from our collections. This lamp features a telescopic shaft and a dual wick kerosene burner for extra illumination.


Our Tiffany lamp (THF186213) as compared to images from Tiffany publications.
In Tiffany publications, the lamp rests on an outer cushion-textured base with six ball-shaped feet. However, the outer base from The Henry Ford’s lamp was missing, with no previous record of its existence when it entered our collection in 1966.
Discussions between Curator of Decorative Arts Charles Sable and conservators led to the decision to create a replica lamp base to ensure both historical accuracy and physical stability to the tall, rather top-heavy floor lamp. The completed object would provide viewers with a more accurate interpretation and the opportunity to experience the object whole, as it was originally designed.
It’s All about the Base
We embarked upon an effort to locate a similar base in museums or private collections to serve as a reference or pattern, to inform the creation of a replacement base—only to discover that the lamp is quite rare. So instead, I decided to create a model base using a CAD (computer-aided design) program, with the design based on photographs from Tiffany publications and auctions. The museum’s lamp was used as a physical frame of reference for measurements and comparisons in CAD. I reached out to several 3D-printing shops to determine if they could use my CAD design to generate a three-dimensional plastic base. Ultimately, the base was printed with the help and generosity of the additive manufacturing team at the Ford Advanced Manufacturing Center.
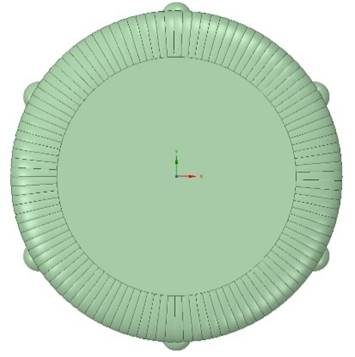
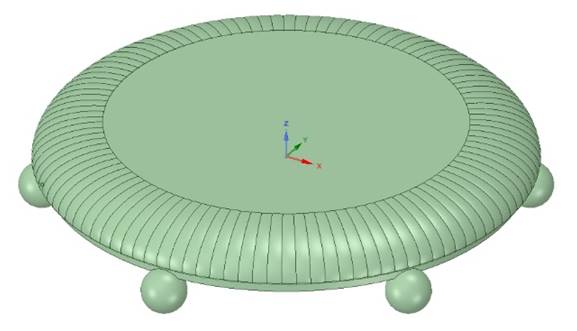
The above images are the CAD model of the base from different angles.
Ford Motor Company and its Advanced Manufacturing Center (AMC) offered their additive manufacturing expertise and capabilities. Their team includes Global Chief Engineer Mike Mikula, Rapid Prototype Subject Matter Expert Scott Gafken, Technical Leader in Additive Manufacturing Harold Sears, Additive Manufacturing Engineer Supervisor Jay Haubenstricke, and Supervisor Additive Manufacturing John Phillips.
Collaborative discussions with Scott Gafken revealed that the process would take about 24 hours, which included printing as well as model cooldown for handling. The EOS P770 was employed as an industrial selective laser sintering (SLS) printer and produced the print in Nylon 12 (also known as Polyamide 12 or PA12). The printing material was selected based on its ability to bear the weight of the lamp, and someday be a candidate for an investment casting, for the creation of a metal base.

The white image shows the Polyamide 12 print of the base at the Ford Advanced Manufacturing Center. The image with painter’s tape was taken during the process of painting the base. Achieving a finish that matched the original metal lamp required the application of several layers of paint. The image with only one small white section shows the completed base after gloss varnish was applied.
Paint Matching
The bronze surface of the lamp was shades of brown with hints of red, orange, and green. These shades are similar to several paint colors: raw umber, chromium oxide green, sepia, burnt sienna, and yellow oxides. The colors were mixed into several formulations to closely match the patina (aged finish) of the lamp. Diluted paint was applied in layers to allow the variations in the tones to be seen. After discussions with the curator and members of our Experience Design department, we made the decision to leave one section of 3D-printed surface unpainted, to allow visitors to see it in the exhibit.
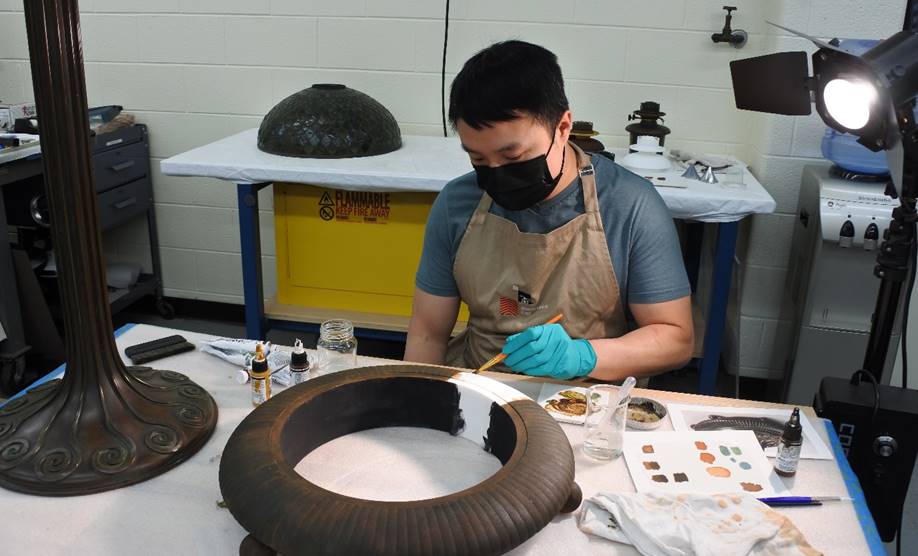

The replica base was painted with the actual lamp present to ensure a match.
Additional Treatment
Beyond the base, other aspects of our conservation treatment included the cleaning of the Tiffany lamp with a bristle brush and vacuum. Wet cleaning included a dilute blend of anionic and nonionic detergents in distilled water, applied with cotton rags and cotton swabs. Residual detergent was then removed with a distilled water wipedown.
A protective barrier of wax was introduced via hot wax application. The bronze surface was heated with a hot air gun and microcrystalline wax was applied and left to cool down. A boar-bristle brush and bamboo picks were used to remove excess wax. The brush and cotton rags were then used to buff the wax layer, resulting in a uniform sheen.


Details of the lamp both before cleaning and after cleaning and wax application.
Additional information on the care of these types of artifacts and more can be found in The Henry Ford’s conservation fact sheets, “The Care and Preservation of Historical Brass and Bronze” and “The Care and Preservation of Glass & Ceramics.”
Please check out this lamp and other Tiffany Studios artifacts in the Louis Comfort Tiffany: Treasures from the Driehaus Collection exhibit before its closing on April 25, 2021.
Cuong Nguyen is Conservator at The Henry Ford.
Additional Readings:
- "Blue Macchia with Yellow Lip" by Dale Chihuly, 1999
- "Tension" by Dan Dailey, 2002
- Frederick Birkhill: The Spark That Ignited a Career
- Photographing Glass
Henry Ford Museum, Ford Motor Company, philanthropy, technology, glass, by Cuong Nguyen, #Behind The Scenes @ The Henry Ford, collections care, conservation, Louis Comfort Tiffany

